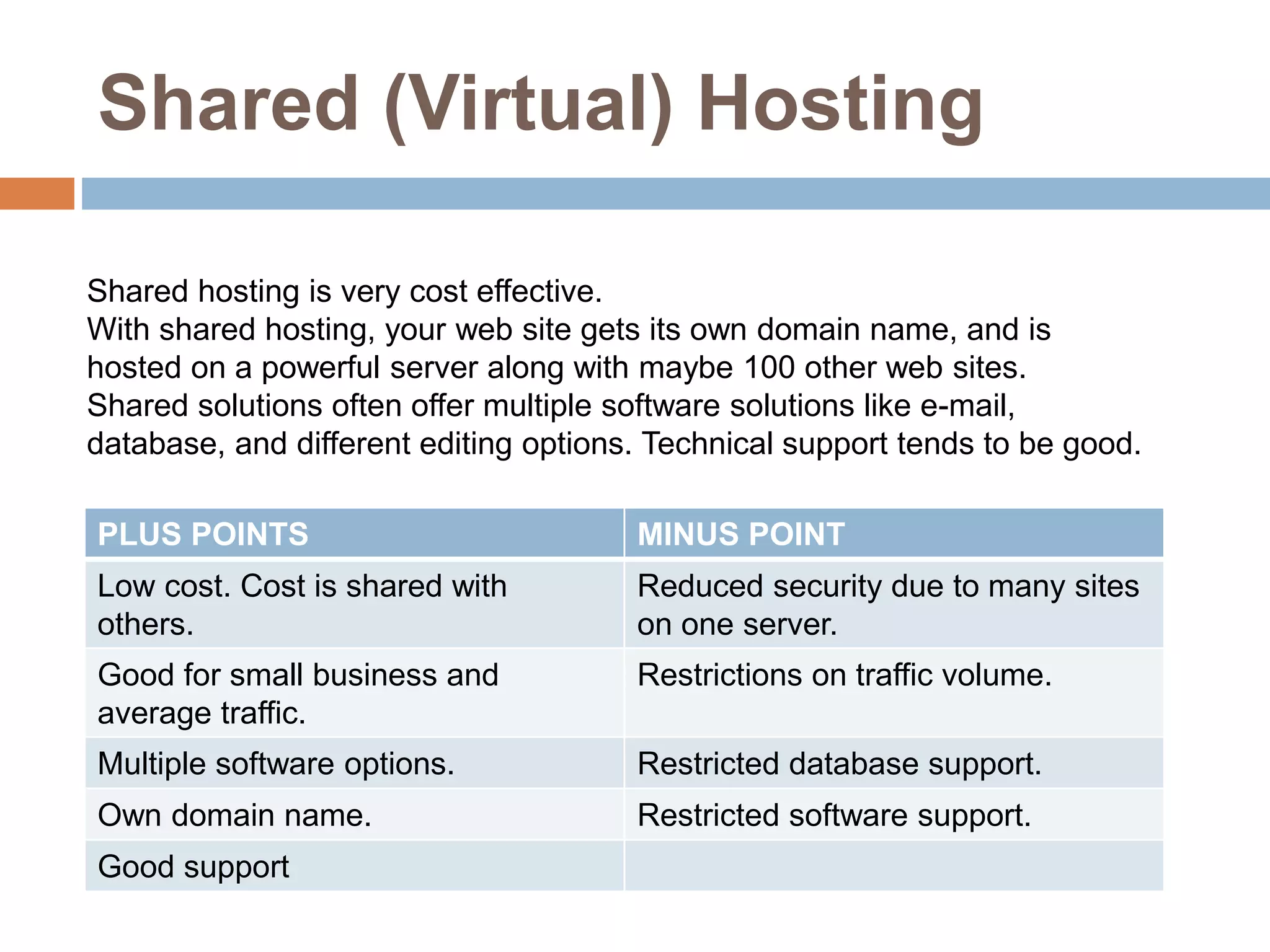
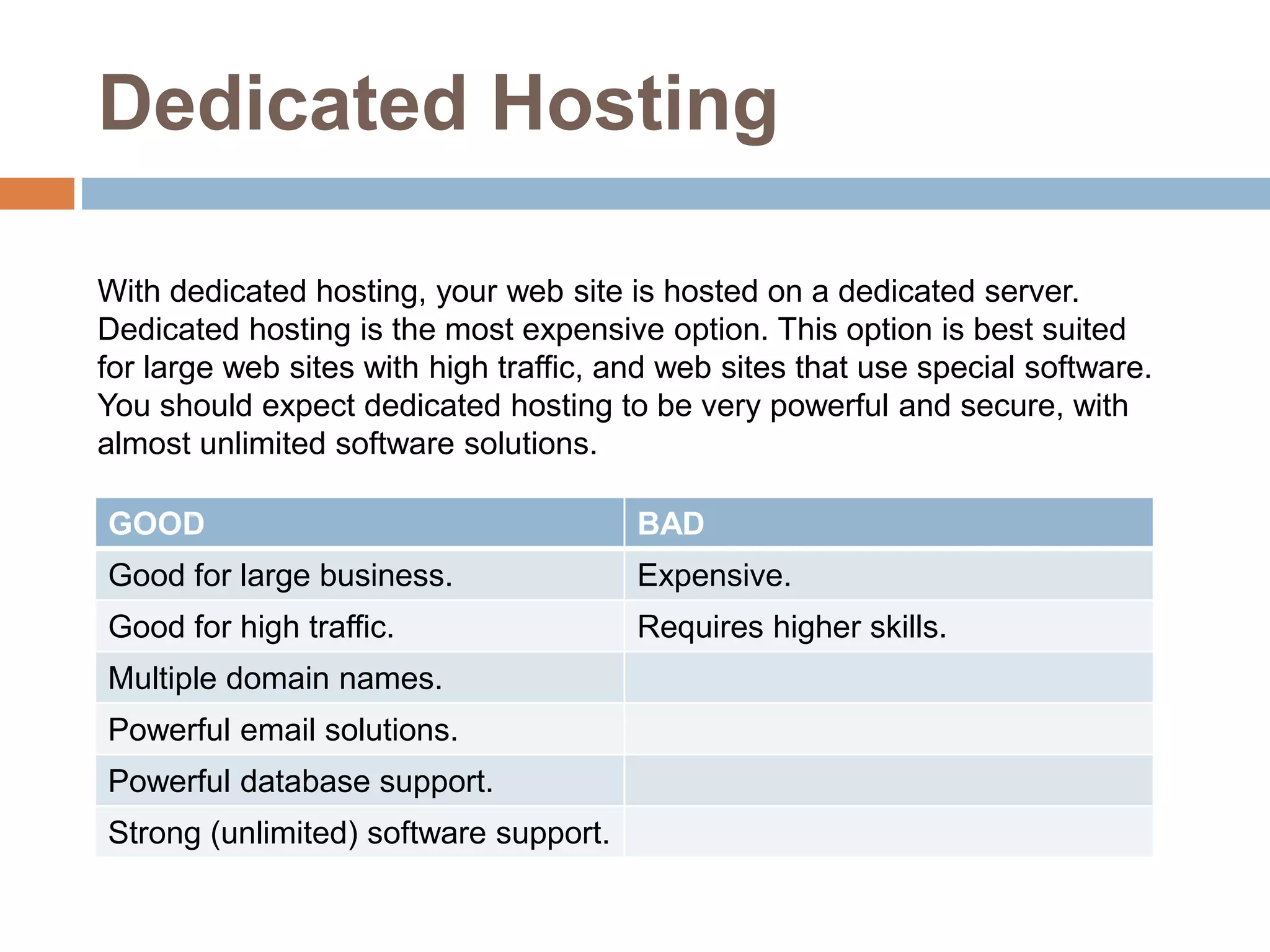
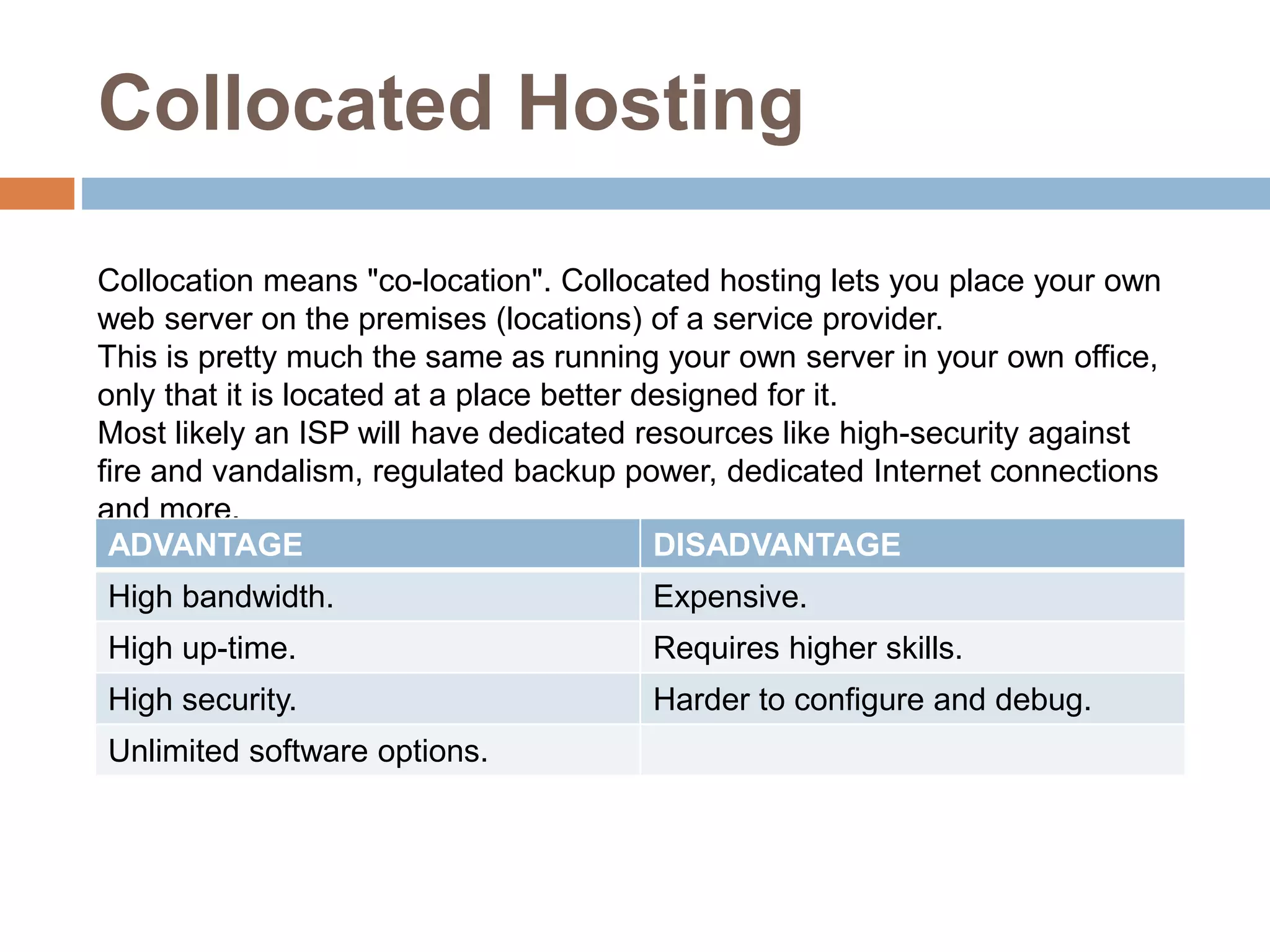
Web hosting involves making a website visible on the internet by storing it on a web server. There are different types of hosting available including free hosting, shared hosting, and dedicated hosting. Free hosting is best for small personal sites but has limitations. Shared hosting is more cost effective and offers domain names and support for common software. Dedicated hosting is the most expensive option suited for high traffic commercial sites needing powerful resources.