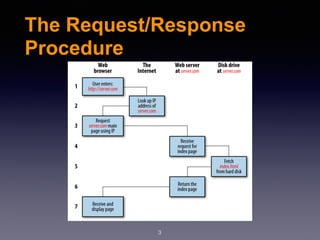
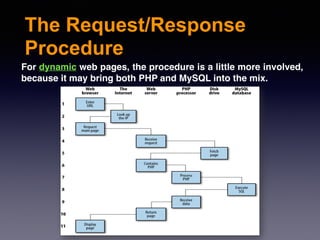
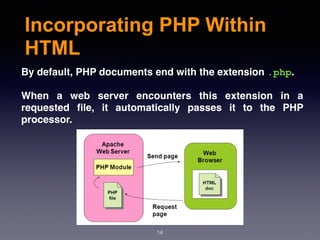
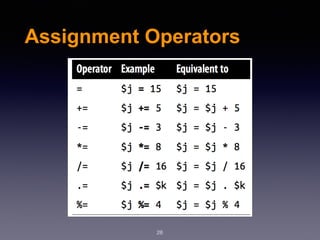
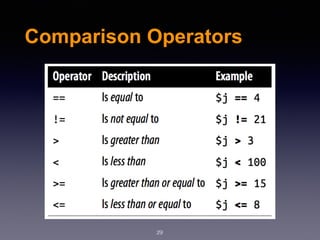
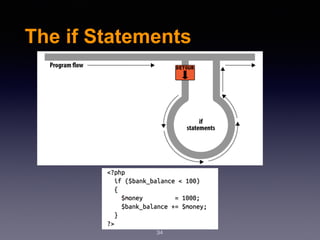
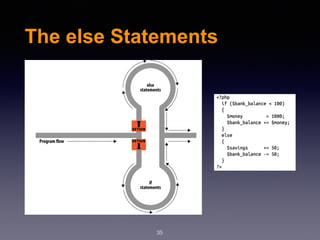
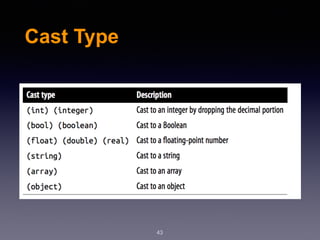
The document provides an introduction to web design and development using PHP. It discusses request/response procedures, using PHP and a web server to generate dynamic web pages. It also covers IDEs, introducing PHP syntax including variables, data types, operators, and control structures like if/else statements and loops. Functions are defined using PHP syntax.