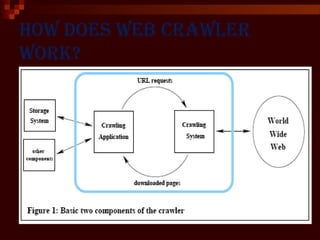
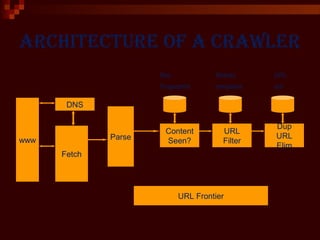
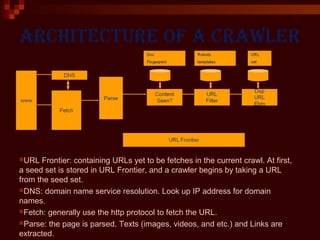
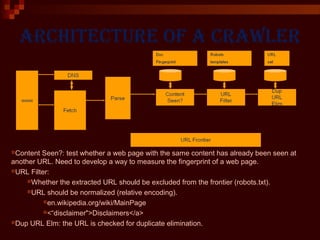
This document provides an introduction to web crawlers. It defines a web crawler as a computer program that browses the World Wide Web in a methodical, automated manner to gather pages and support functions like search engines and data mining. The document outlines the key features of crawlers, including robustness, politeness, distribution, scalability, and quality. It describes the basic architecture of a crawler, including the URL frontier that stores URLs to fetch, DNS resolution, page fetching, parsing, duplicate URL elimination, and filtering based on robots.txt files. Issues like prioritizing URLs, change rates, quality, and politeness policies are also discussed.