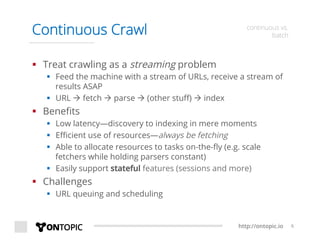
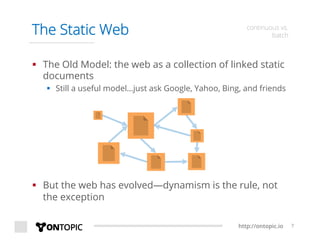
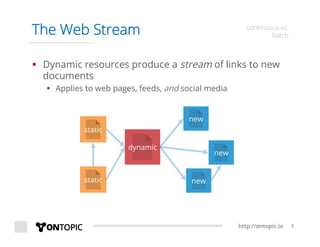
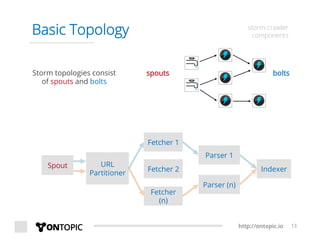
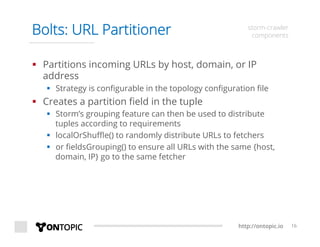
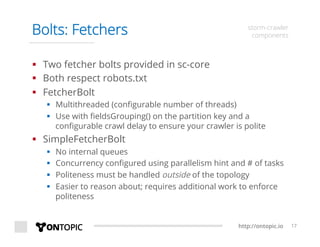
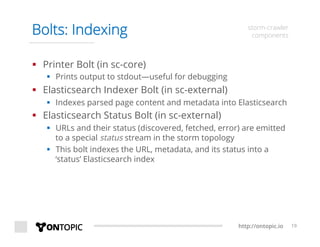
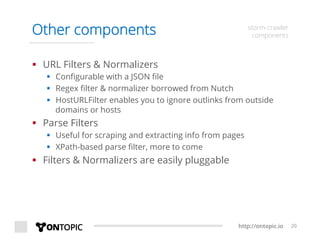
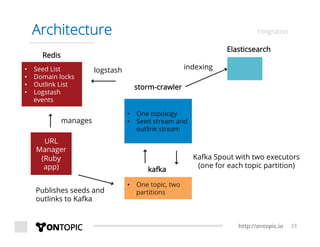
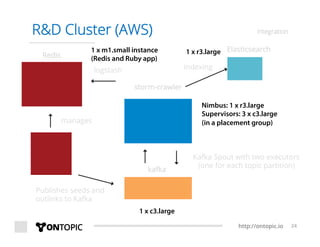
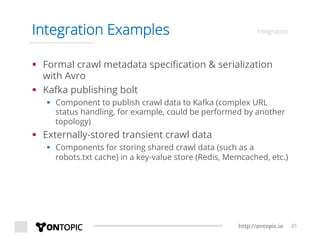
The document provides an overview of Storm Crawler, a real-time distributed web crawling framework built on Apache Storm, allowing for continuous and efficient crawling. It discusses the advantages of continuous crawling over traditional batch methods, highlighting low latency and better resource allocation. The document also outlines the components of Storm Crawler and its integration with technologies like Elasticsearch and Kafka, along with various use cases and deployment examples.