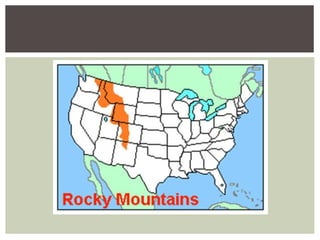
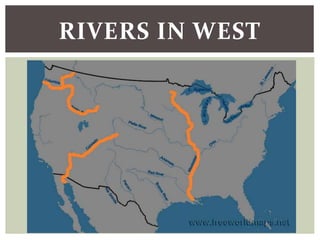
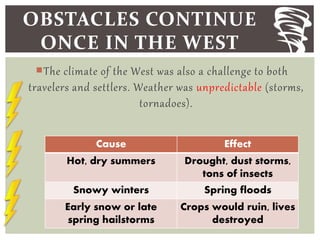
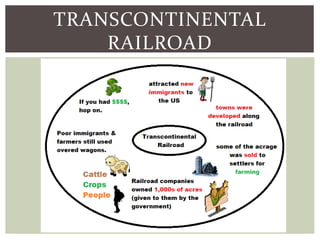
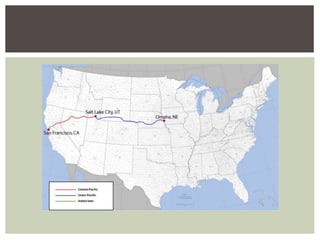
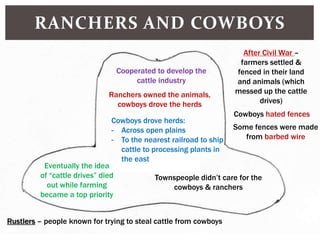
The document discusses the key factors that influenced westward expansion in the United States, including geographic obstacles, technologies, policies, and the social and economic impacts. It addresses how physical features, climate, resources, railroads, and the Homestead Act affected travel and settlement. It also examines conflicts between miners, farmers, ranchers, and various ethnic groups, as well as the effects of expansion on Native Americans, including land disputes, warfare, and changes in federal policy.