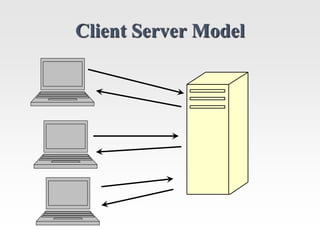
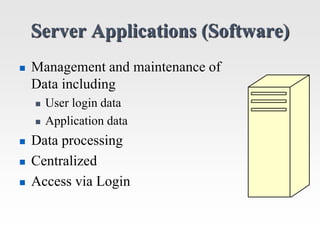
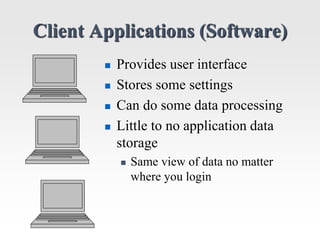
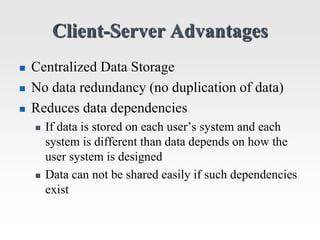
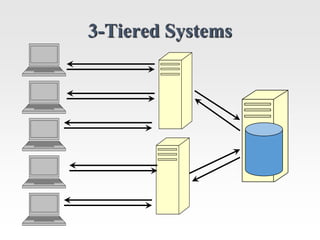
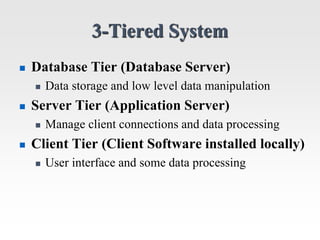
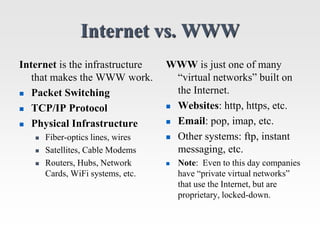
This document discusses the client-server model for web applications. It describes the roles of client and server applications, with the server handling data management and the client providing the user interface. A classic example of an early banking system is provided to illustrate how client-server works. The document then introduces the three-tier architecture with separate database, application, and client tiers. It also provides background on the internet, World Wide Web, and early web application technologies like CGI, ColdFusion, ASP, JSP, and PHP.