The document is a presentation about web design and development using jQuery. It introduces jQuery and why it is useful, how to include jQuery, and describes 21 helpful jQuery methods such as addClass(), removeClass(), attr(), val(), html(), click(), append(), and more. Each method is explained in 1-2 paragraphs with examples of how to use the method and its parameters. The document concludes with references to the jQuery API documentation for each method.










![.removeClass()
11
.removeClass( [className]):
className :
Type: String
One or more space-separated classes to be removed from
the class attribute of each matched element.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wd-6-171230122322/85/Web-Design-Development-Session-6-11-320.jpg)

































![.append()
49
.append(content, [content]):
content :
Type: htmlString or Element or Text or Array or jQuery.
content :
Type: htmlString or Element or Text or Array or jQuery.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wd-6-171230122322/85/Web-Design-Development-Session-6-49-320.jpg)
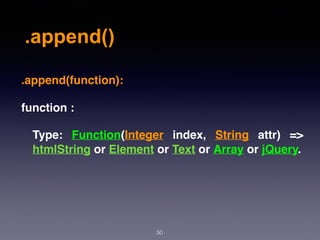



![.prepend()
54
.prepend(content, [content]):
content :
Type: htmlString or Element or Text or Array or jQuery.
content :
Type: htmlString or Element or Text or Array or jQuery.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wd-6-171230122322/85/Web-Design-Development-Session-6-54-320.jpg)

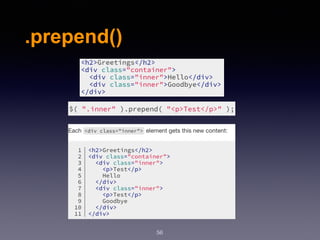


![.after()
59
.after(content, [content]):
content :
Type: htmlString or Element or Text or Array or jQuery.
content :
Type: htmlString or Element or Text or Array or jQuery.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wd-6-171230122322/85/Web-Design-Development-Session-6-59-320.jpg)




![.before()
64
.before(content, [content]):
content :
Type: htmlString or Element or Text or Array or jQuery.
content :
Type: htmlString or Element or Text or Array or jQuery.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wd-6-171230122322/85/Web-Design-Development-Session-6-64-320.jpg)




![.remove()
69
.remove([selector]):
selector :
Type: String
A selector expression that filters the set of
matched elements to be removed.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wd-6-171230122322/85/Web-Design-Development-Session-6-69-320.jpg)















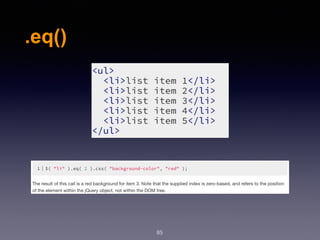








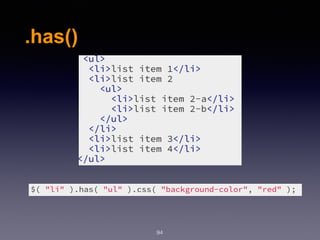


![.parent()
97
.parent([selector]):
seletor :
Type: Selector
A string containing a selector expression to
match elements against.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wd-6-171230122322/85/Web-Design-Development-Session-6-97-320.jpg)


