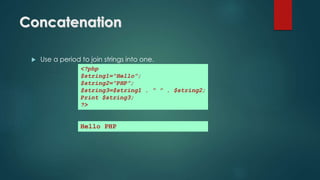
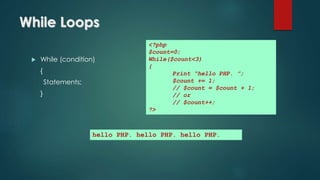
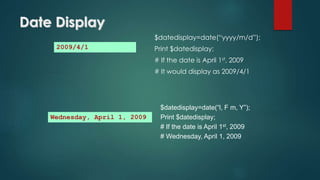
The document details the specifications for an online shopping system using PHP, outlining both functional and non-functional requirements. It provides a brief history of PHP development from its inception in 1994 to its current state, highlighting key features and uses of the language. The document also covers PHP syntax, variable usage, control structures, and provides examples of PHP code functionalities.