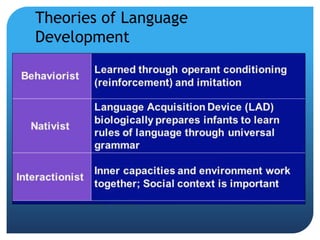
Language develops through a series of stages from infancy through adulthood. Infants begin with crying and cooing, then progress to babbling and first words between 10-15 months. By 18-24 months, children use two-word phrases to communicate. In early childhood, children rapidly expand their vocabulary and grammar skills, learning rules of syntax, morphology, and semantics. Literacy instruction begins in preschool through activities like dialogic reading. In middle childhood, children further develop reading, writing, and metalinguistic skills. Adolescents gain skills in vocabulary, metaphor, and literary analysis. In adulthood, vocabulary increases until late life when retrieval difficulties and slowed processing may occur, though communication remains adequate.