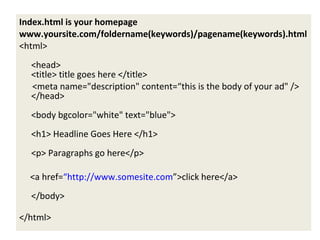
The document outlines how websites and search engines operate, covering topics such as domain names, web hosting, and the creation of web pages using HTML and CSS. It emphasizes the importance of choosing memorable domain names, the advantages of content management systems like WordPress, and search engine optimization strategies for better visibility online. Overall, it provides a comprehensive overview for creating and maintaining an effective online presence.