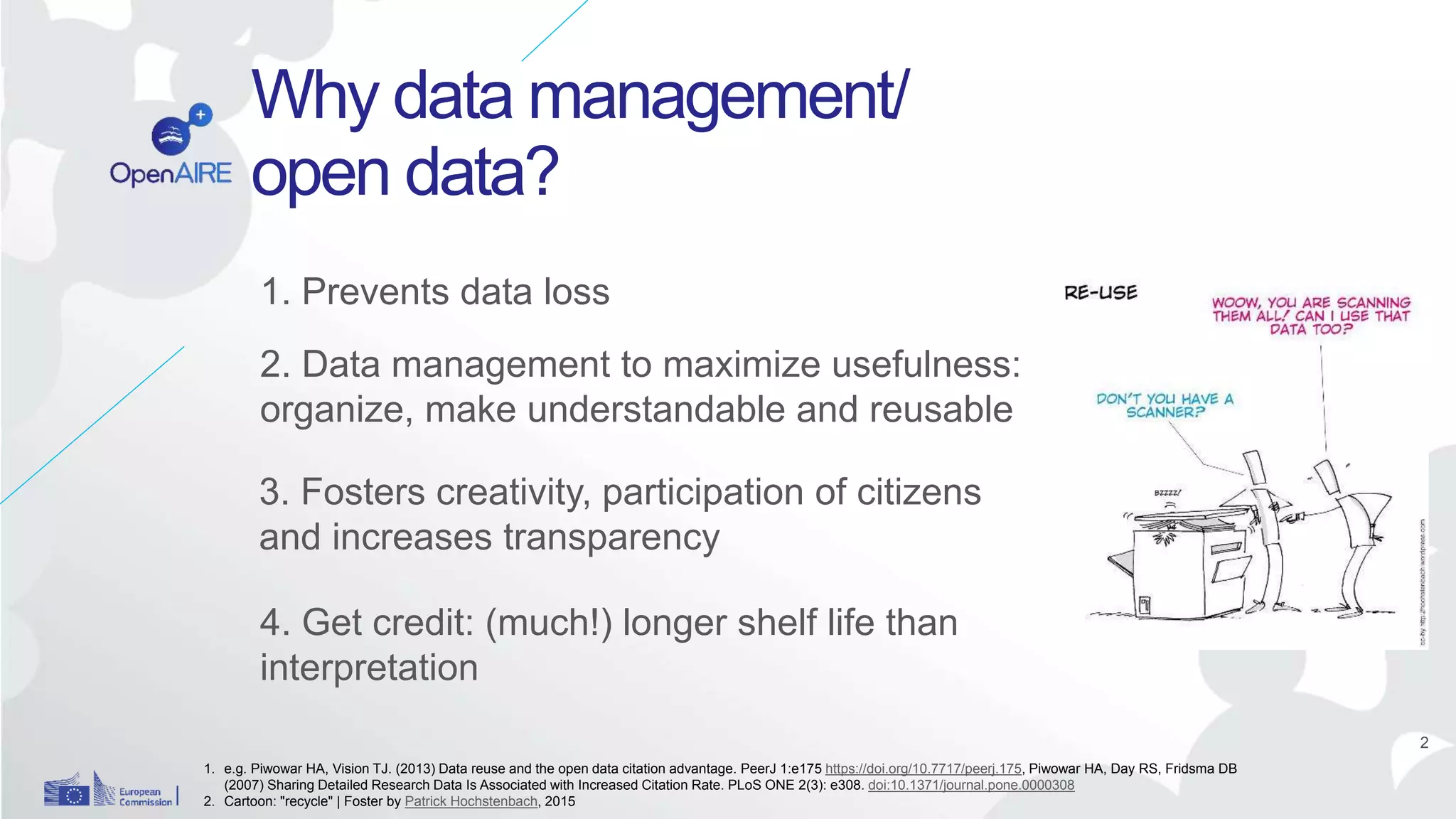
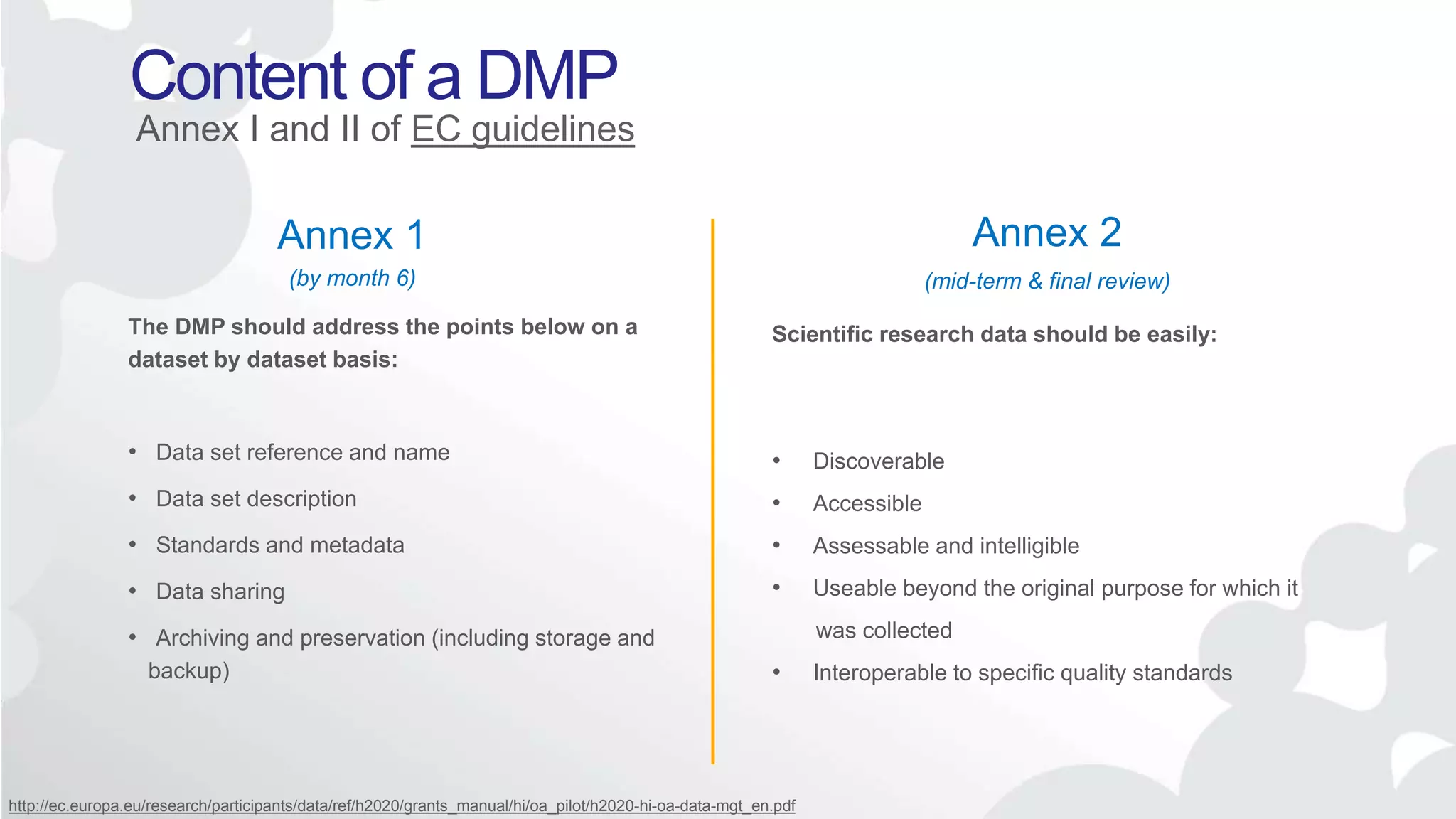
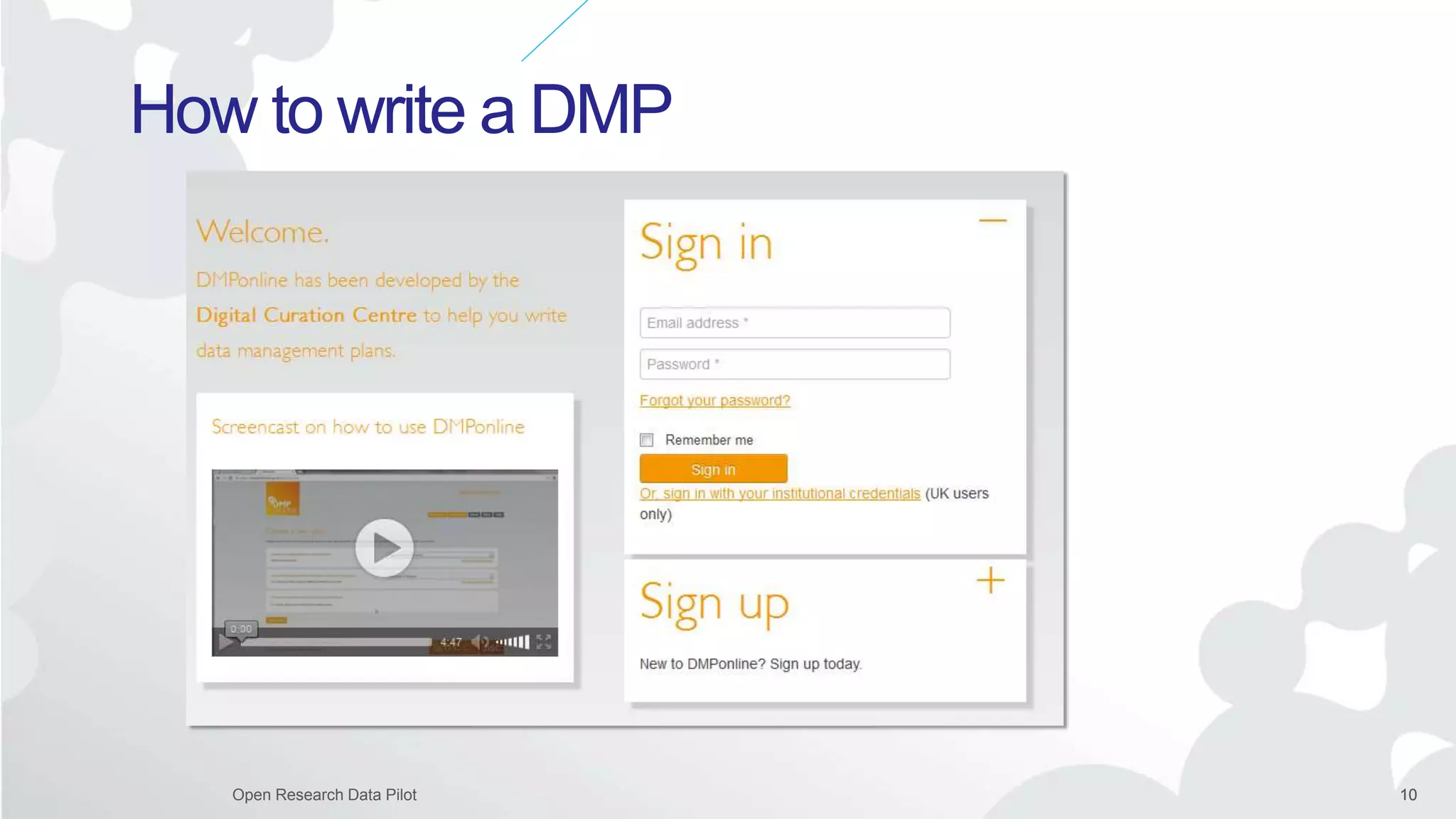
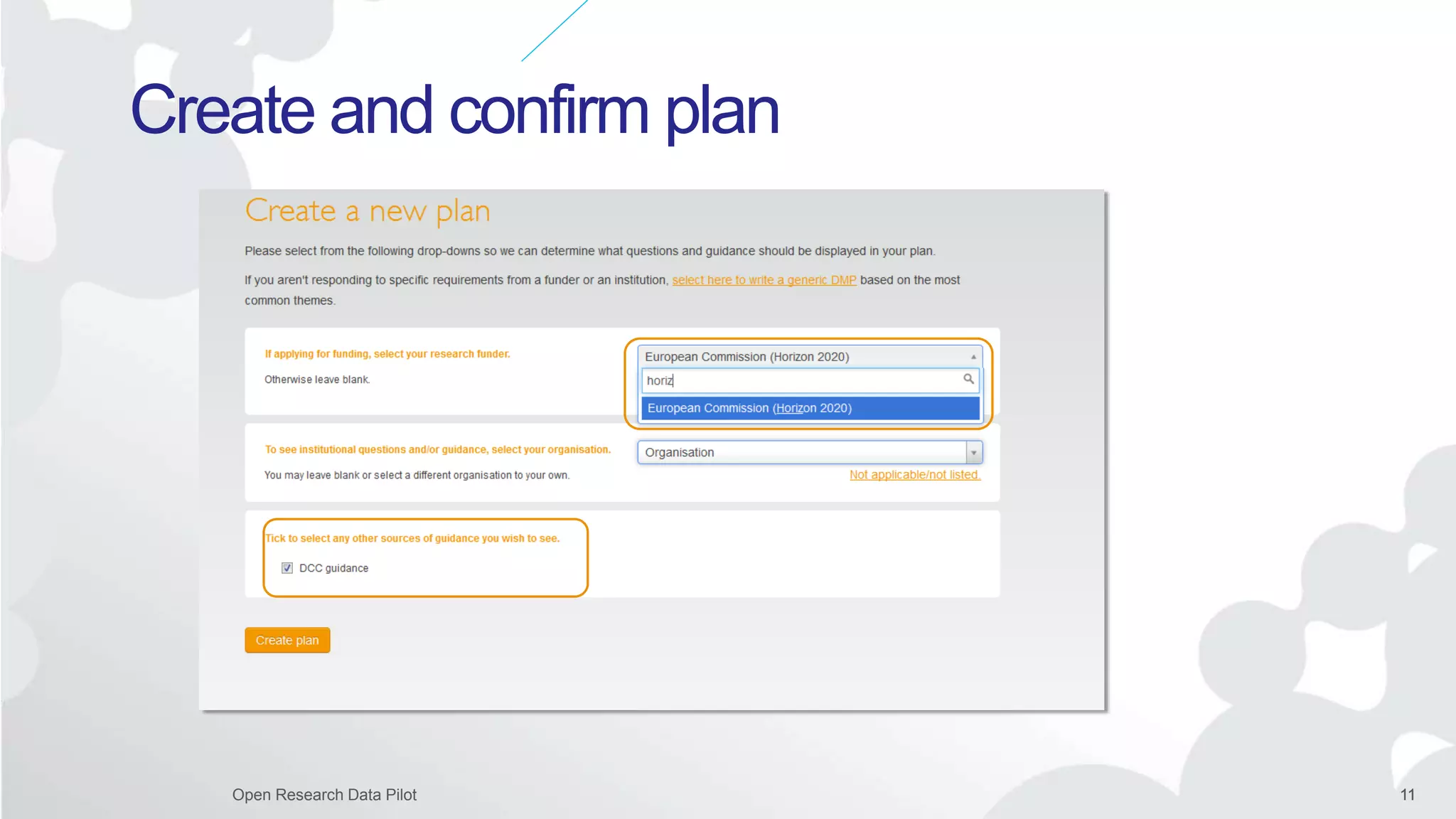
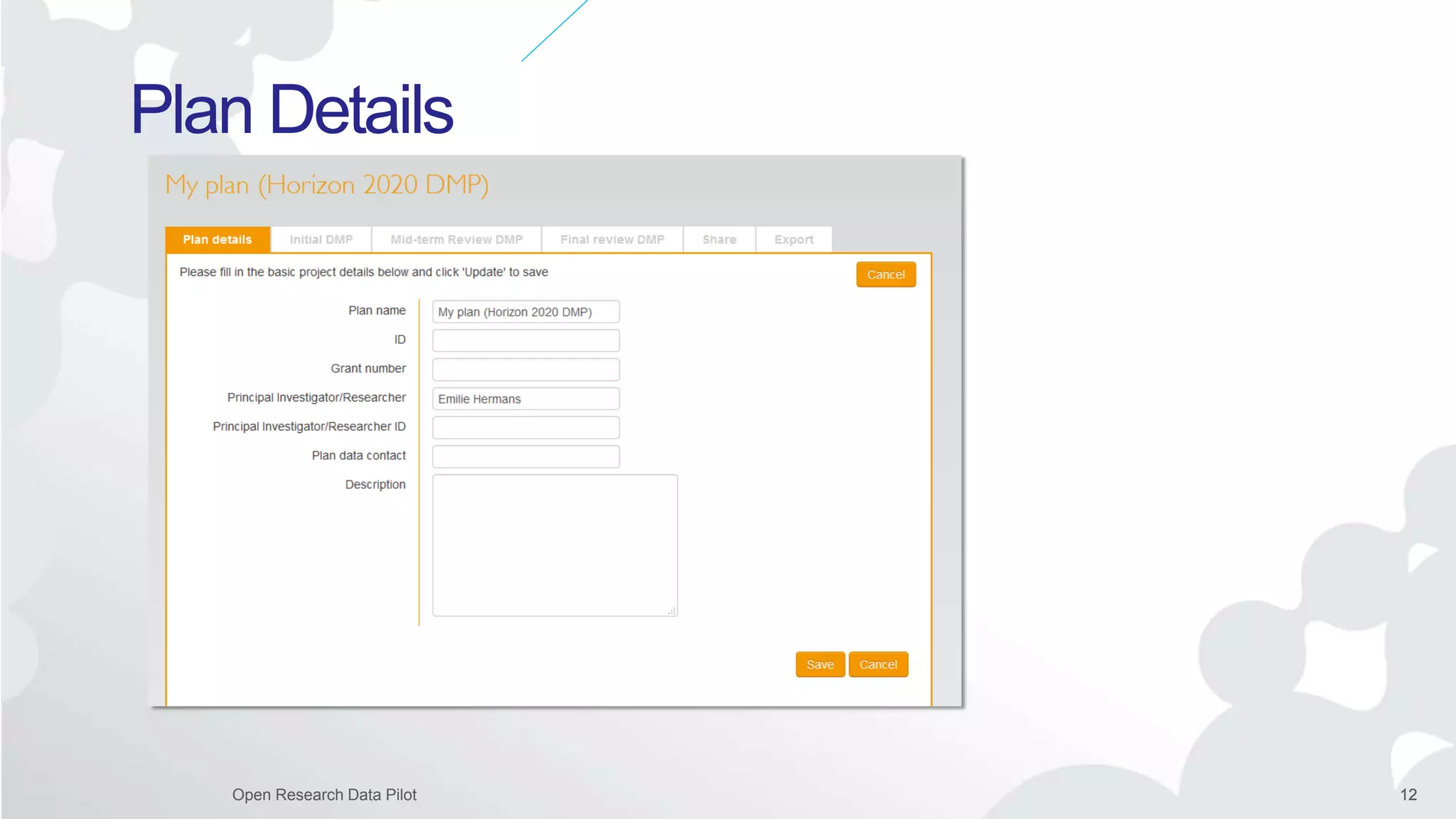
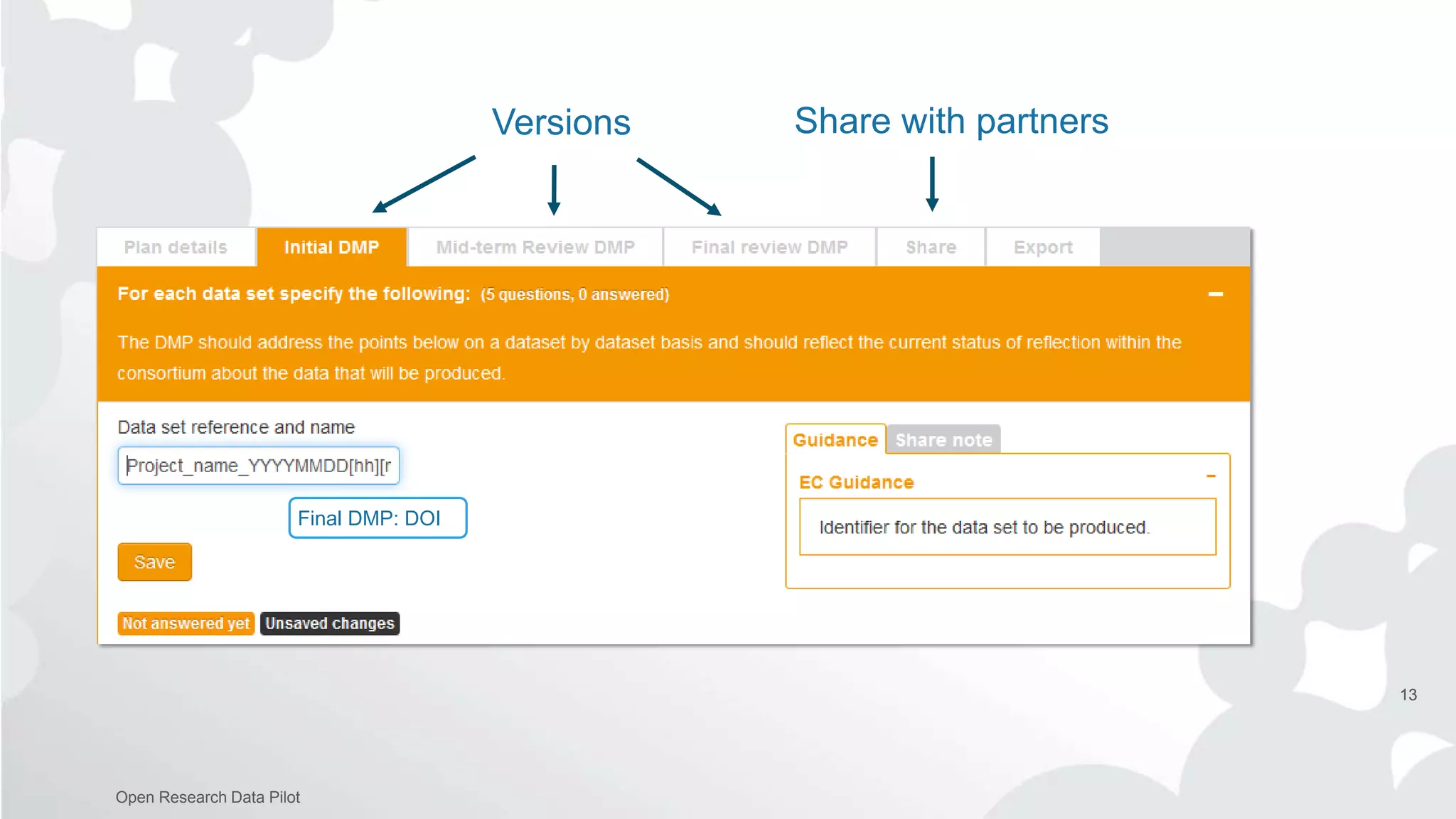
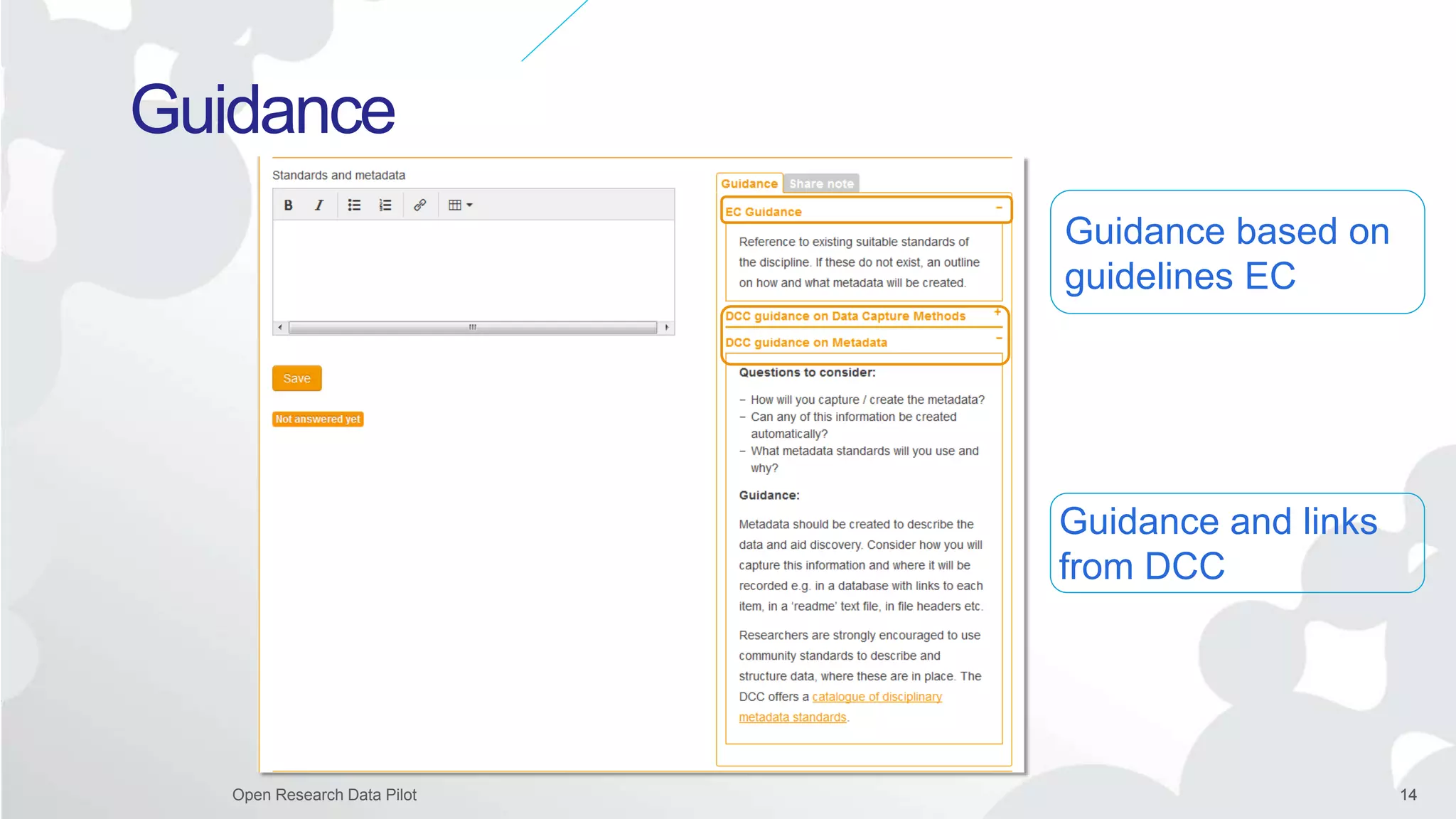
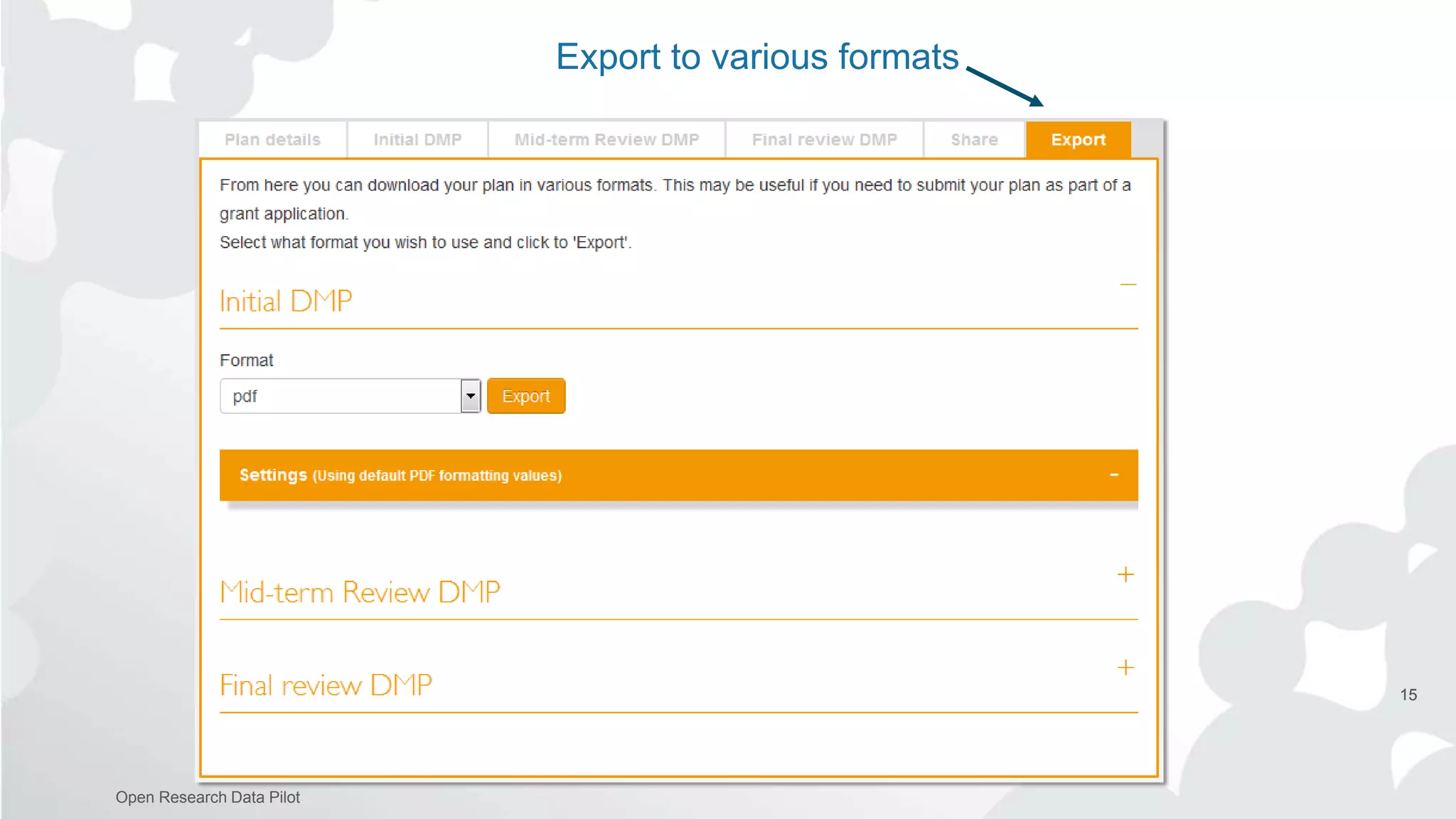
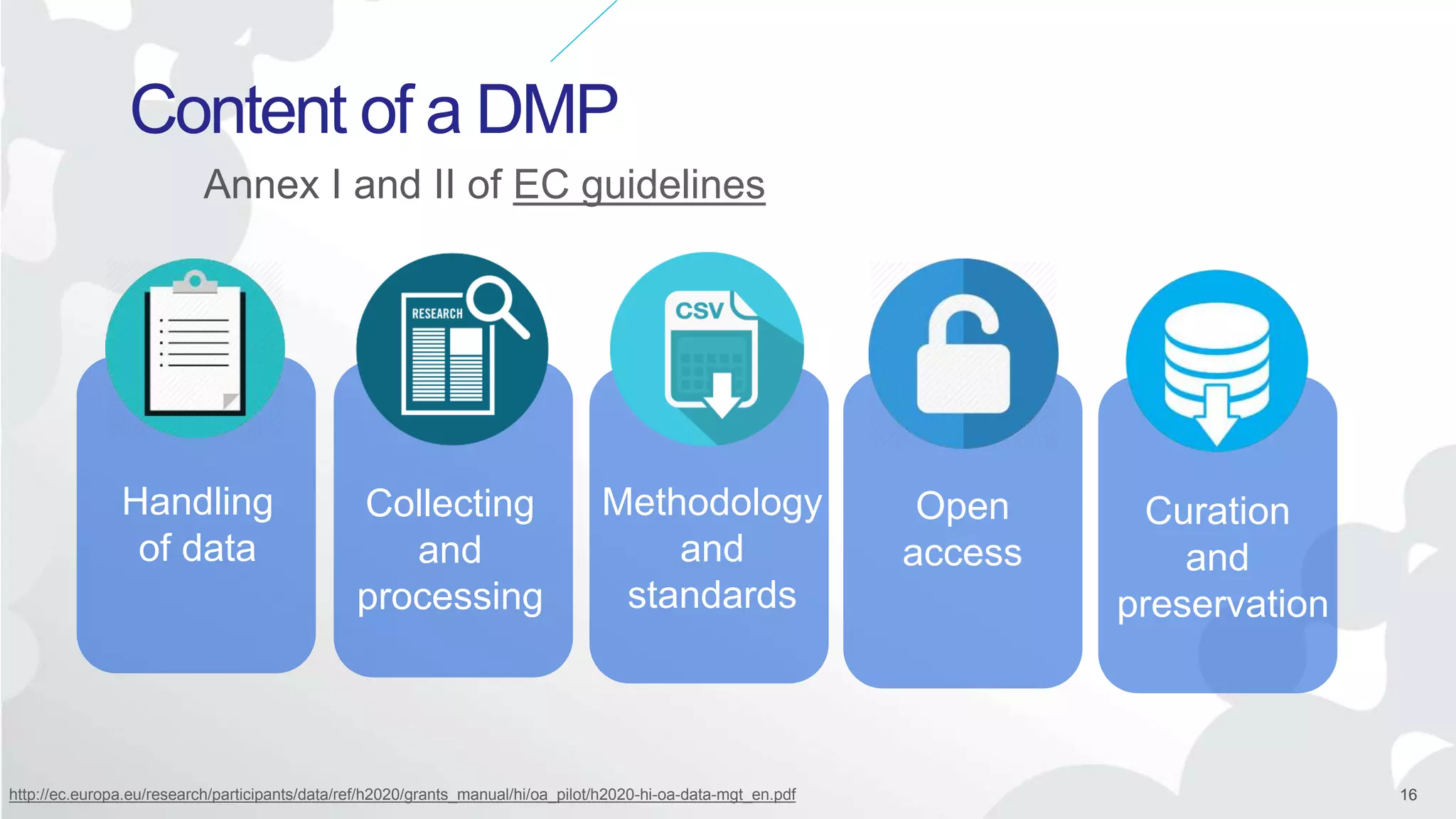
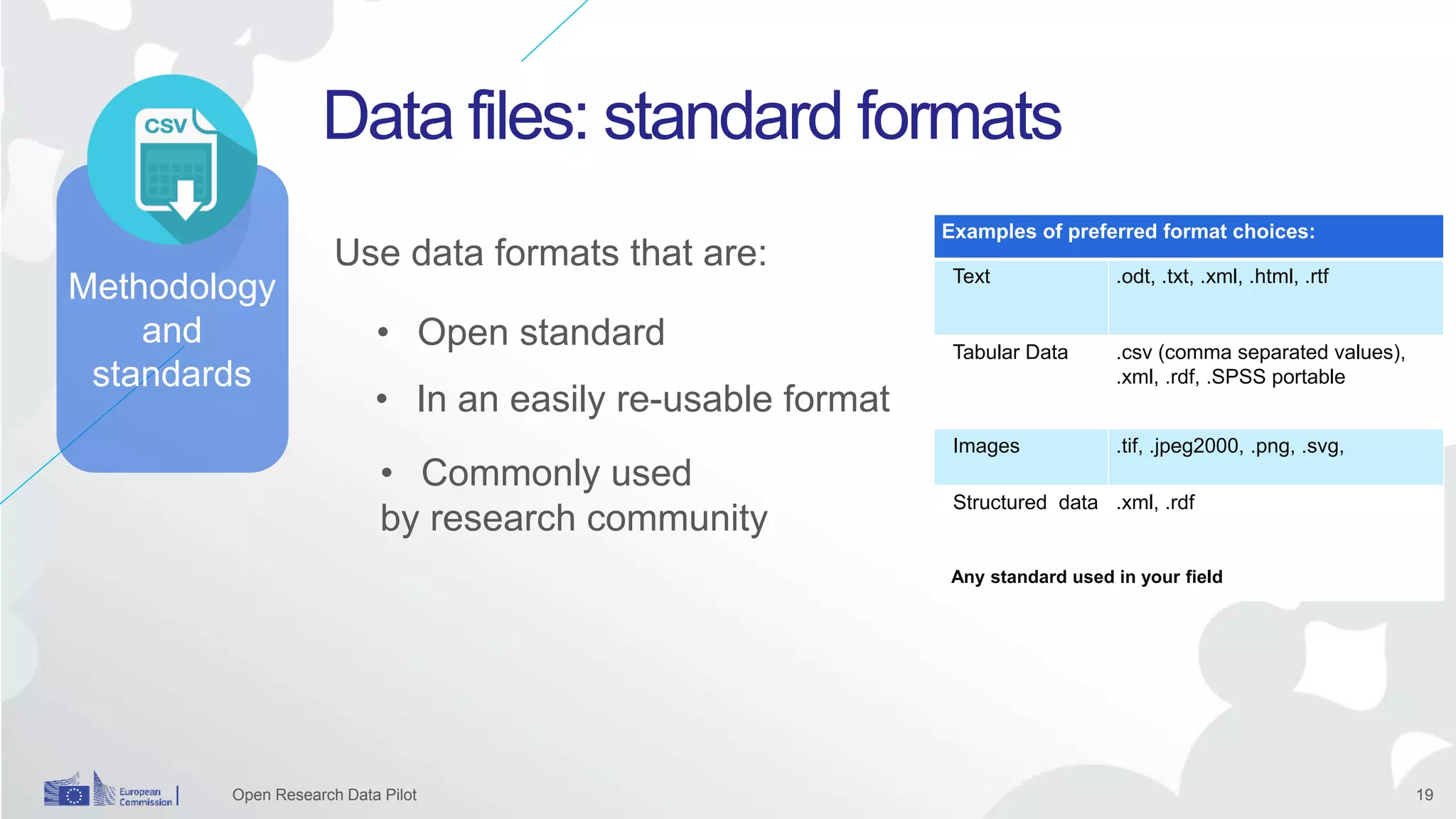
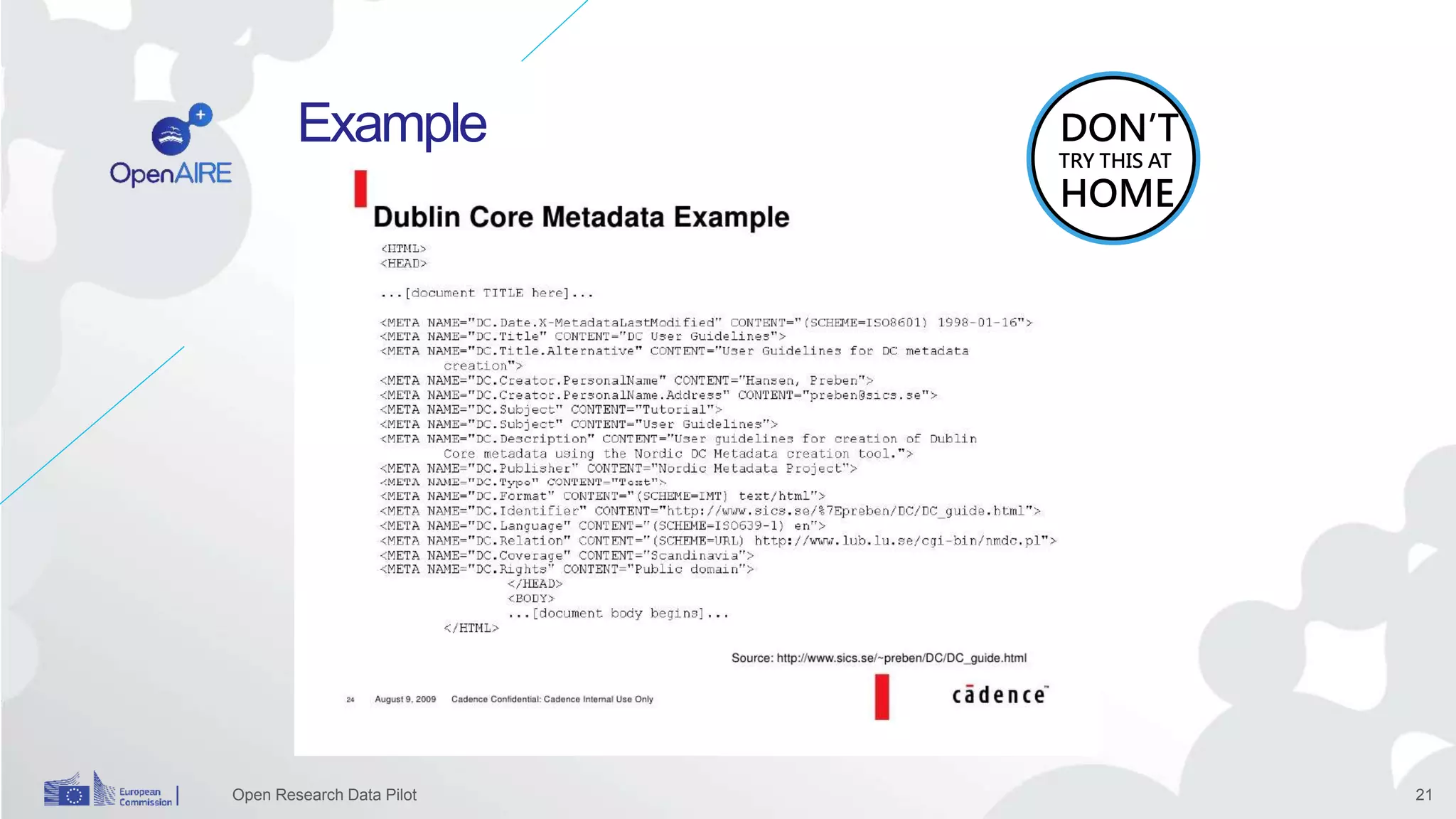
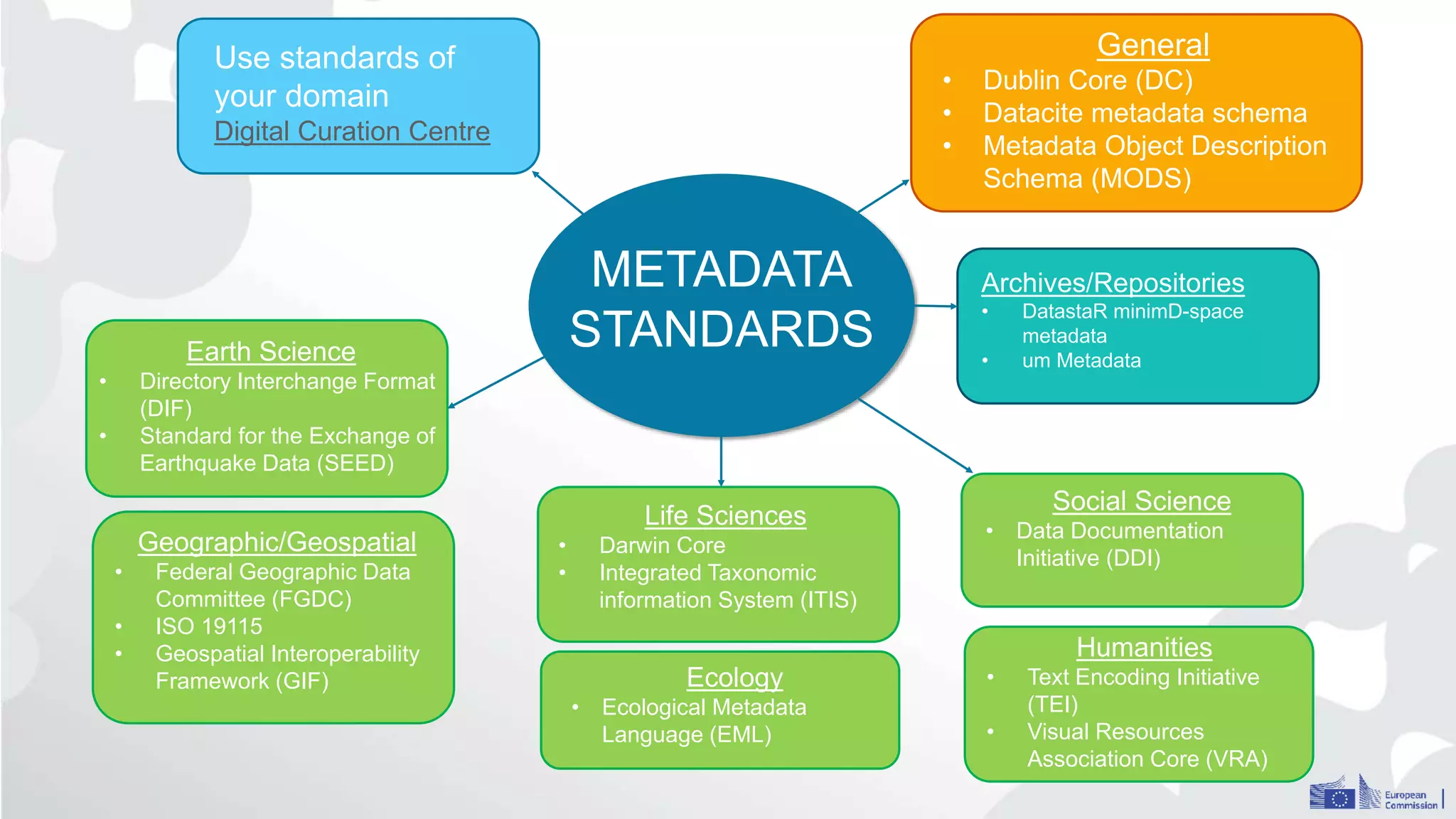
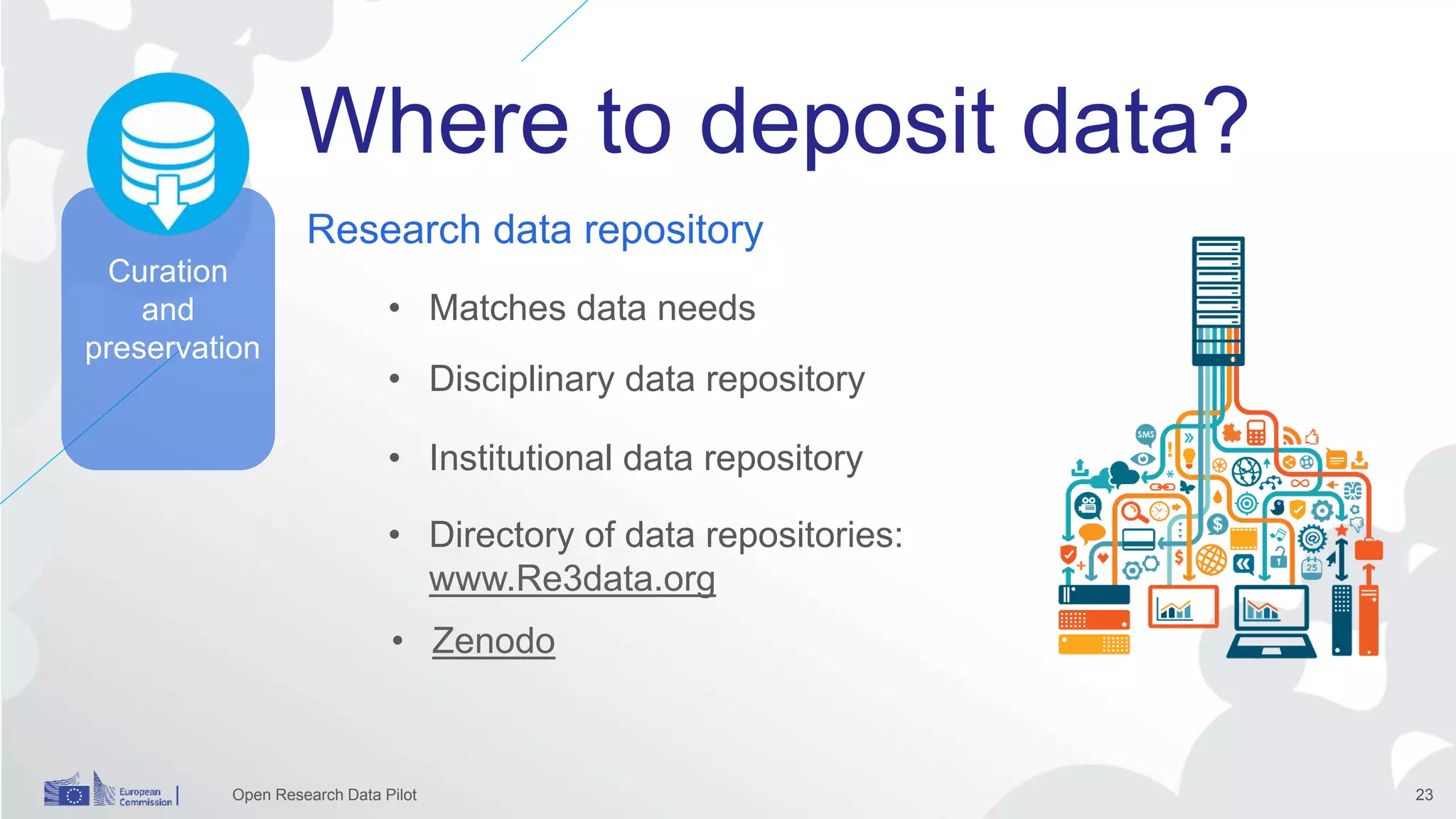
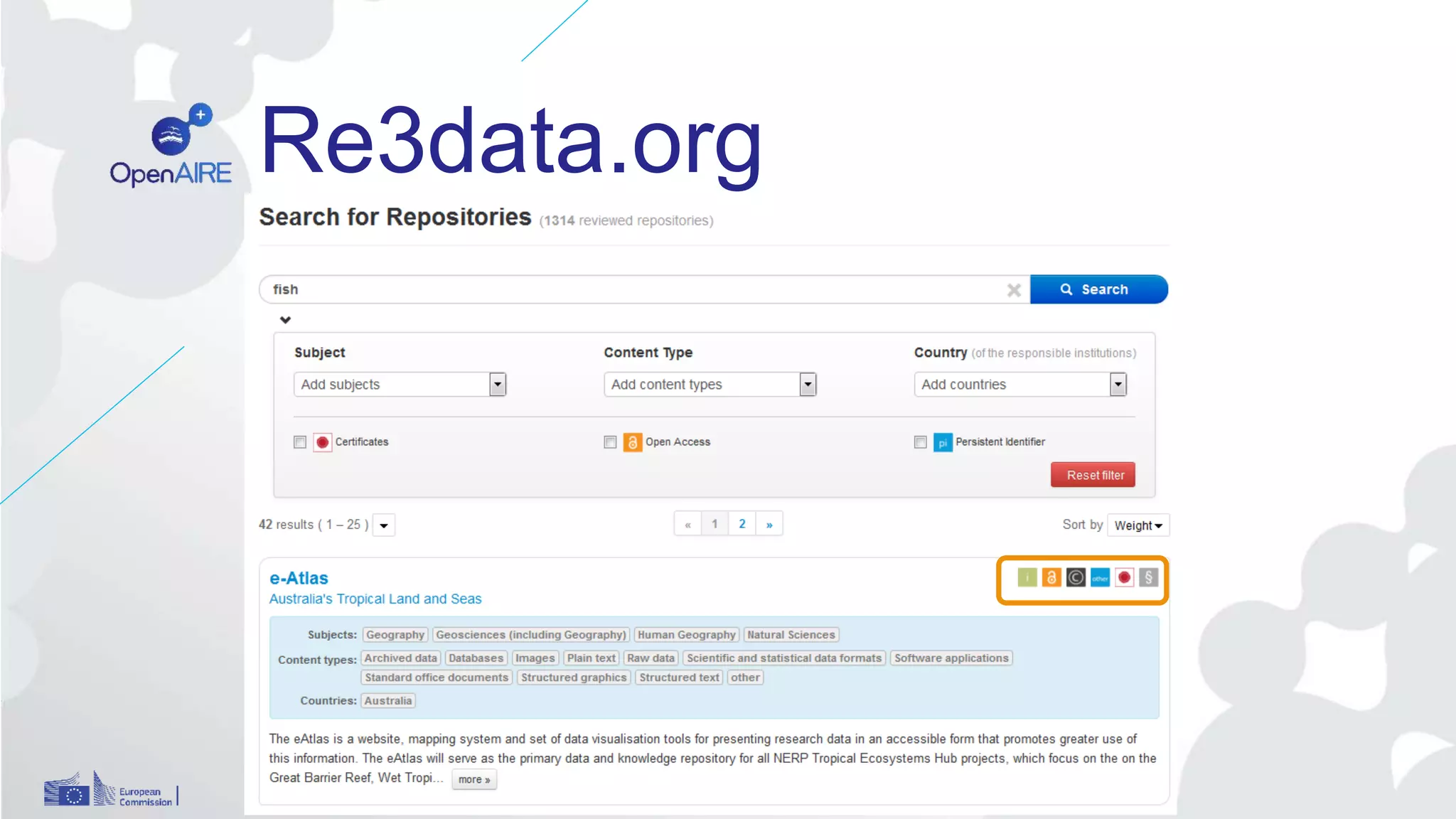
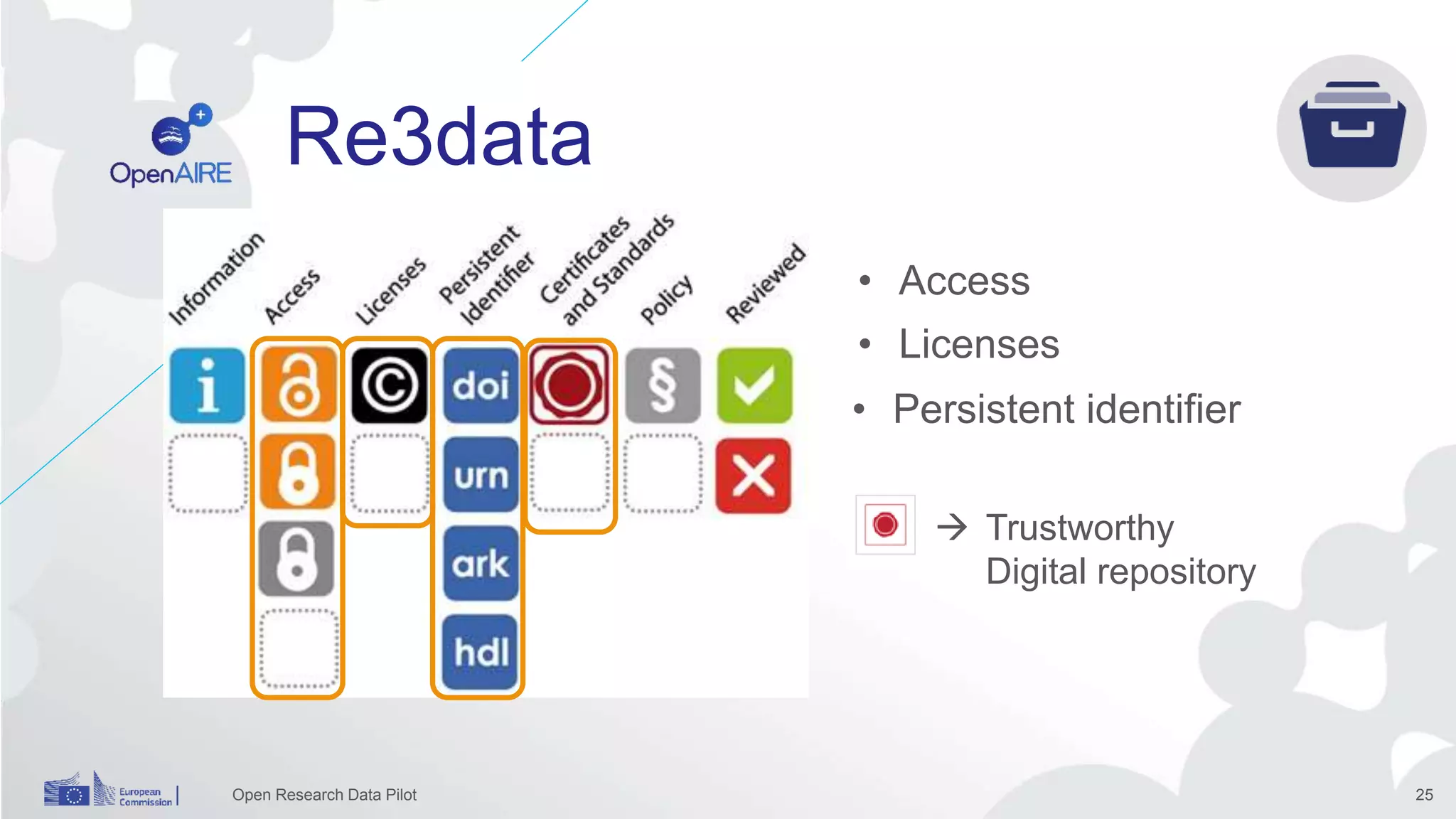
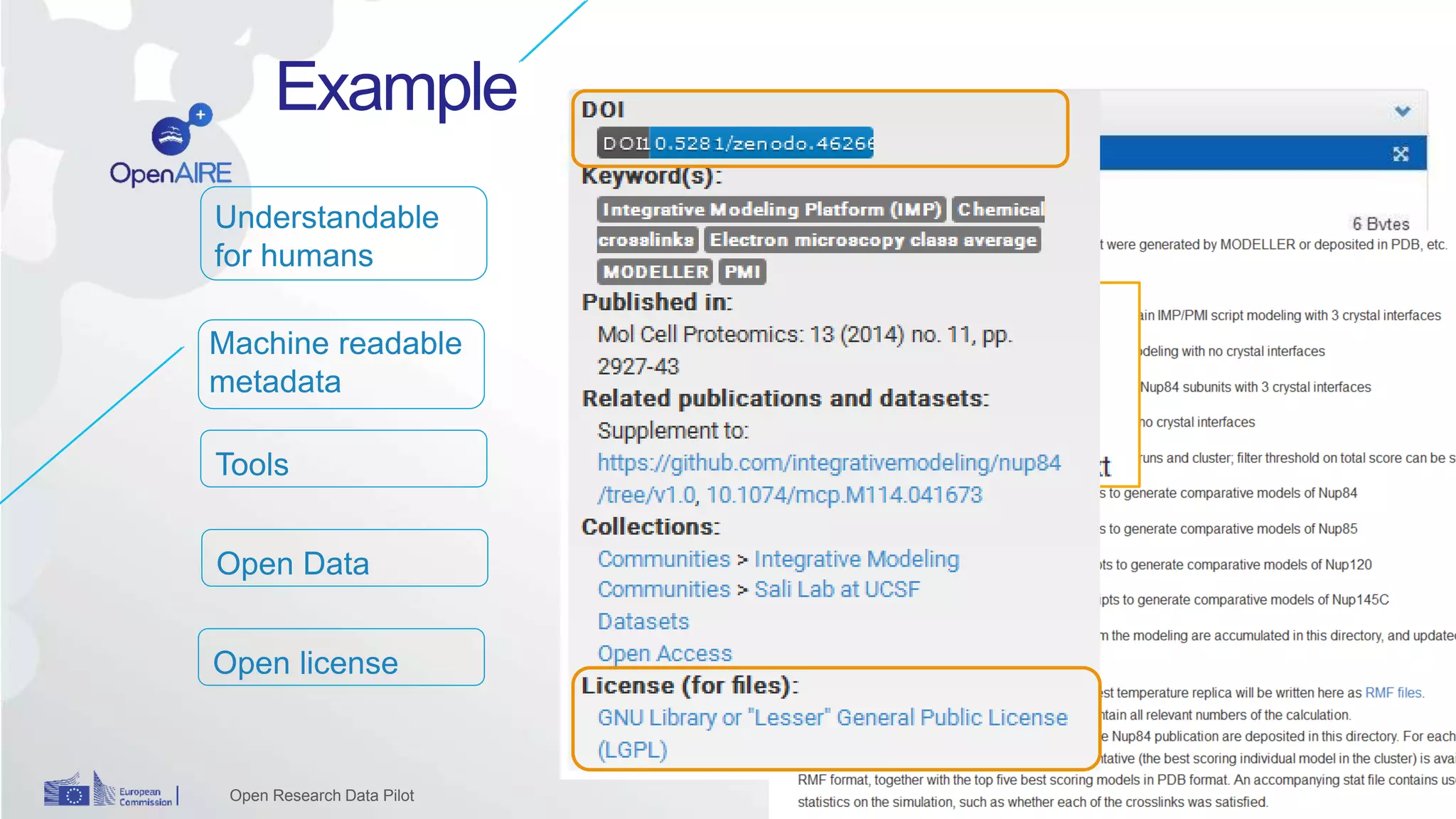
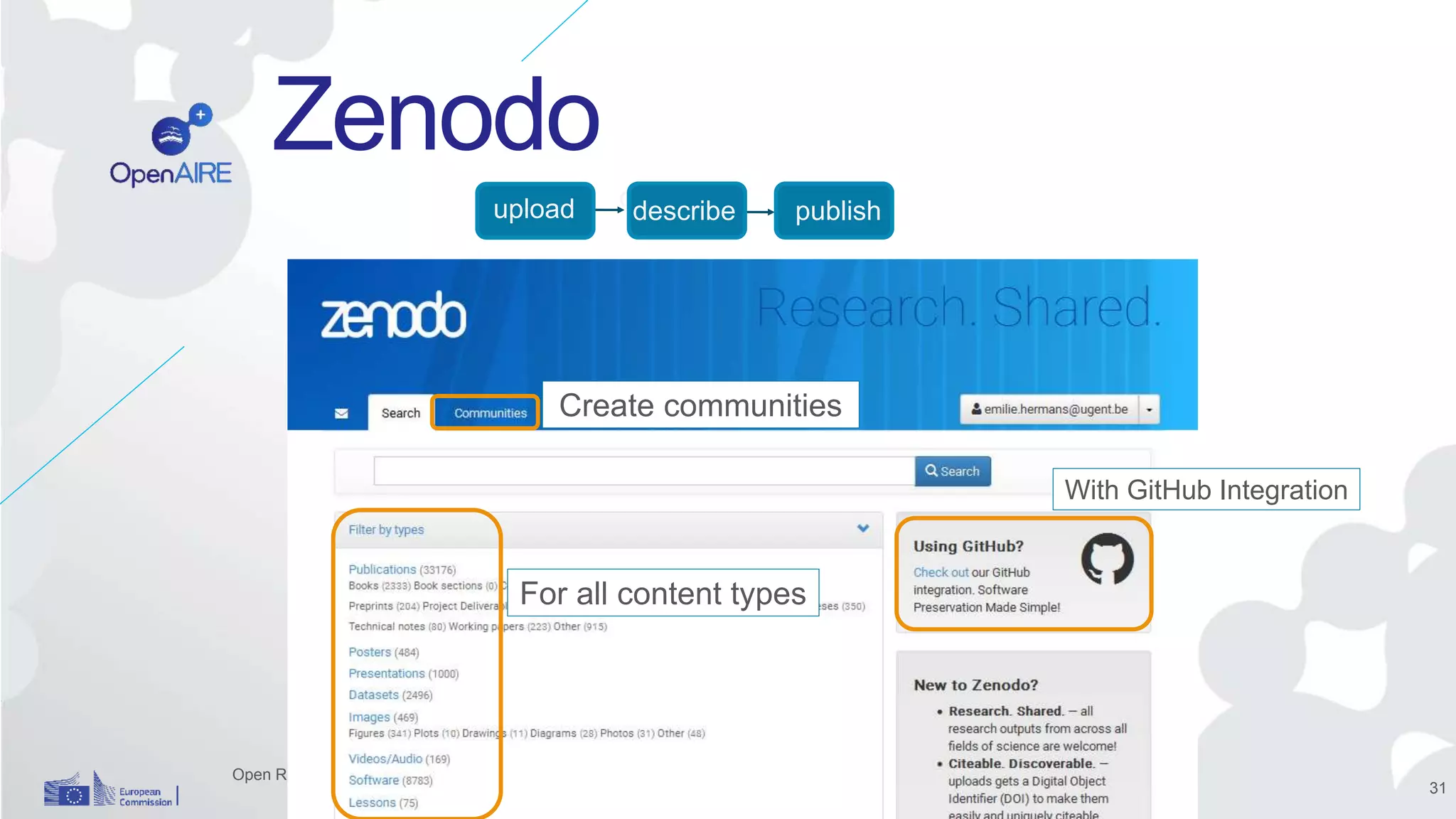
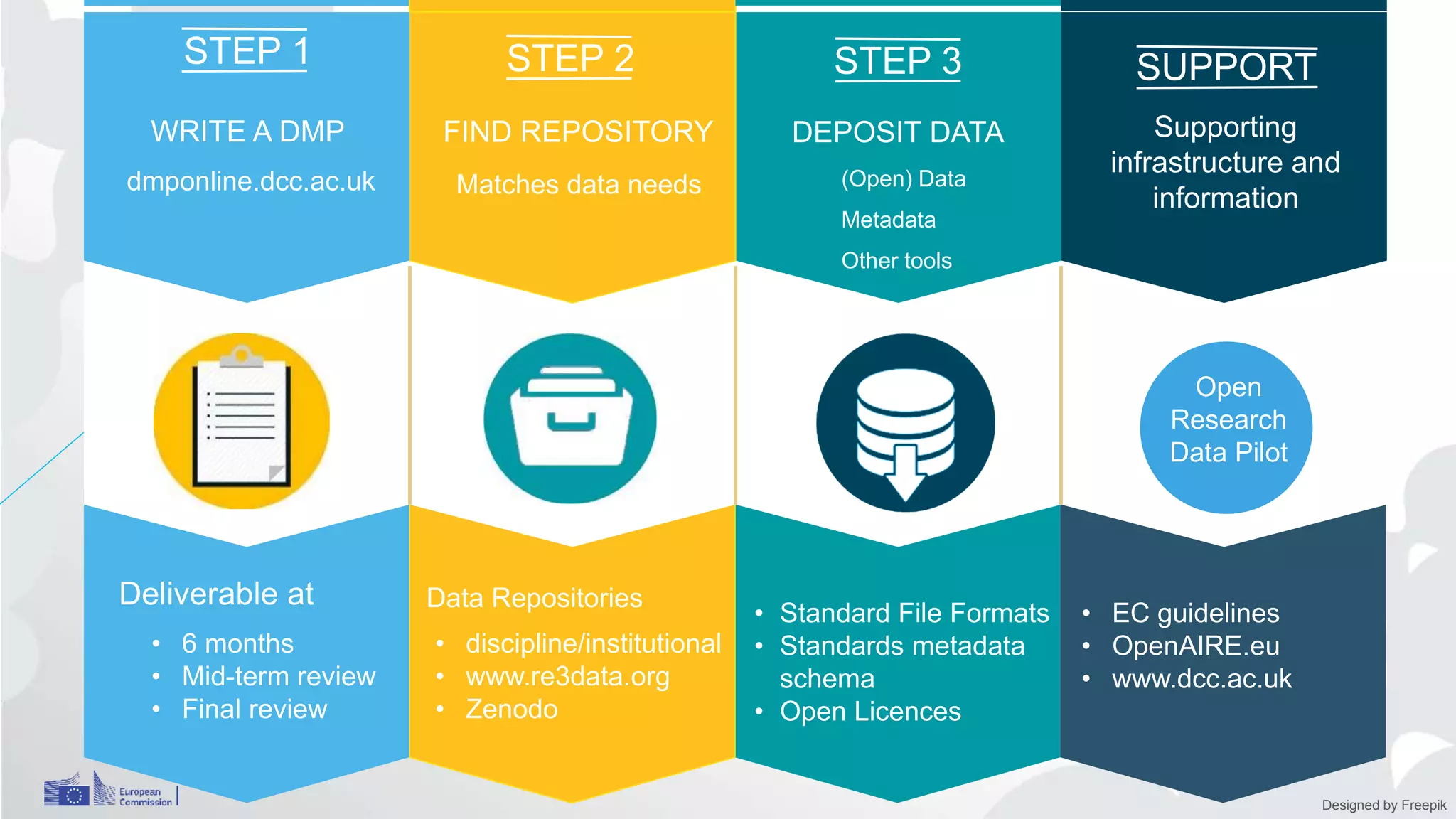
The Open Research Data Pilot under Horizon 2020 promotes data management and open access to research data, encouraging transparency and maximized resource use. Participants must develop a Data Management Plan (DMP) and deposit data in designated repositories, allowing for flexibility in opting out when necessary. The initiative includes guidance and tools for effective data handling and sharing to enhance scientific collaboration and impact.