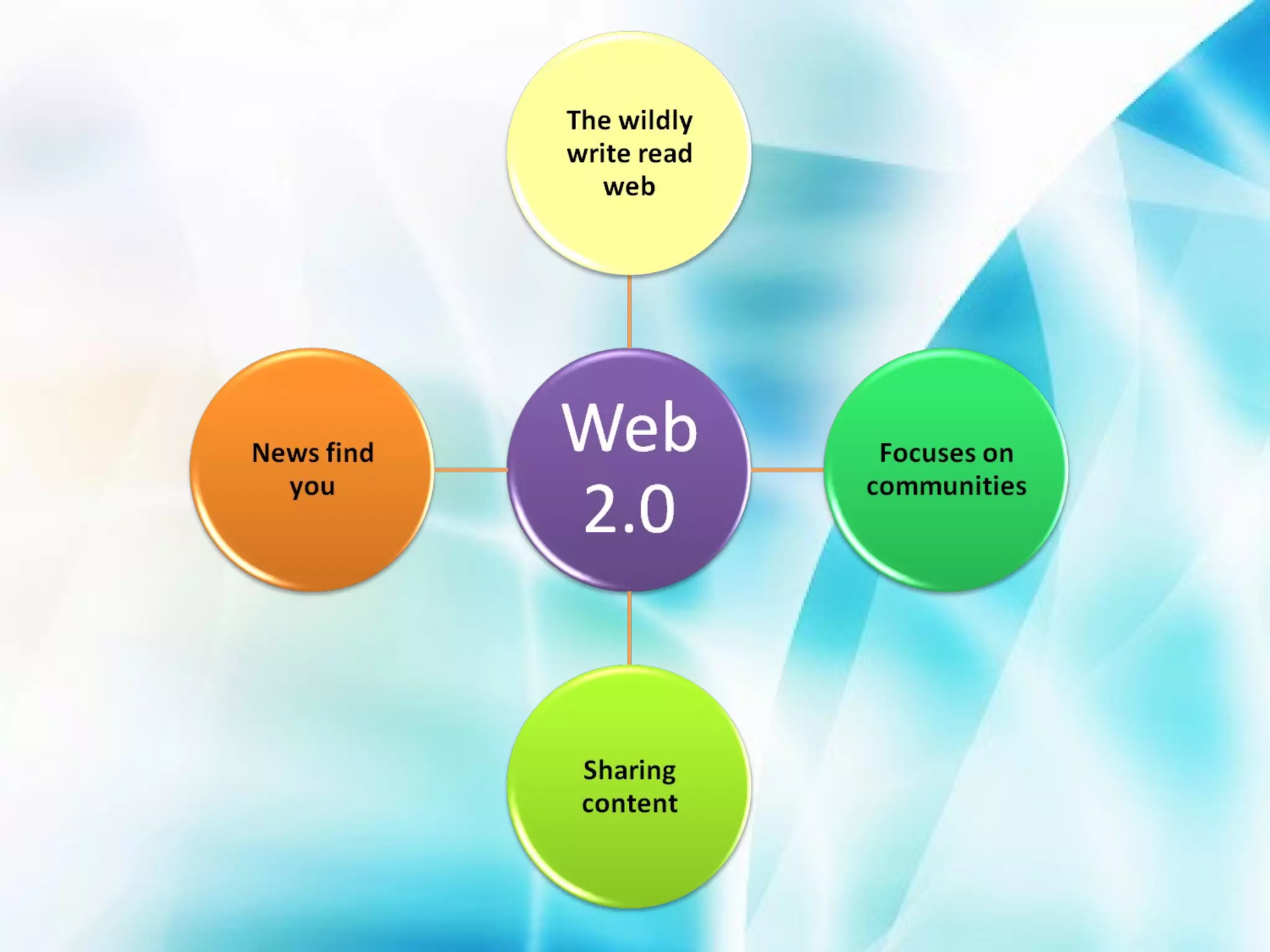
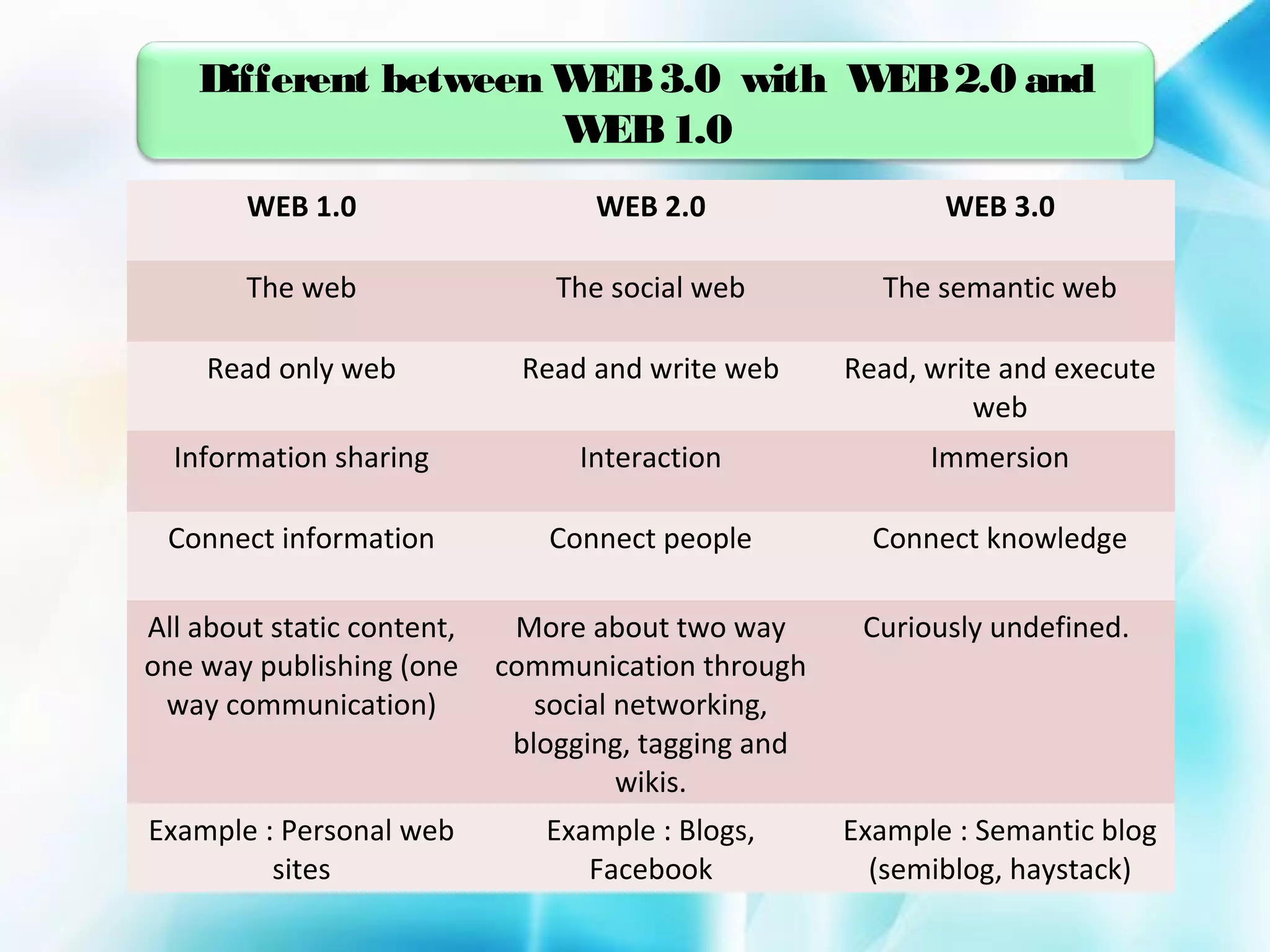
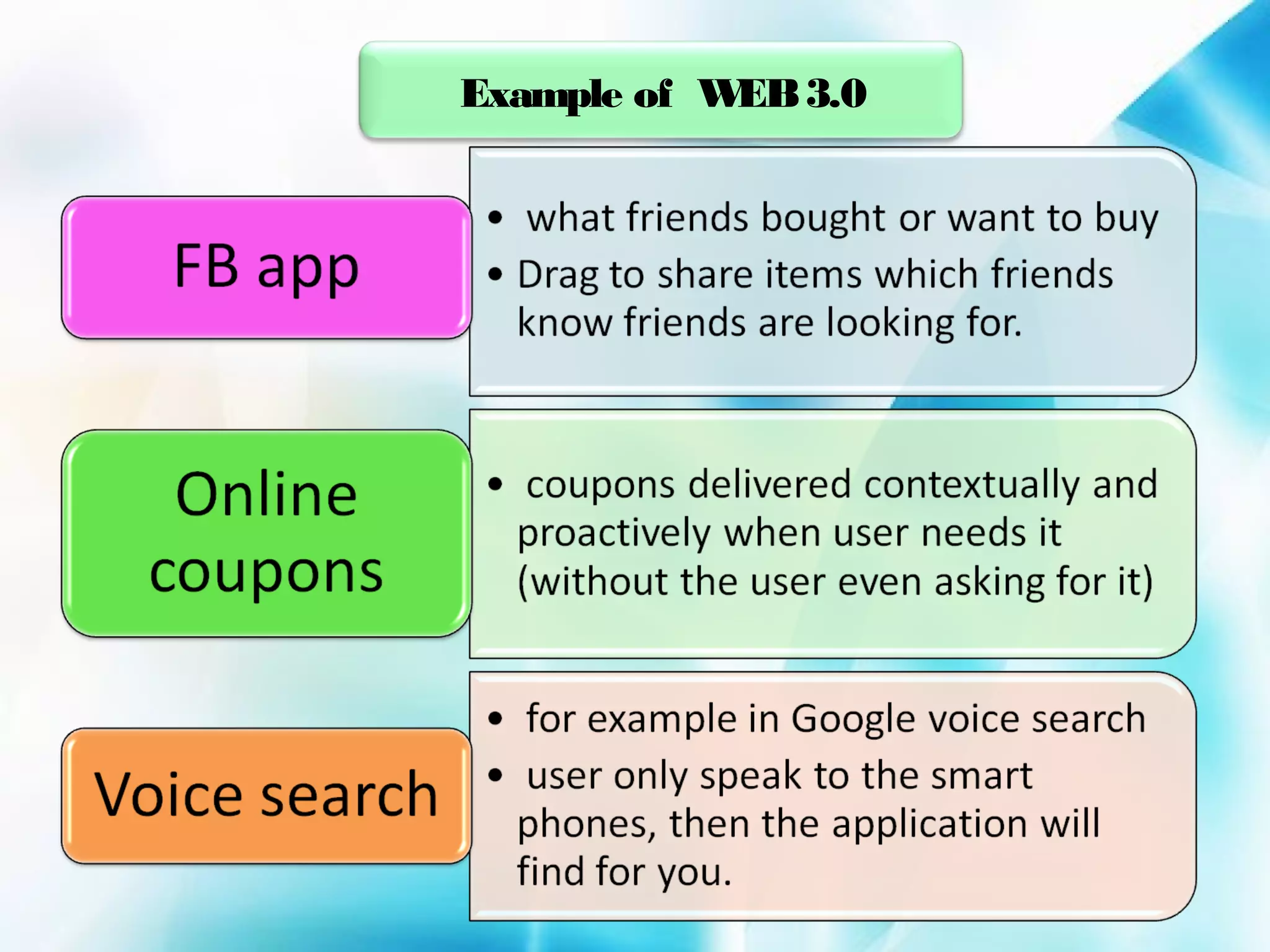
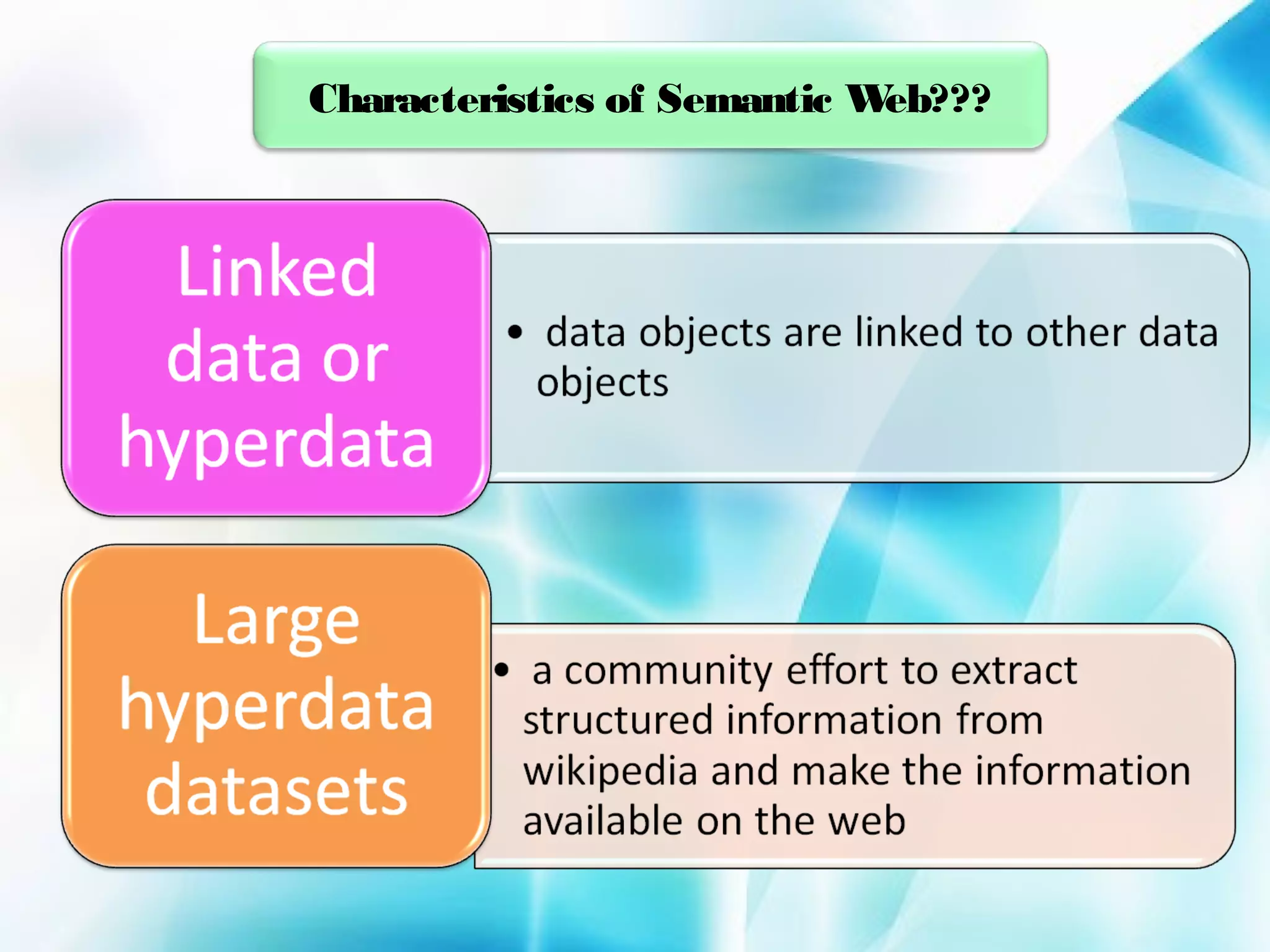
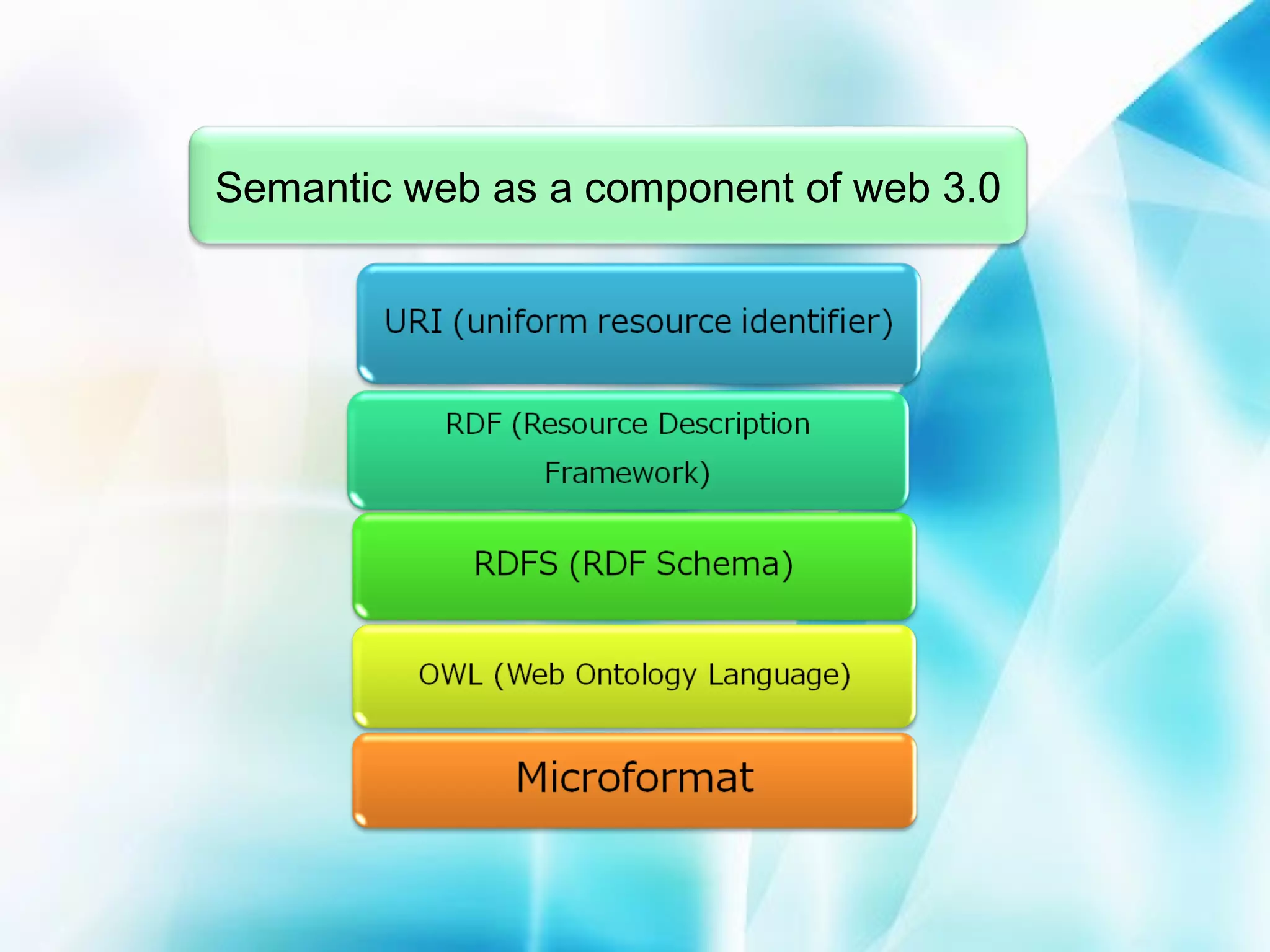
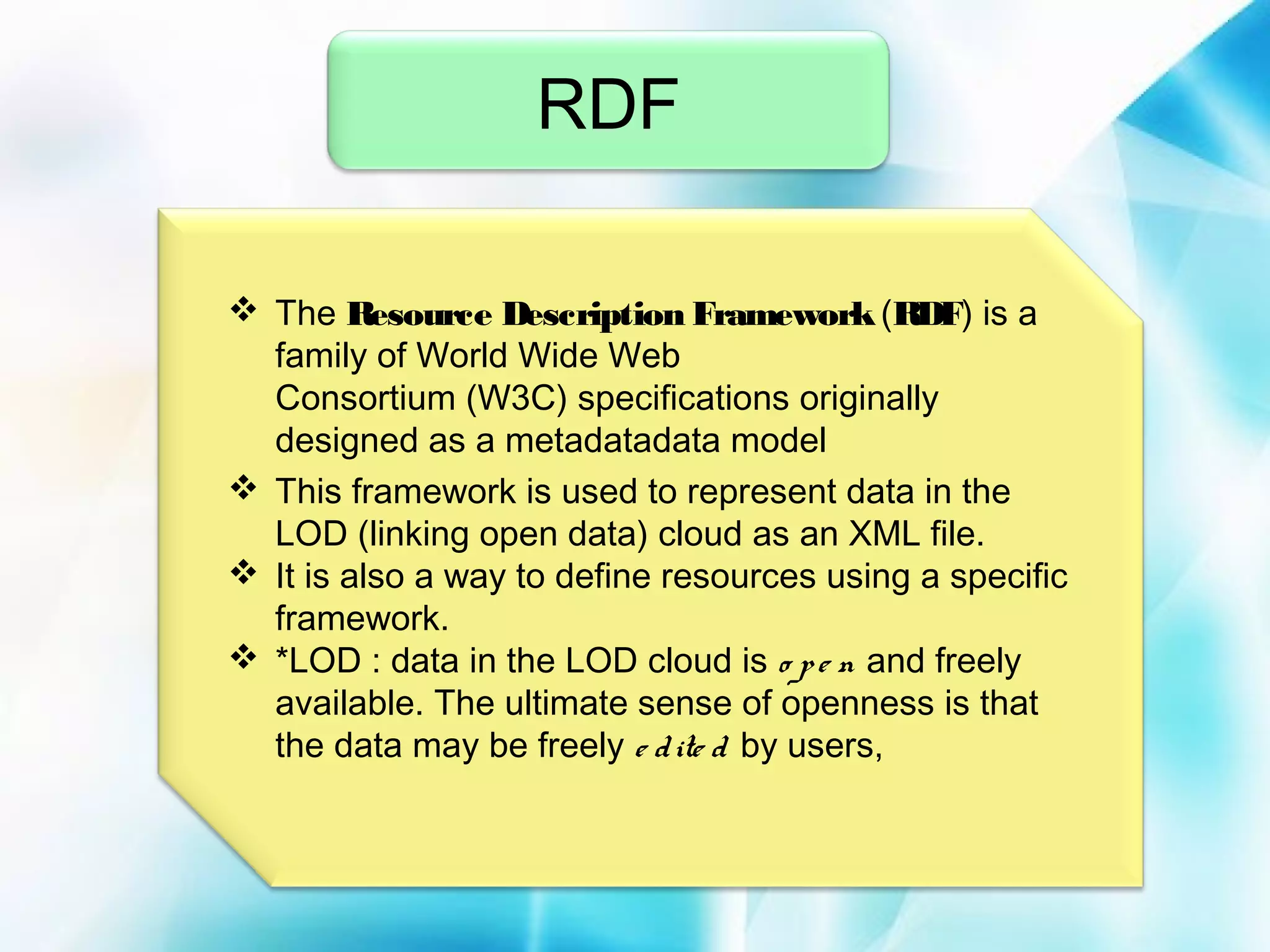
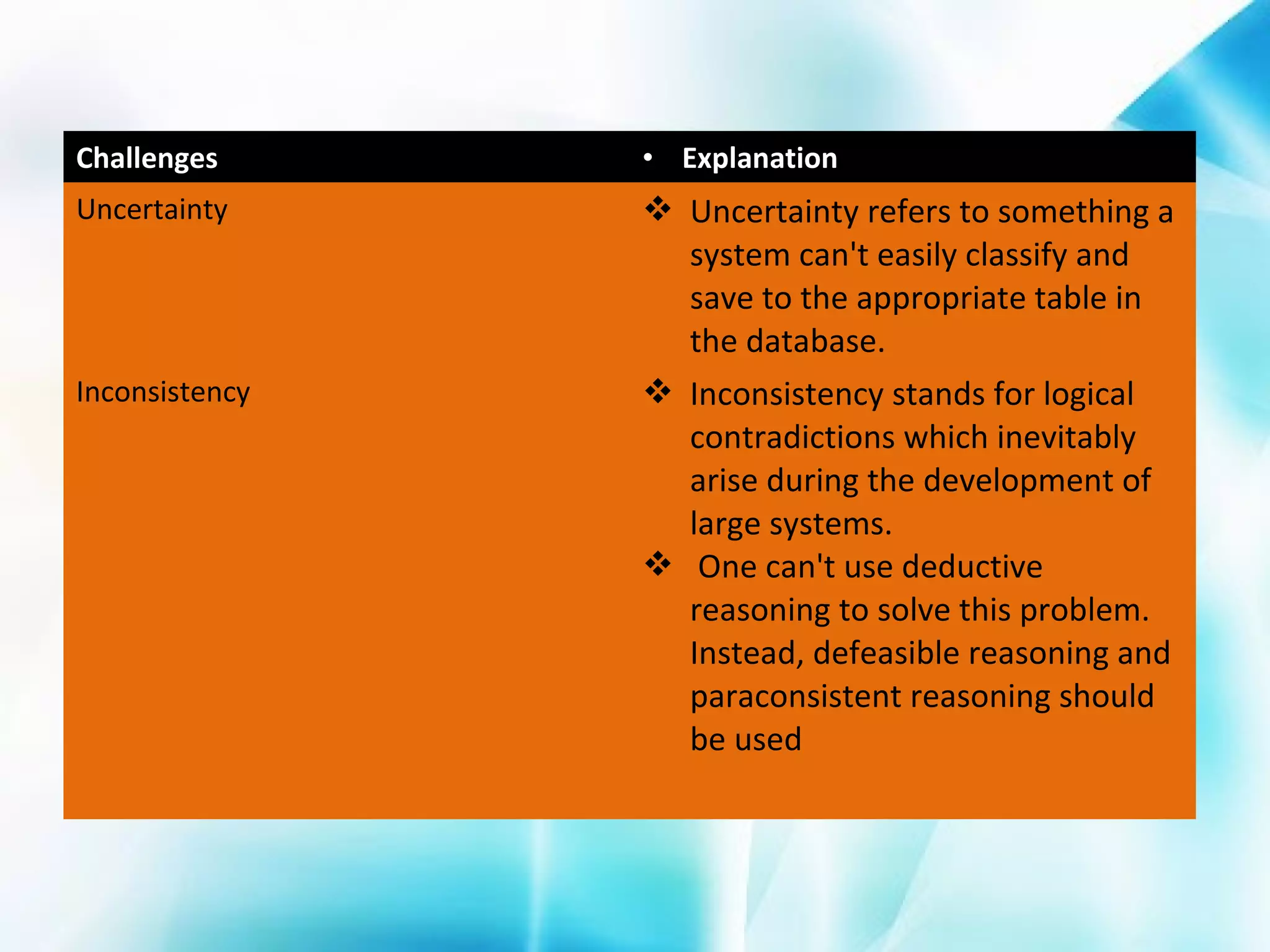
The document discusses the evolution of the World Wide Web from version 1.0 to the proposed version 3.0. Web 1.0 allowed only one-way consumption of information from static web pages. Web 2.0 enabled two-way interaction and user-generated content through technologies like blogs and social media. Proposed Web 3.0 would feature a semantic web with interconnected knowledge and intelligent systems that can understand language and context. It faces challenges of vastness, vagueness, uncertainty, inconsistency, and potential for deceit in user-generated information.