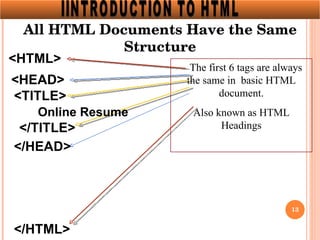
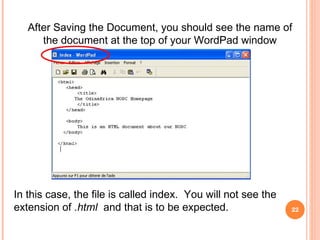
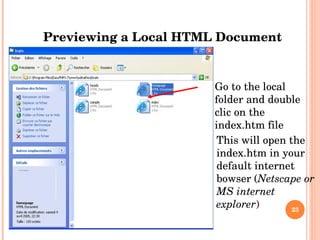
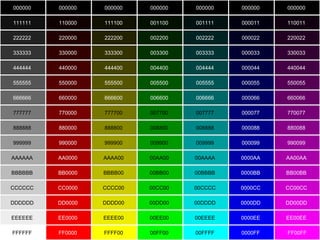
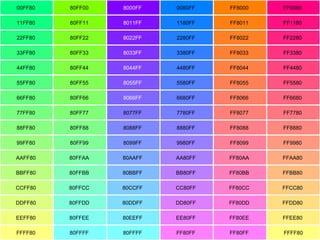
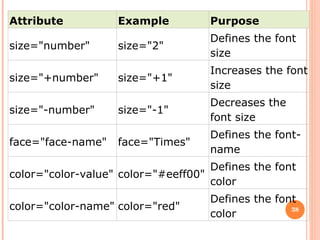
The document introduces HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) and its basic structure and elements. It discusses the history and development of HTML, including its early versions. It also provides examples of common HTML tags for text formatting, headings, and background colors.