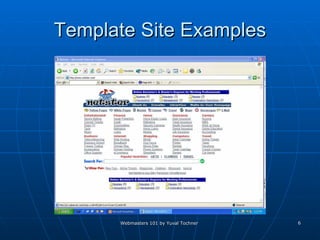
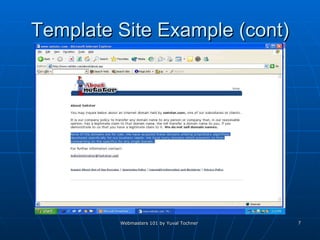
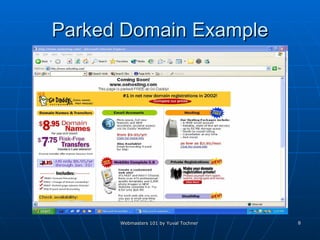
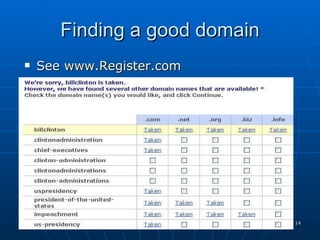
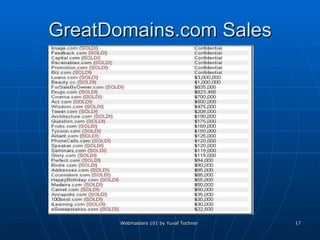
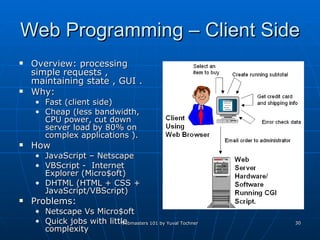
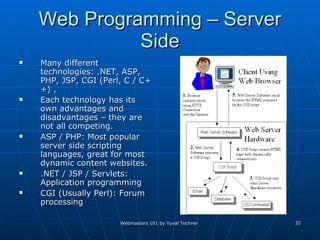
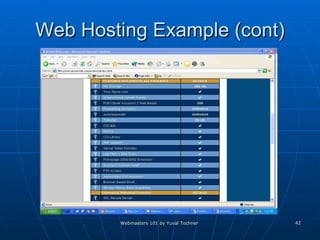
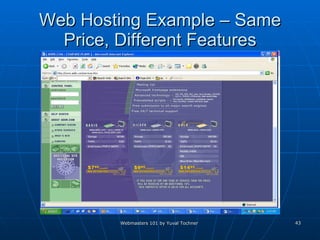
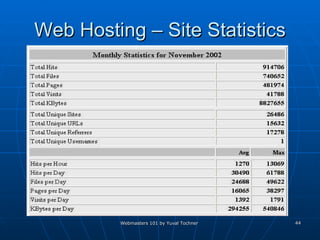
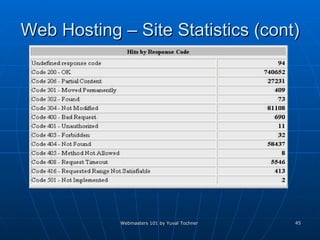
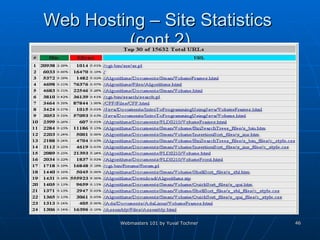
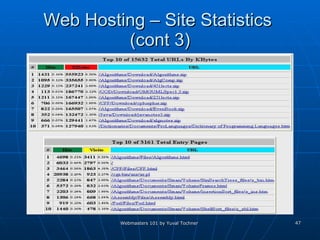
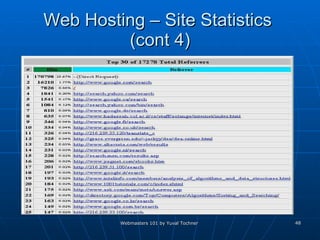
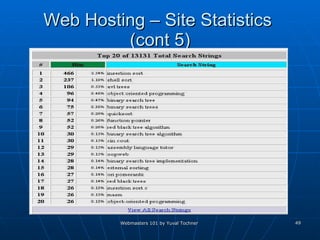
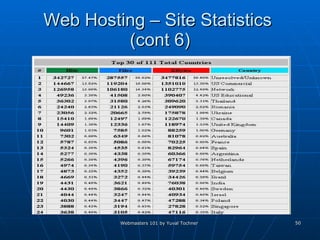
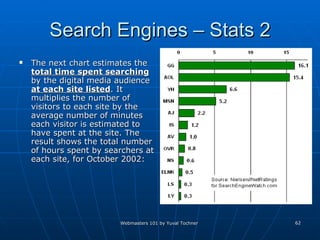
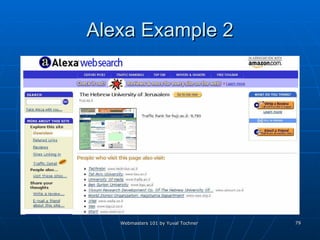
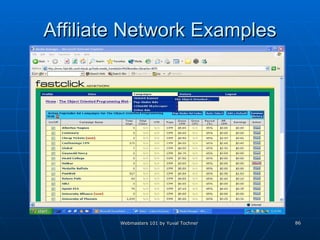
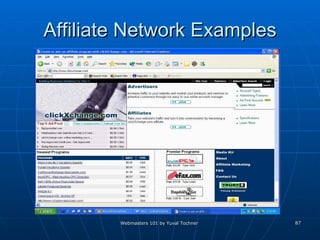
This document provides an overview of topics for webmasters, including domain registration, web design, web programming, web hosting, e-commerce, search engines, pay-per-click advertising, Alexa analytics, and affiliate networks. It discusses choosing a domain name and registrar, options for web design like templates and content management systems, client-side and server-side programming, shared vs dedicated hosting, setting up an online storefront, search engine optimization, Google AdWords, using Alexa for site analytics, and popular affiliate networks.