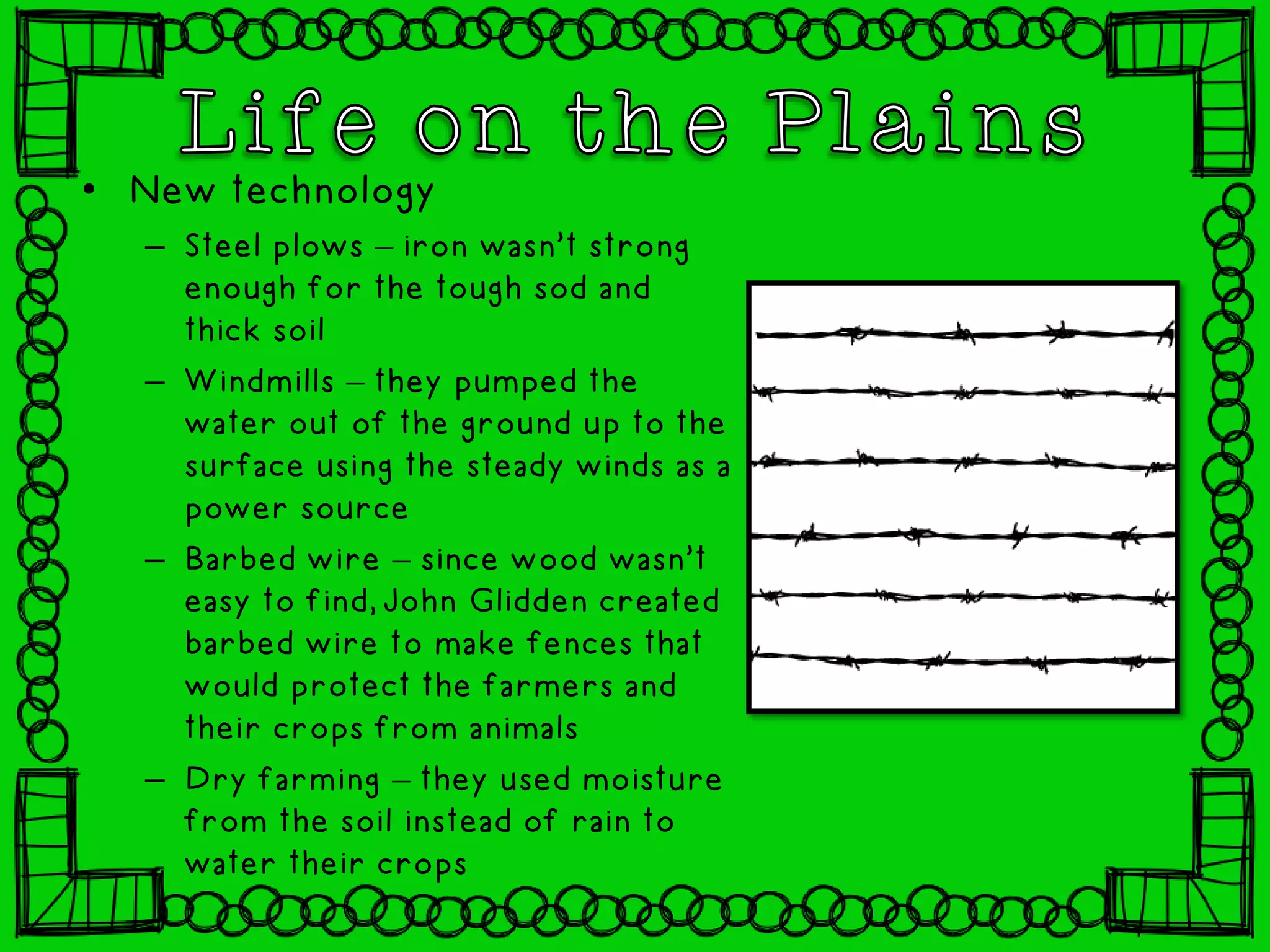
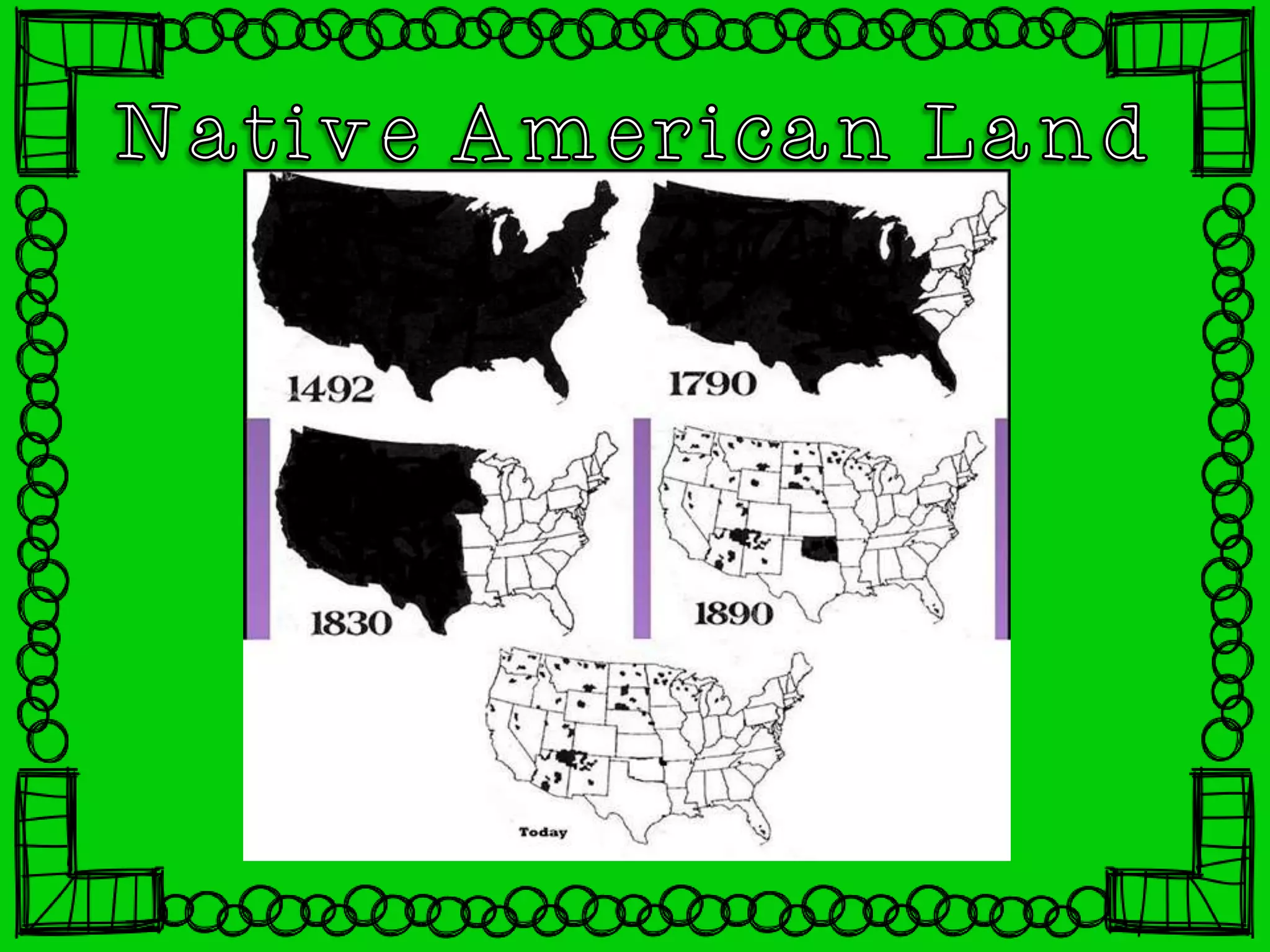
The document summarizes the development of transportation and settlement in the American West between the mid-1800s to late 1800s. It describes how the Transcontinental Railroad was built to connect the East and West Coasts, encouraging widespread migration to the region. It also discusses the expansion of farming, ranching, mining and cities throughout the West, and the conflicts that arose with Native Americans over land.