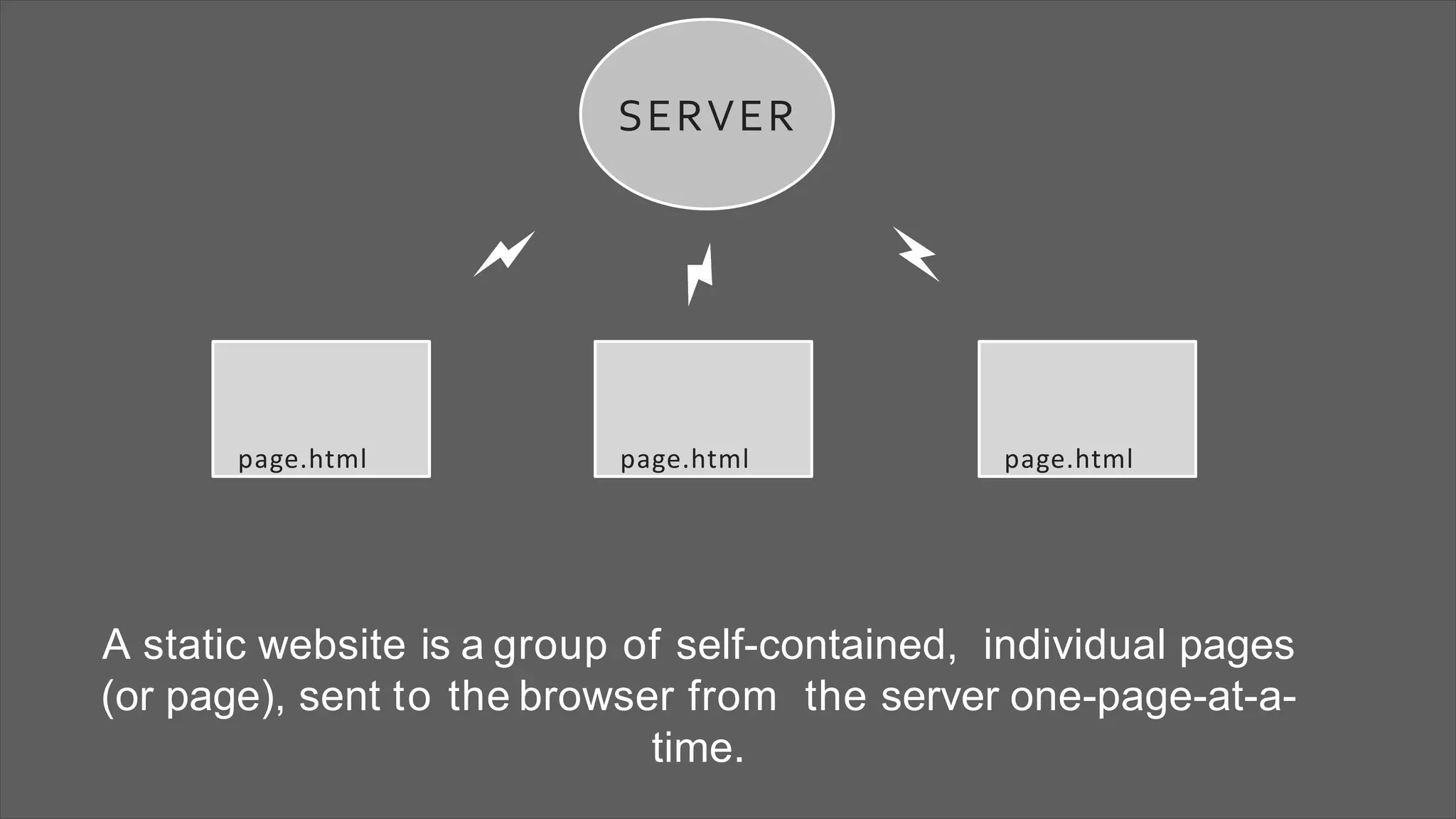
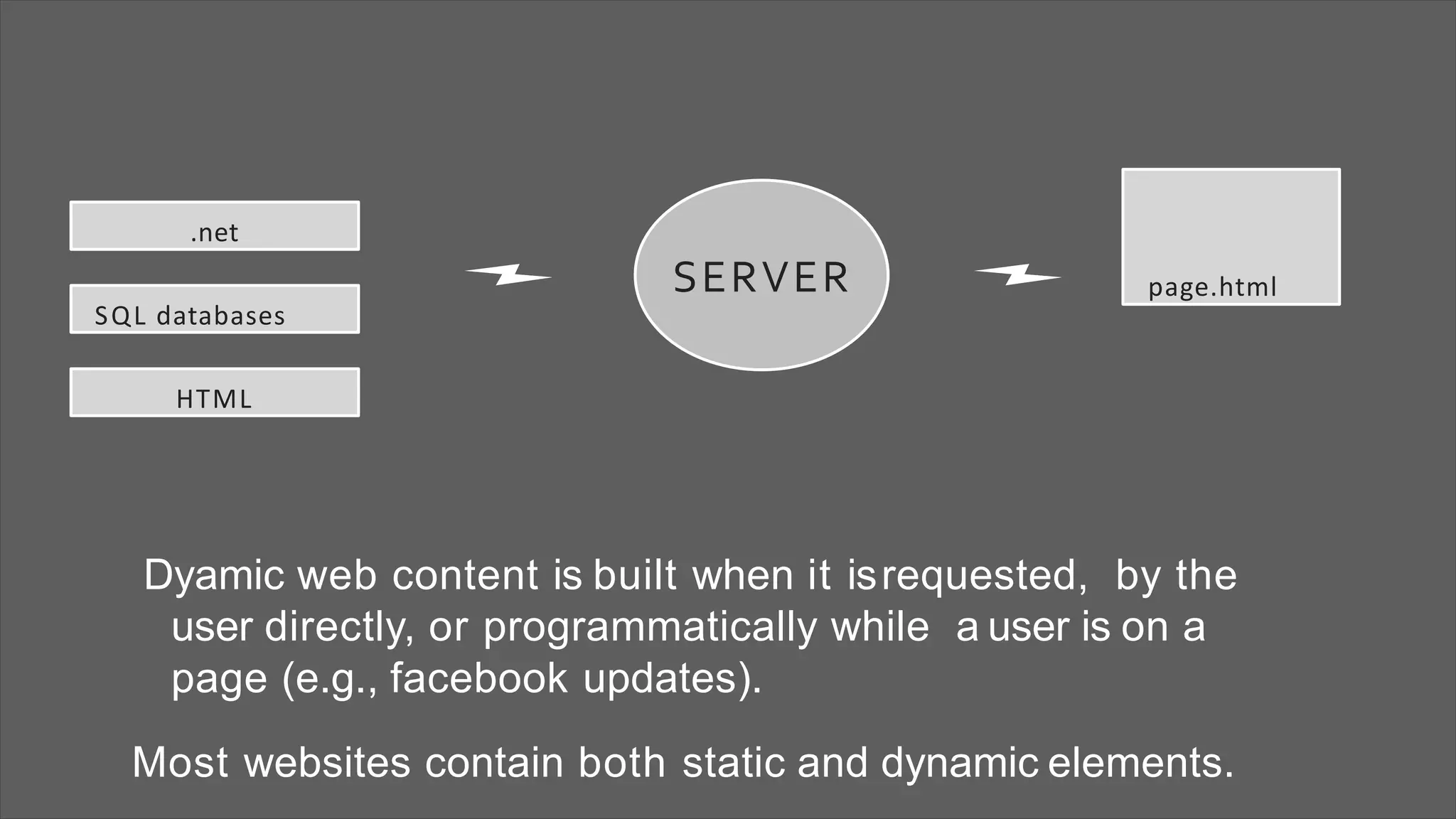
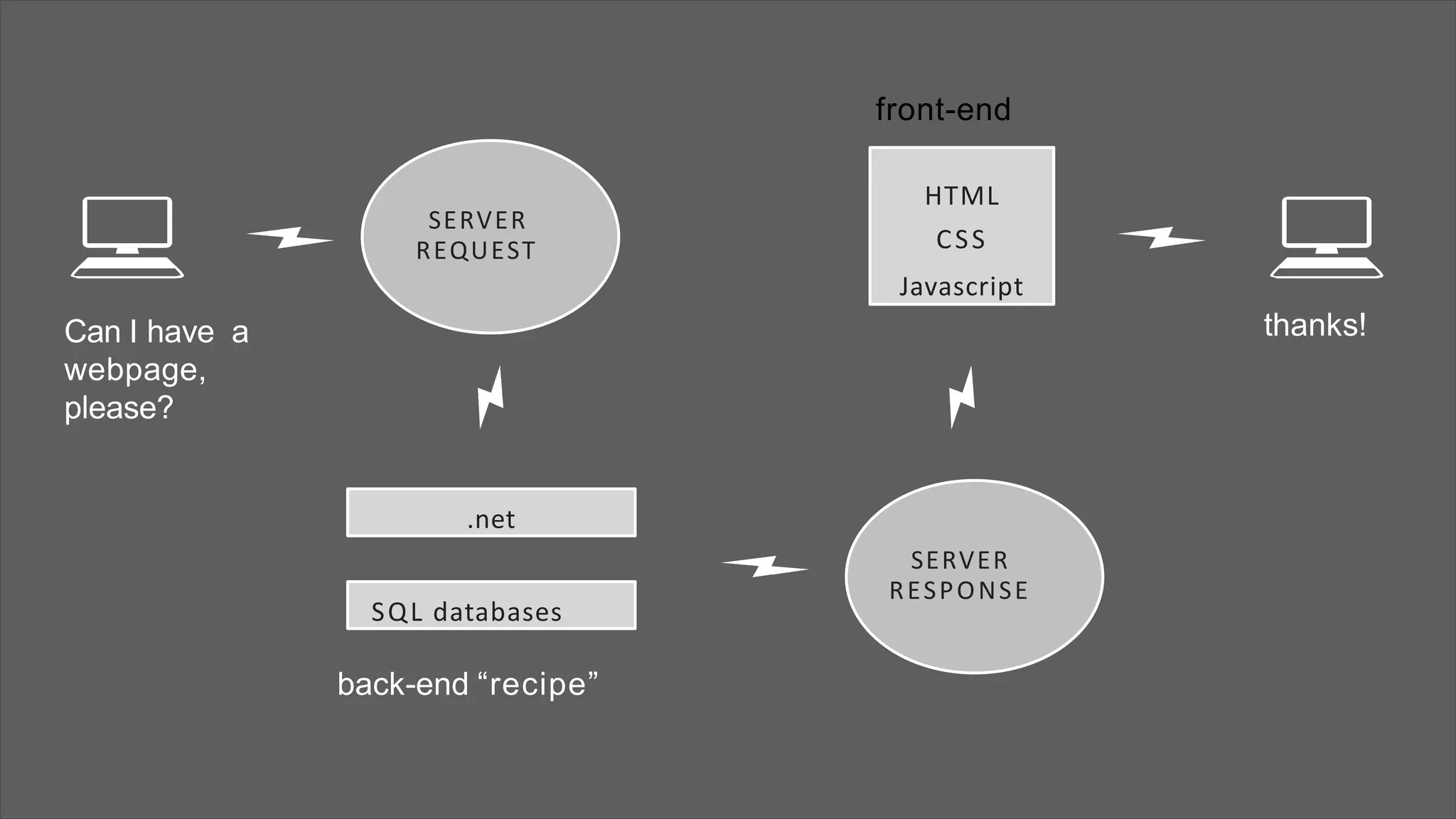
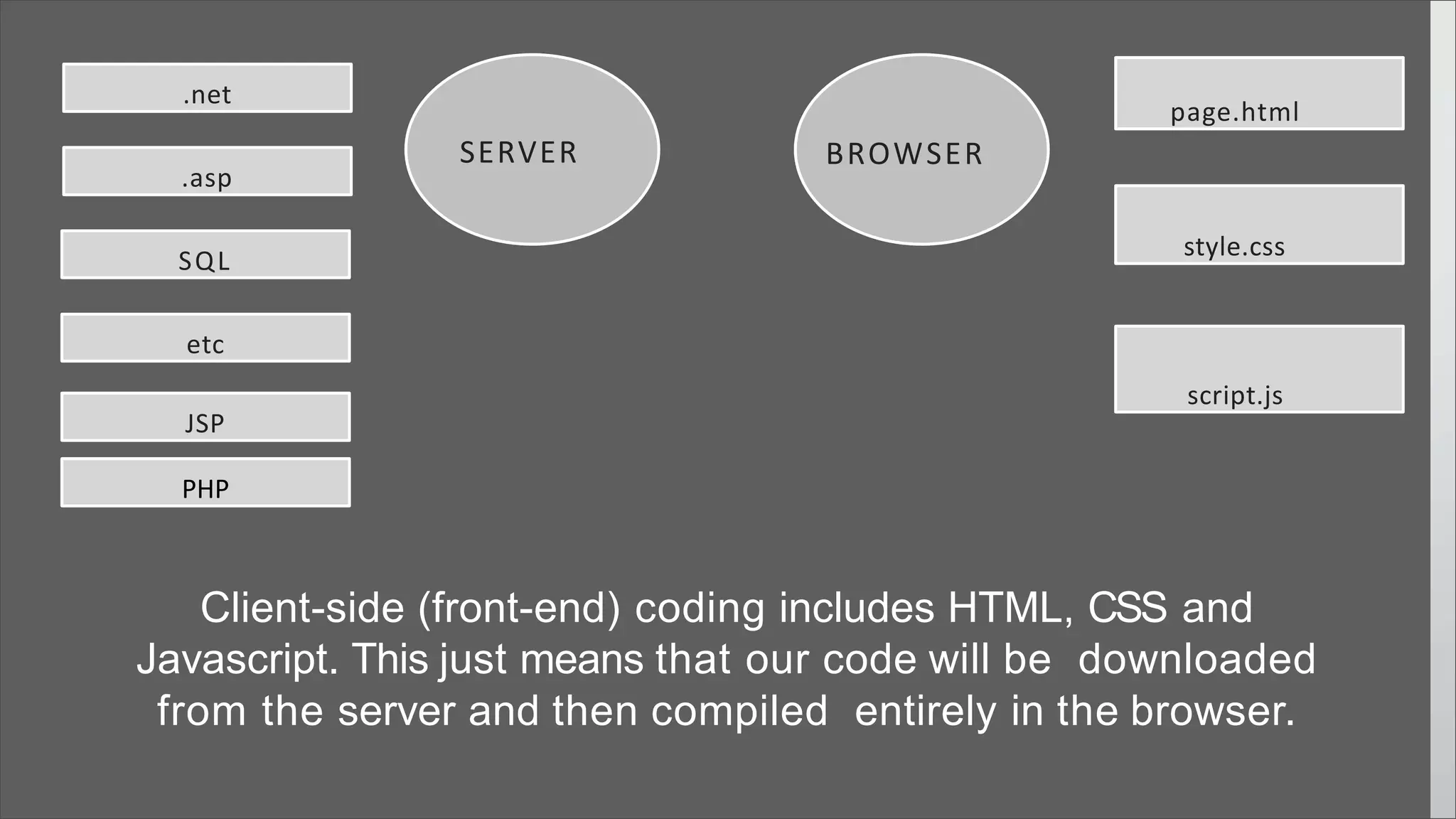
The document provides an overview of web development concepts, focusing on static and dynamic web pages, server-side vs client-side coding, and the PHP programming language. It describes PHP's features, installation environments, and basic syntax, covering variable types, constants, operators, decision-making statements, and loops. Additionally, it highlights PHP's capabilities in handling forms, database interactions, and user session management.










































![Numeric Array
These arrays can store numbers, strings and any object but their index will be prepresented by numbers. By
default array index starts from zero.
Example
Following is the example showing how to create and access numeric arrays.
Here we have used array() function to create array.This function is explained in function reference. <html>
<body>
<?php
/* First method to create array. */
$numbers = array( 1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
foreach( $numbers as $value )
{
echo "Value is $value <br />";
}
/* Second method to create array. */
$numbers[0] = "one";
$numbers[1] = "two";
$numbers[2] = "three";
$numbers[3] = "four";
$numbers[4] = "five";
foreach( $numbers as $value )
{
echo "Value is $value <br />";
}
?>
</body>
</html>
Output becomes
Value is 2
Value is 3
Value is 4
Value is 5
Value is one
Value is two
Value is three
Value is four
Value is five](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontophp-200716212853/75/Introduction-to-php-55-2048.jpg)

![Example
<html>
<body>
<?php
/* First method to associate create array. */
$salaries = array(
"mohammad" => 2000,
"qadir" => 1000,
"zara" => 500
);
echo "Salary of mohammad is ".
$salaries['mohammad'] . "<br />";
echo "Salary of qadir is ". $salaries['qadir'].
"<br />";
echo "Salary of zara is ". $salaries['zara'].
"<br />";](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontophp-200716212853/75/Introduction-to-php-57-2048.jpg)
![Cont..
/* Second method to create array. */
$salaries['mohammad'] = "high";
$salaries['qadir'] = "medium";
$salaries['zara'] = "low";
echo "Salary of mohammad is ". $salaries['mohammad'] . "<br
/>";
echo "Salary of qadir is ". $salaries['qadir']. "<br />";
echo "Salary of zara is ". $salaries['zara']. "<br />";
?>
</body>
</html>
>
This will produce following result: Salary of
mohammad is 2000
Salary of qadir is 1000
Salary of zara is 500
Salary of mohammad is high
Salary of qadir is medium
Salary of zara is low](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontophp-200716212853/75/Introduction-to-php-58-2048.jpg)

![Cont..
Now the two-dimensional $cars array contains four arrays, and it has two indices: row and column.
To get access to the elements of the $cars array we must point to the two indices (row and column):
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<?php
$cars = array
(
array("Volvo",22,18),
array("BMW",15,13),
array("Saab",5,2),
array("Land Rover",17,15)
);
echo $cars[0][0].": In stock: ".$cars[0][1].", sold: ".$cars[0][2].".<br>";
echo $cars[1][0].": In stock: ".$cars[1][1].", sold: ".$cars[1][2].".<br>";
echo $cars[2][0].": In stock: ".$cars[2][1].", sold: ".$cars[2][2].".<br>";
echo $cars[3][0].": In stock: ".$cars[3][1].", sold: ".$cars[3][2].".<br>";
?>
</body>
</html>
This will produce following result:
Volvo: In stock: 22, sold: 18.
BMW: In stock: 15, sold: 13.
Saab: In stock: 5, sold: 2.
Land Rover: In stock: 17, sold: 15.
Name Stock Sold
Volvo 22 18
BMW 15 13
Saab 5 2
Land Rover 17 15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontophp-200716212853/75/Introduction-to-php-60-2048.jpg)






















![PHPCreate/Retrieve a Cookie
EXAMPLE:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<?php
$cookie_name = "user";
$cookie_value = "John Doe";
setcookie($cookie_name, $cookie_value, time() + (86400 * 30), "/"); // 86400 = 1 day
?>
<html>
<body>
<?php
if(!isset($_COOKIE[$cookie_name])){
echo "Cookie named '" . $cookie_name . "' is not set!";
} else {
echo "Cookie '" . $cookie_name . "' is set!<br>";
echo "Value is: " . $_COOKIE[$cookie_name];
}
?>
<p><strong>Note:</strong>You might have to reload the page to see the value of the cookie.</p>
</body>
</html>
This will display following result:
Cookie 'user' is set!
Value is: John Doe](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontophp-200716212853/75/Introduction-to-php-84-2048.jpg)


![Starting a PHPSession
• A PHP session is easily started by making a call to the session_start() function.This
function first checks if a session is already started and if none is started then it starts
one. It is recommended to put the call to session_start() at the beginning of the page.
• Session variables are stored in associative array called $_SESSION[].These variables can
be accessed during lifetime of a session.
• The following example starts a session then register a variable called counterthat is
incremented each time the page is visited during the session.
• Make use of isset()function to check if session variable is already set or not.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontophp-200716212853/75/Introduction-to-php-88-2048.jpg)
![Example
• <?php
// Start the session
session_start();
?>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<?php
// Set session variables
$_SESSION["favcolor"] = "green";
$_SESSION["favanimal"] = "cat";
echo "Session variables are set.";
?>
</body>
</html>
This will display following result:
Session variables are set.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontophp-200716212853/75/Introduction-to-php-89-2048.jpg)

![Example
• <?php
session_start();
?>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<?php
// Echo session variables that were set on
previous page
echo "Favorite color is " . $_SESSION["favcolor"] .
".<br>";
echo "Favorite animal is " .
$_SESSION["favanimal"] . ".";
?>
</body>
</html>
This will display following result:
Favorite color is green.
Favorite animal is cat.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontophp-200716212853/75/Introduction-to-php-91-2048.jpg)
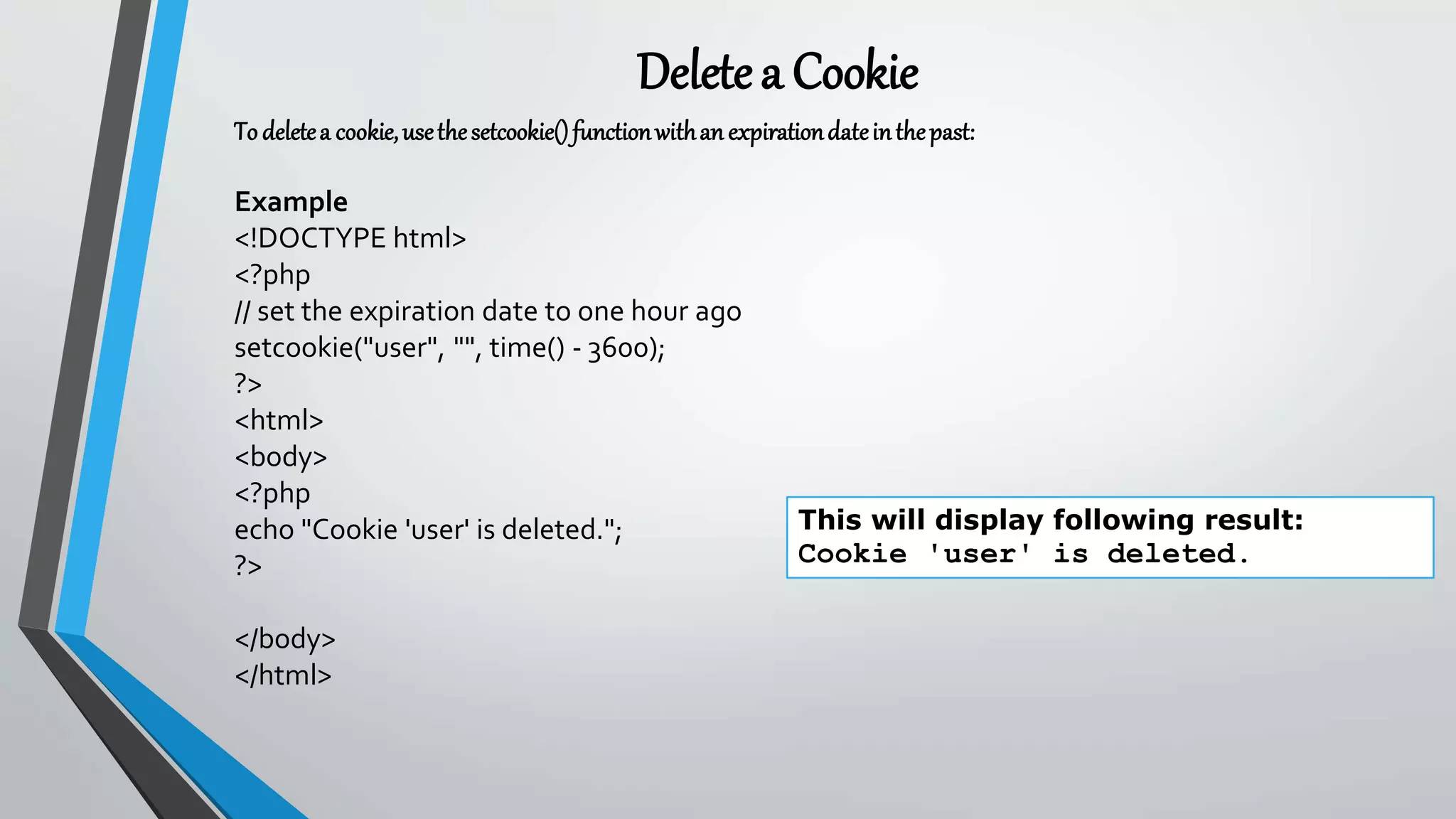
![• A PHP session can be destroyed by session_destroy()function. This function does not need any
argument and a single call can destroy all the session variables. If you want to destroy a single session
variable then you can use unset()function to unset a session variable.
• Here is the example to unset a single variable:
<?php
unset($_SESSION['counter']);
?>
• Here is the call which will destroy all the session variables:
<?php
session_destroy();
?>
Destroyinga PHPSession](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontophp-200716212853/75/Introduction-to-php-92-2048.jpg)


