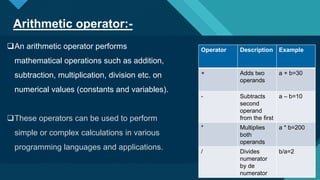
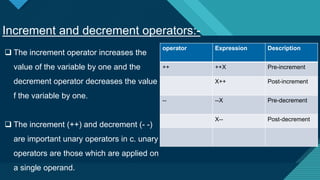
Operators in C are symbols that perform operations on operands. There are several types of operators in C including arithmetic, assignment, increment/decrement, relational, logical, conditional, bitwise, and binary operators. Operators allow programmers to perform math operations, comparisons, assignments, and logic on data in a C program.