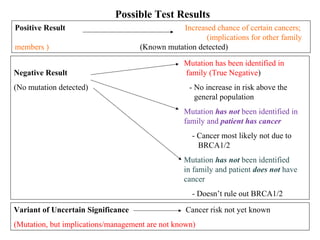
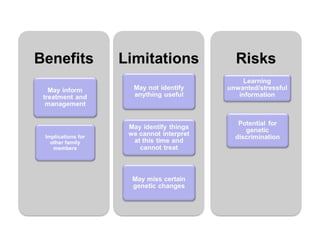
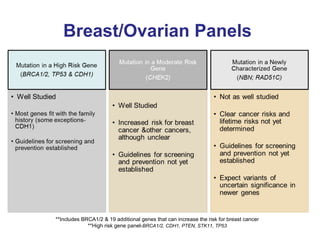
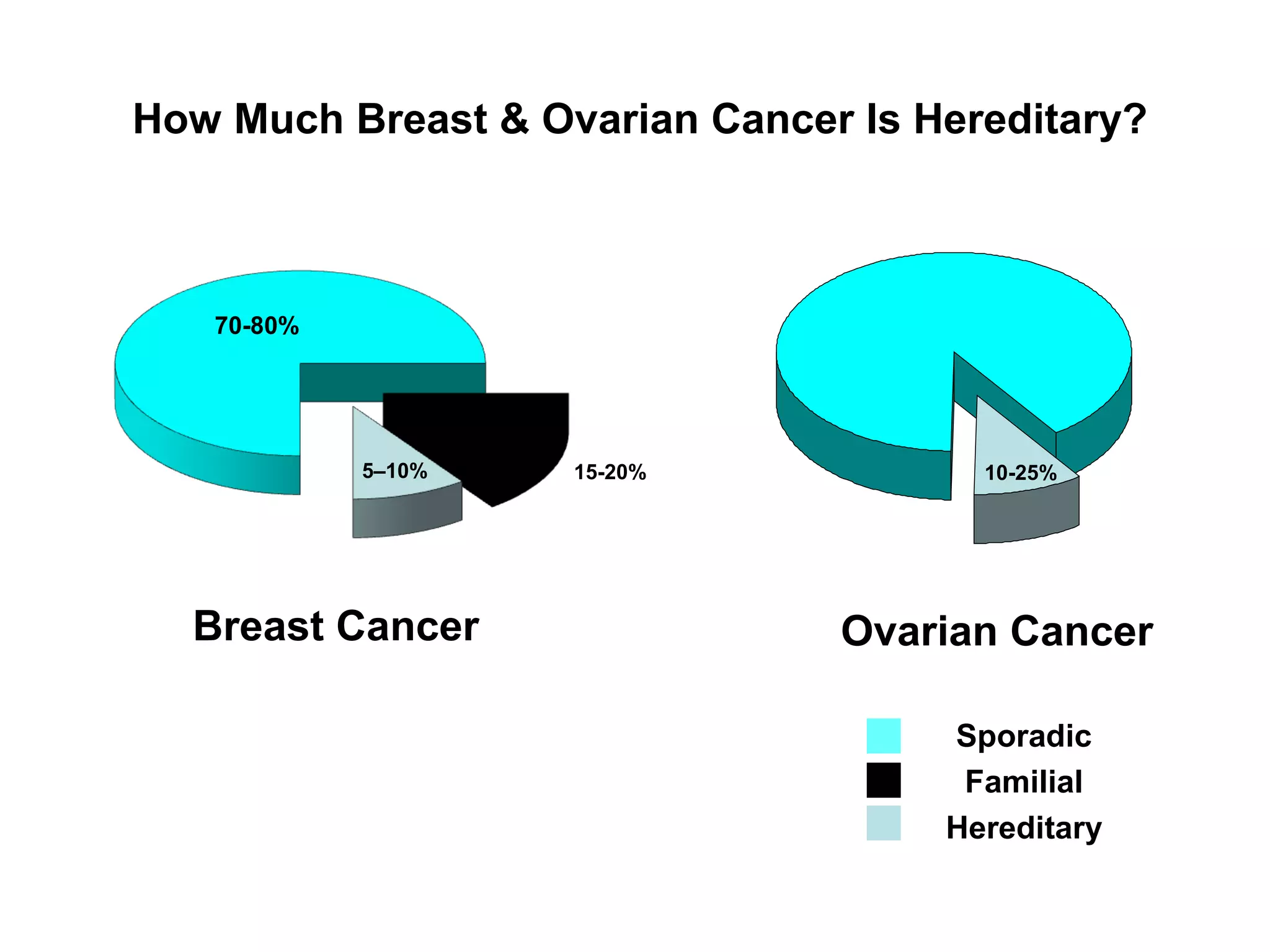
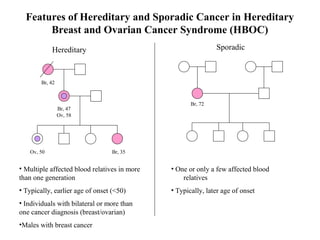
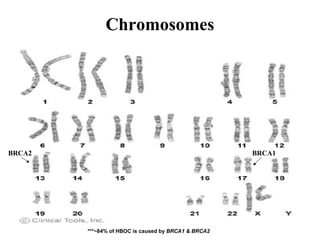
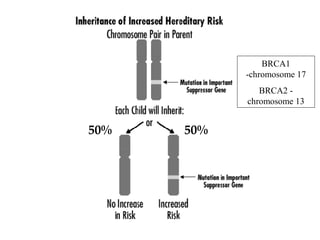
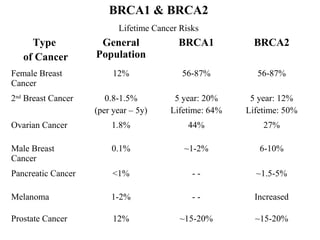
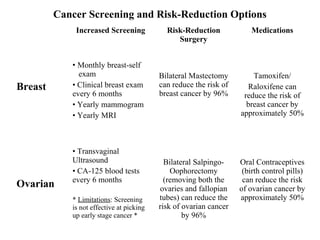
The document summarizes information about hereditary breast and ovarian cancer syndrome (HBOC). It finds that 10-25% of breast cancer and 5-10% of ovarian cancer is considered hereditary. The majority of HBOC cases, around 84%, are caused by mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes. Carriers of BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations have significantly increased lifetime risks of developing breast cancer (56-87% for both genes) and ovarian cancer (44% for BRCA1, 27% for BRCA2) compared to the general population. Genetic testing for BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations is available to assess cancer risk and guide risk-reducing medical or
![Genetic Testing for Breast Cancer
BRCA1
BRCA2
ATGCCGTATAGCTAGTCGATGTACG
• Blood Test
• Misspellings, Deleted, or Added DNA [i.e., mutation]
• Tests offered:
-Analysis of BRCA1 & BRCA2 genes [3-4 weeks]
-Breast/Ovarian Panels [12 weeks]
-Targeted mutation analysis (when family mutation is known) [3 weeks]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/web-140424160000-phpapp01/85/Web-hboc-visual-aids-7-320.jpg)