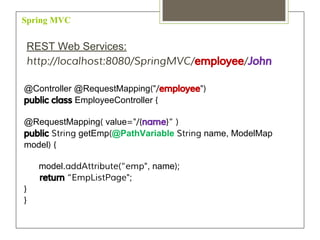
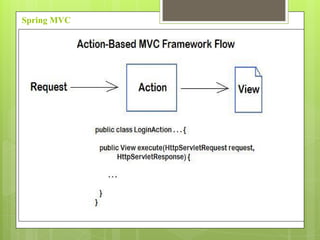
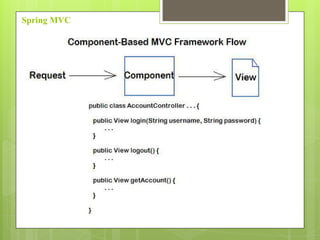
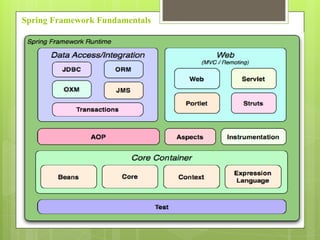
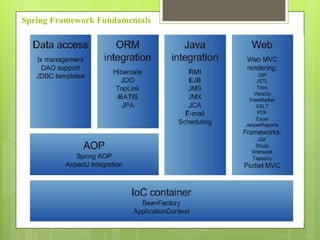
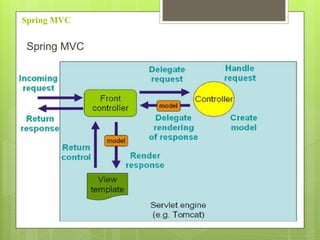
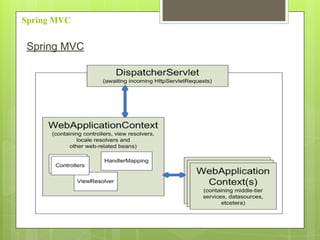
Spring MVC is a web MVC framework that provides a reusable presentation layer for web applications. It removes boilerplate code and standardizes navigation flow and validation. Spring MVC controllers handle HTTP requests and delegate work to service objects. It uses the front controller design pattern and is view-agnostic, allowing different view technologies. Spring MVC applications are configured through XML files and use annotations for components and request mapping.



























![Spring MVC
Bean Validation Framework JSR-303:
public class Employee {
@NotNull
@Pattern(regexp = "[a-z-A-Z]*")
private String firstName;
@Size(min=2, max=15)
private String lastName;
@Past
private Date birthDate;
@Email (message=“Invalid Email “)
private String email;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/springmvc-130725141628-phpapp02/85/Design-Development-of-Web-Applications-using-SpringMVC-34-320.jpg)