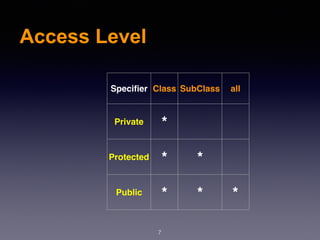
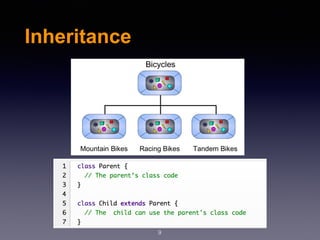
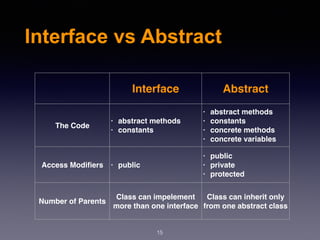
This document provides an overview of various object-oriented programming concepts in PHP including constructors, static methods, constants, encapsulation, access levels, inheritance, interfaces, abstract classes, and traits. It defines each concept and provides examples. Constructors initialize object properties when an object is created. Static methods are called on a class rather than an object. Constants are declared in uppercase. Encapsulation controls property and method visibility. Access levels include private, protected, and public. Inheritance allows a subclass to inherit from a parent class. Interfaces define methods a class must implement without defining how. Abstract classes serve as templates for child classes. Traits allow classes to reuse methods from multiple sources to prevent code duplication.