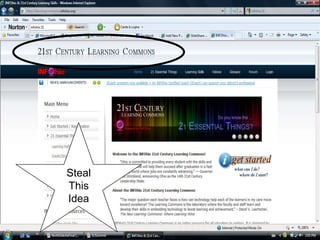
1. The document discusses strategic priorities for libraries and how library strategies must change, focusing on transformations. It emphasizes prioritizing programs over collections, driving reference with data and analytics, and balancing physical and virtual services.
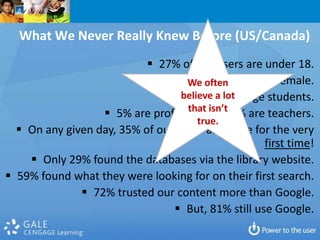
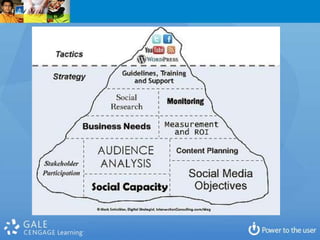
2. Specific challenges discussed include setting priorities and making sacrifices, developing an innovation culture, program evaluation, balancing backroom and front room services, and investing in staff development.
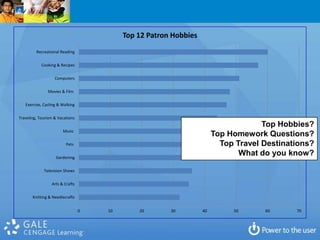
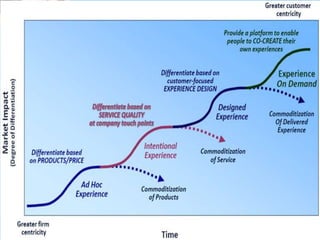
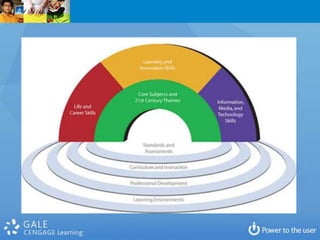
3. The document argues that libraries should focus on experiences rather than transactions, drive services with an understanding of patrons' top questions, and conceptualize services around answering questions and programs rather than collections.