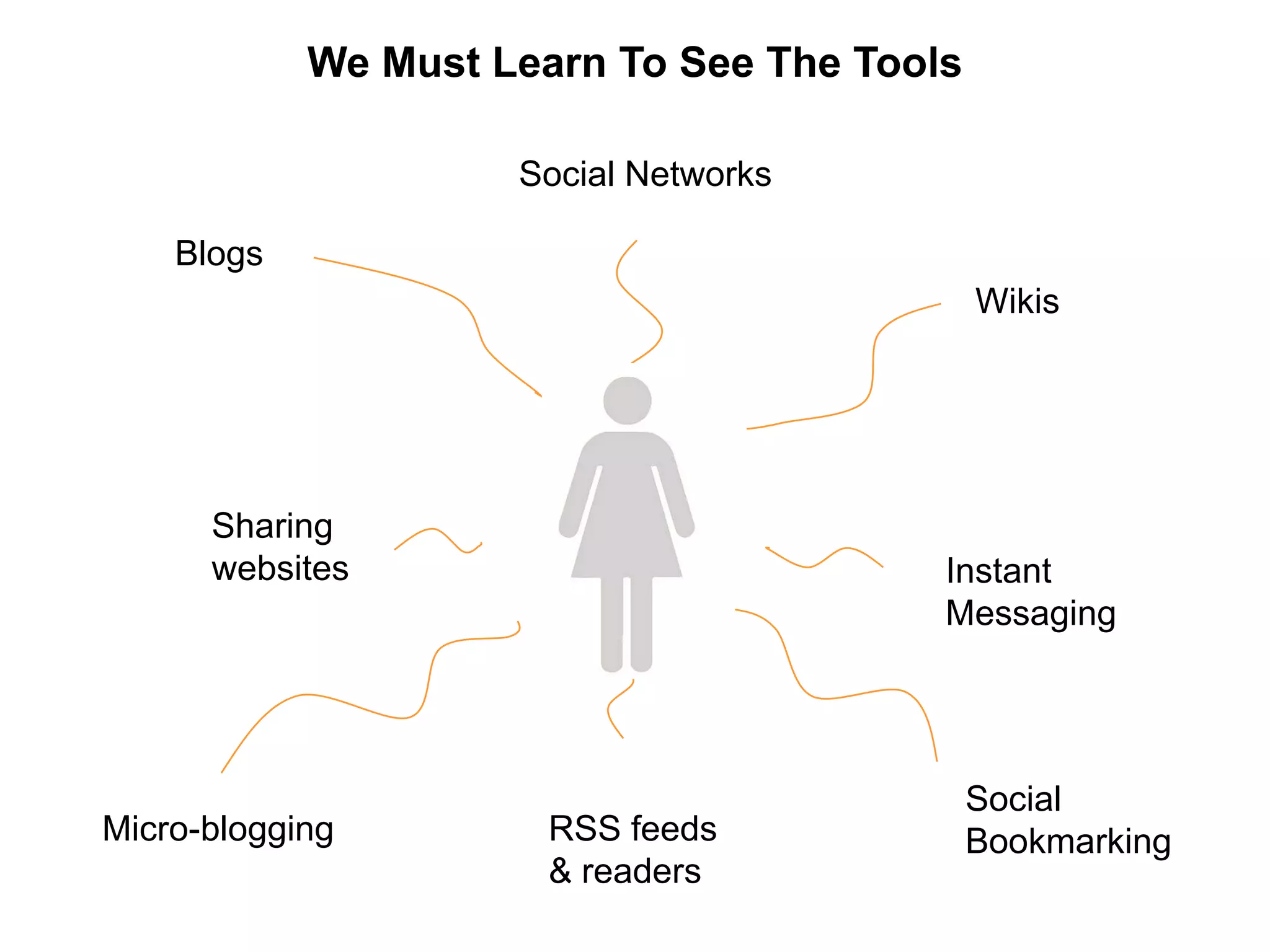
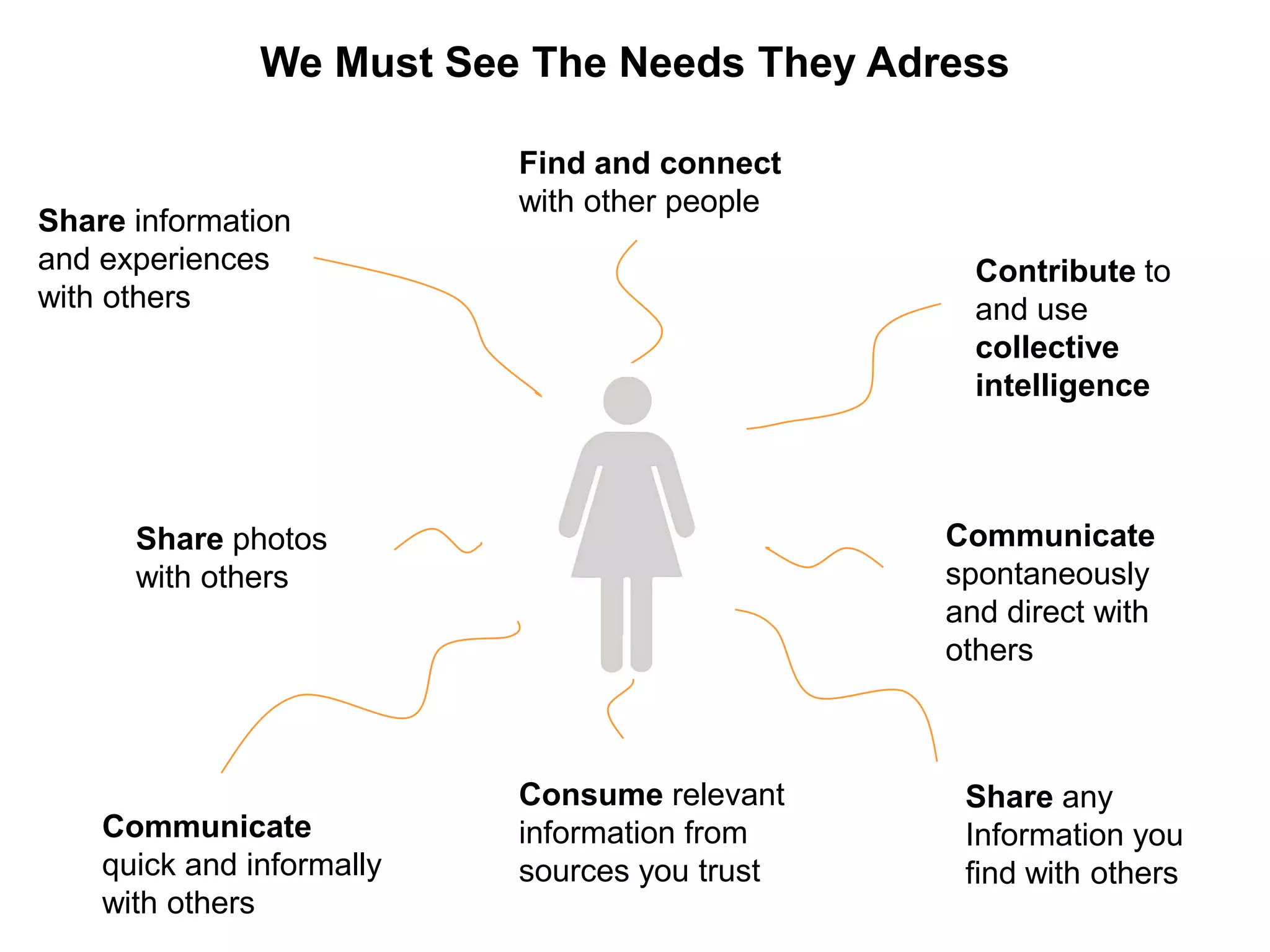
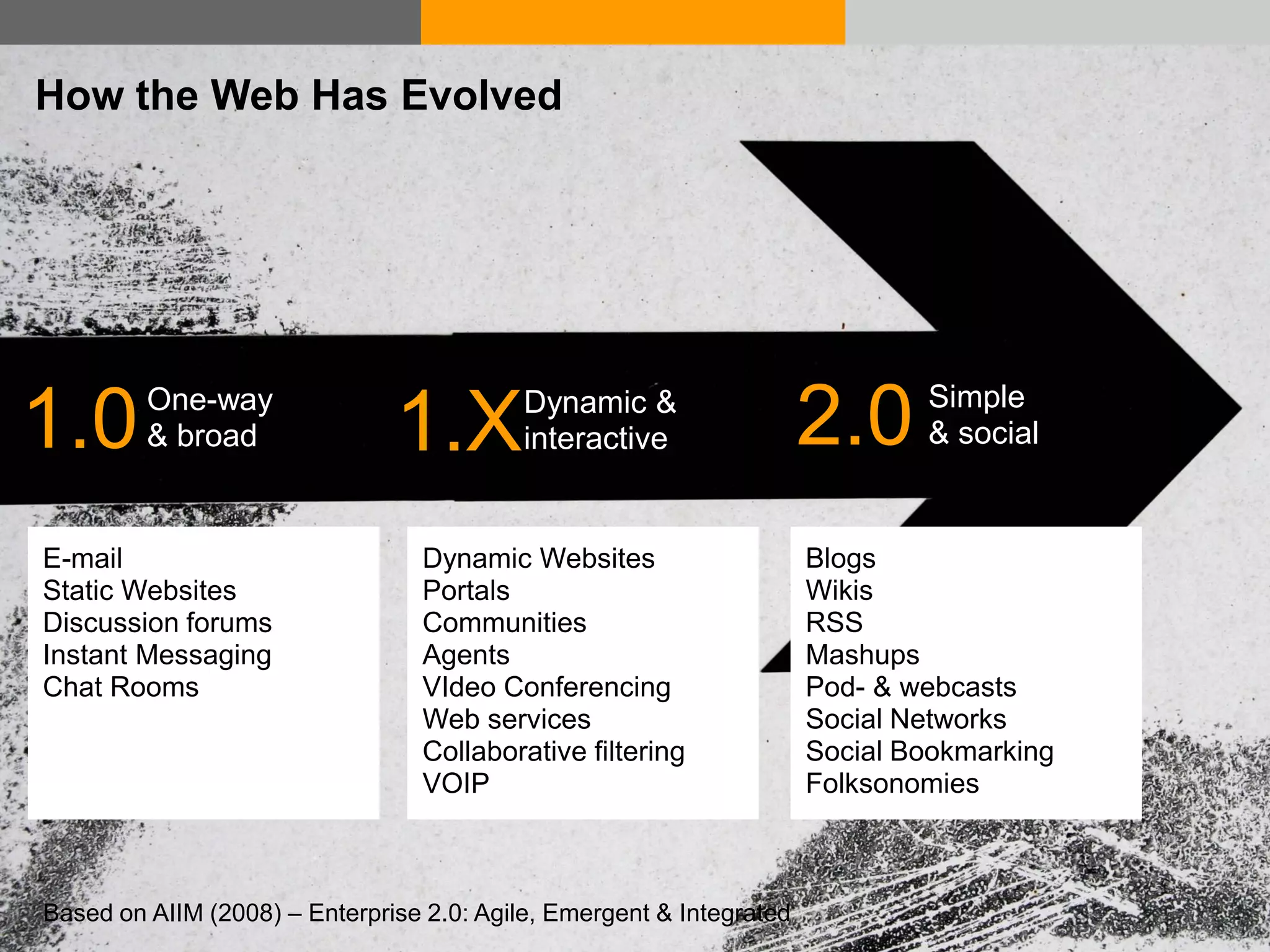
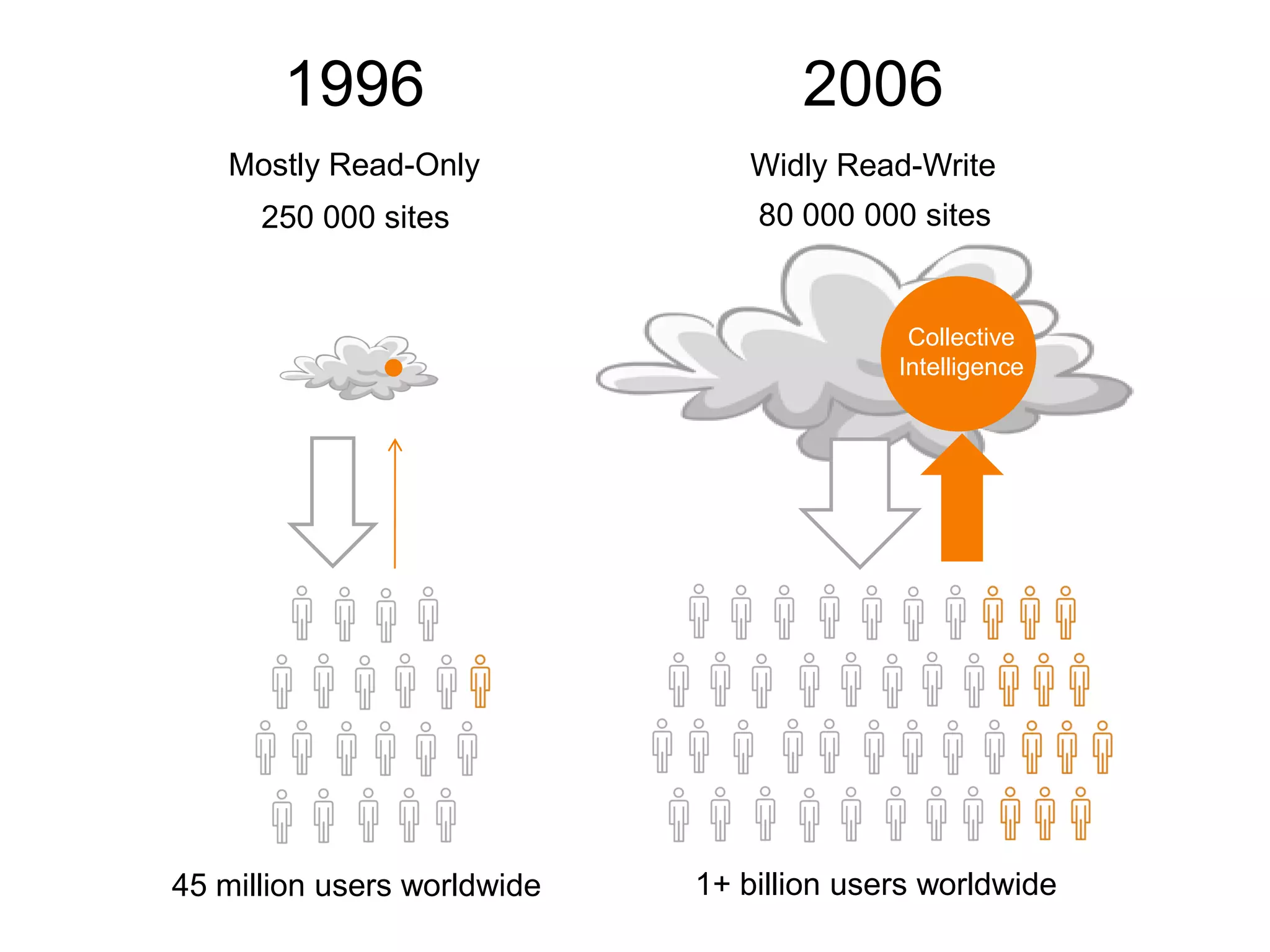
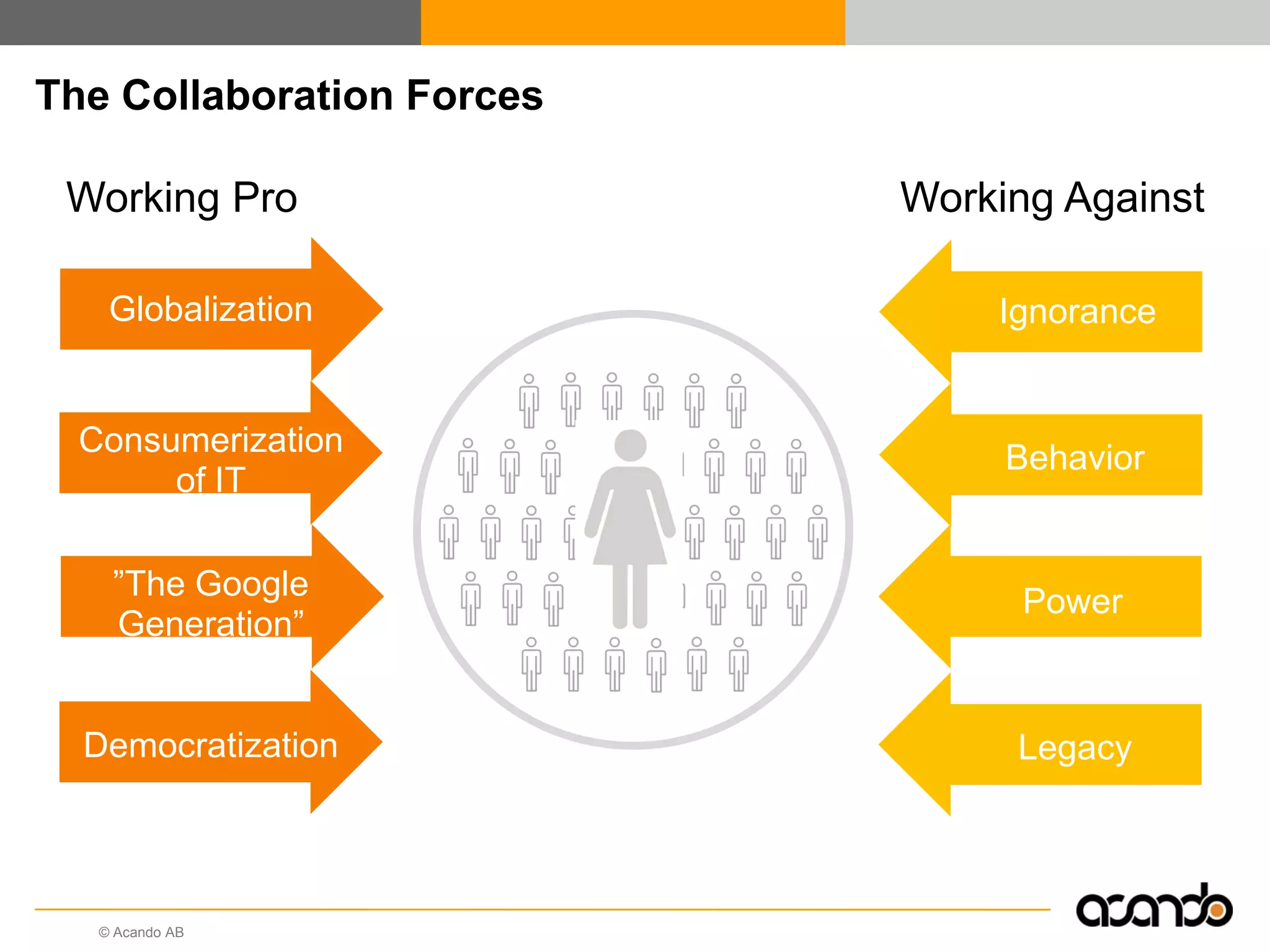
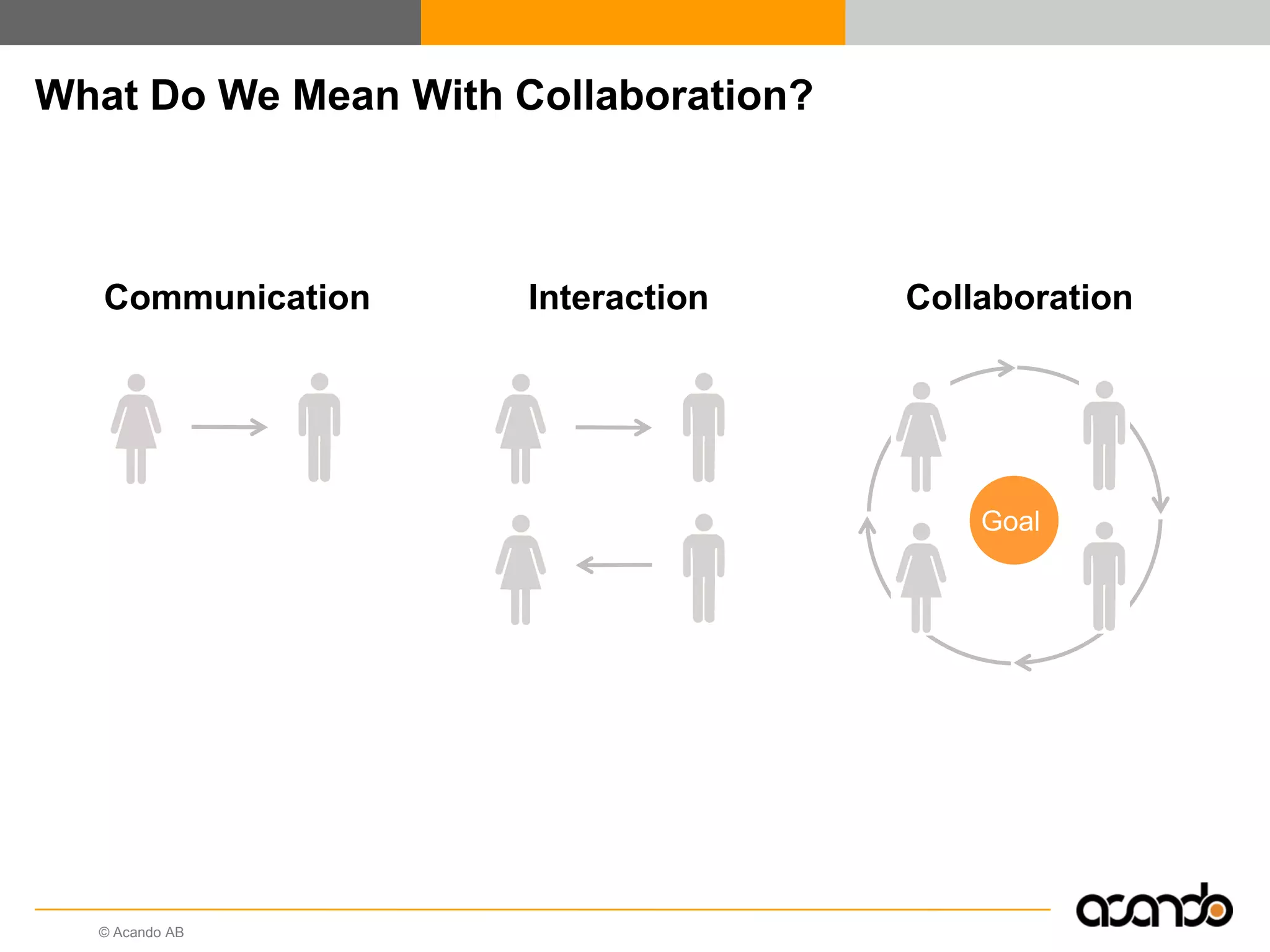
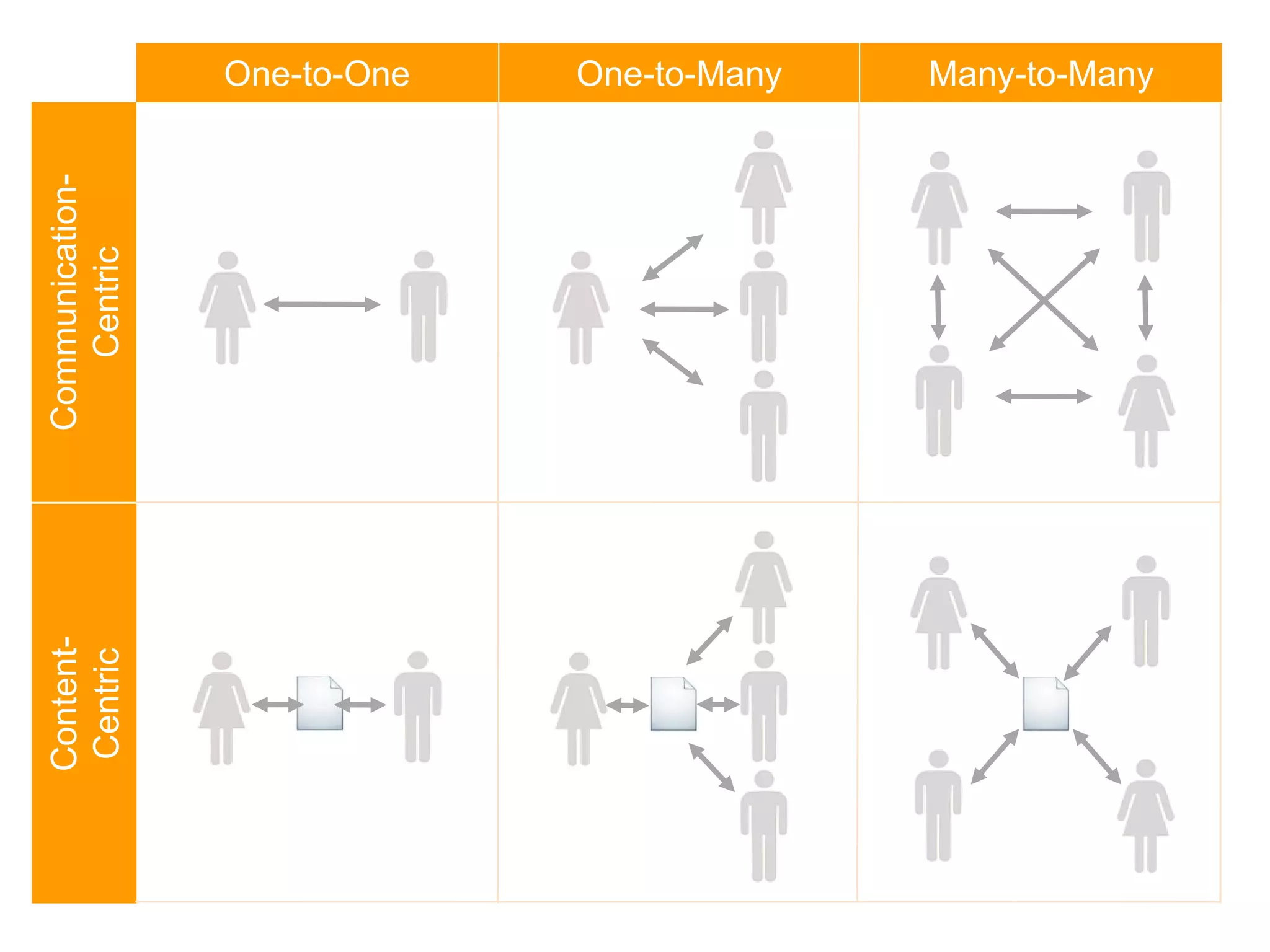
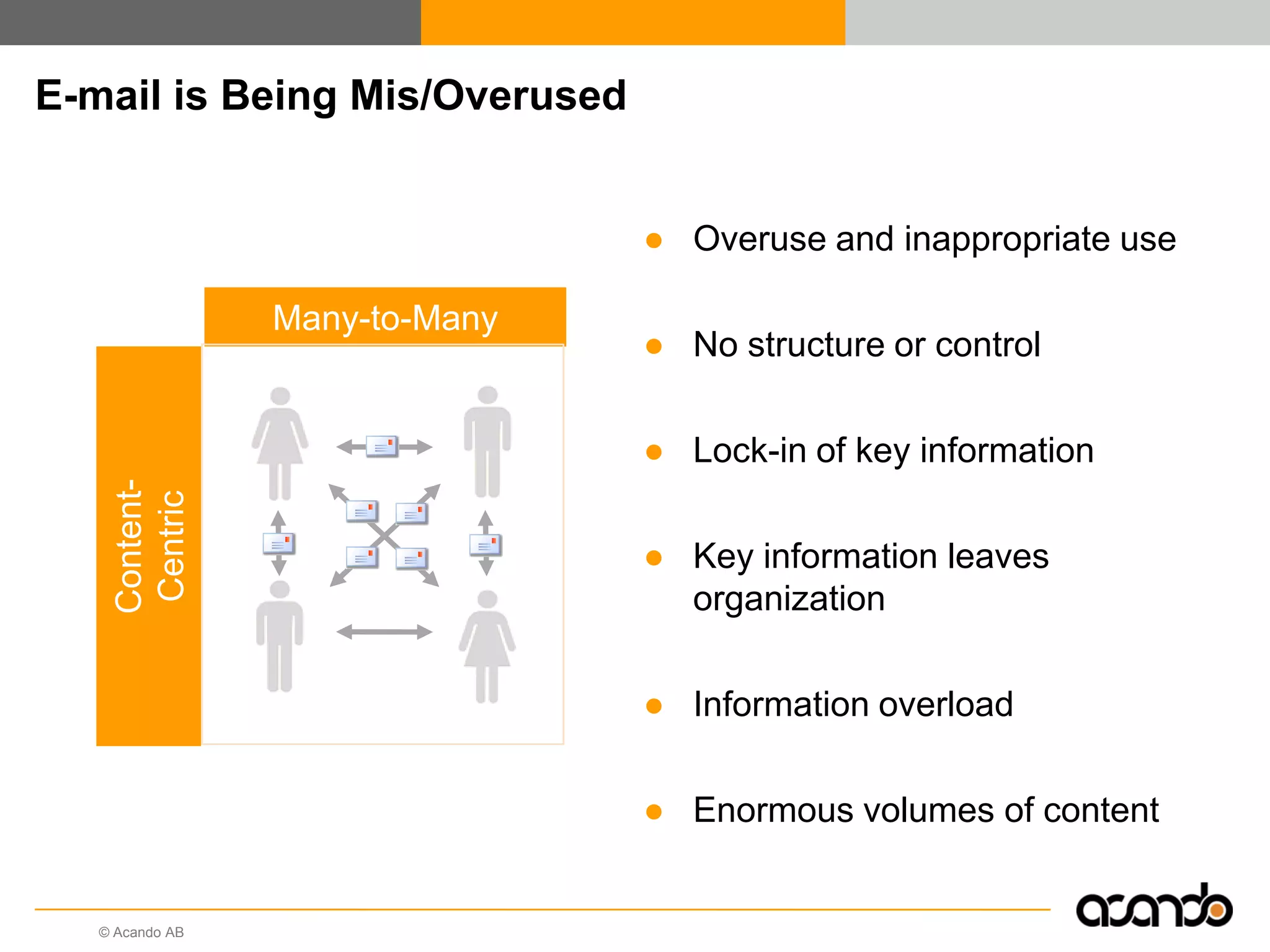
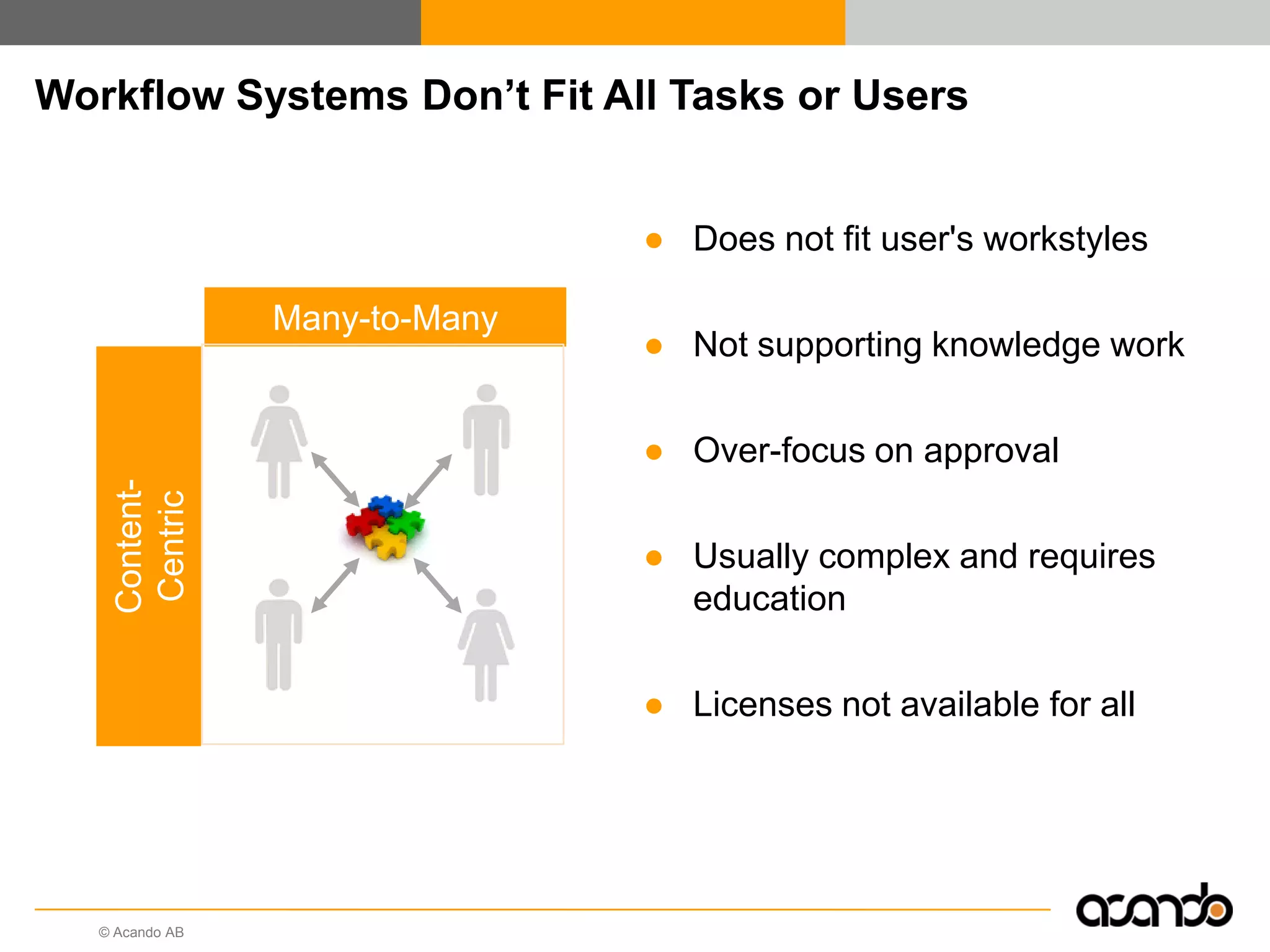
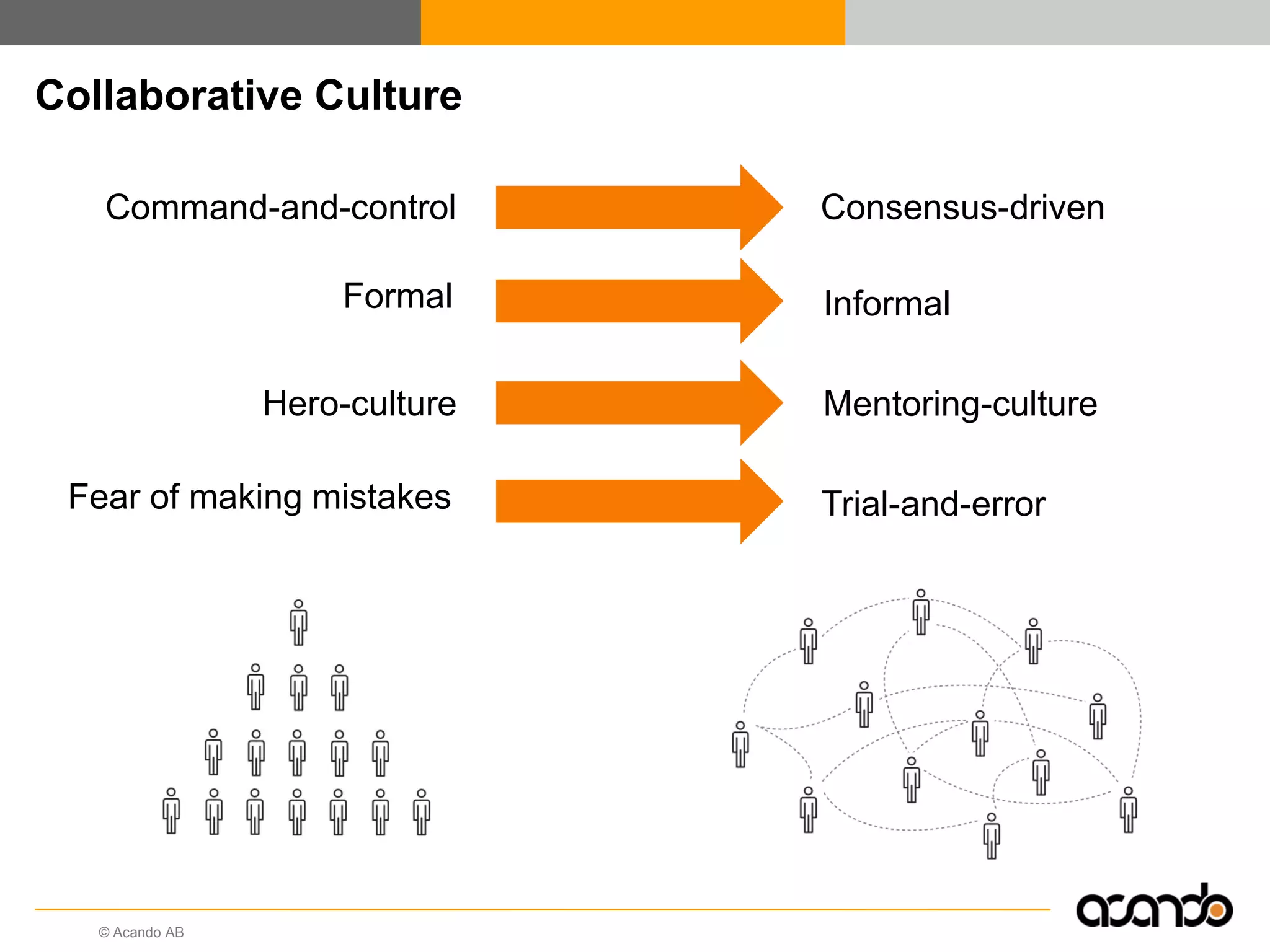
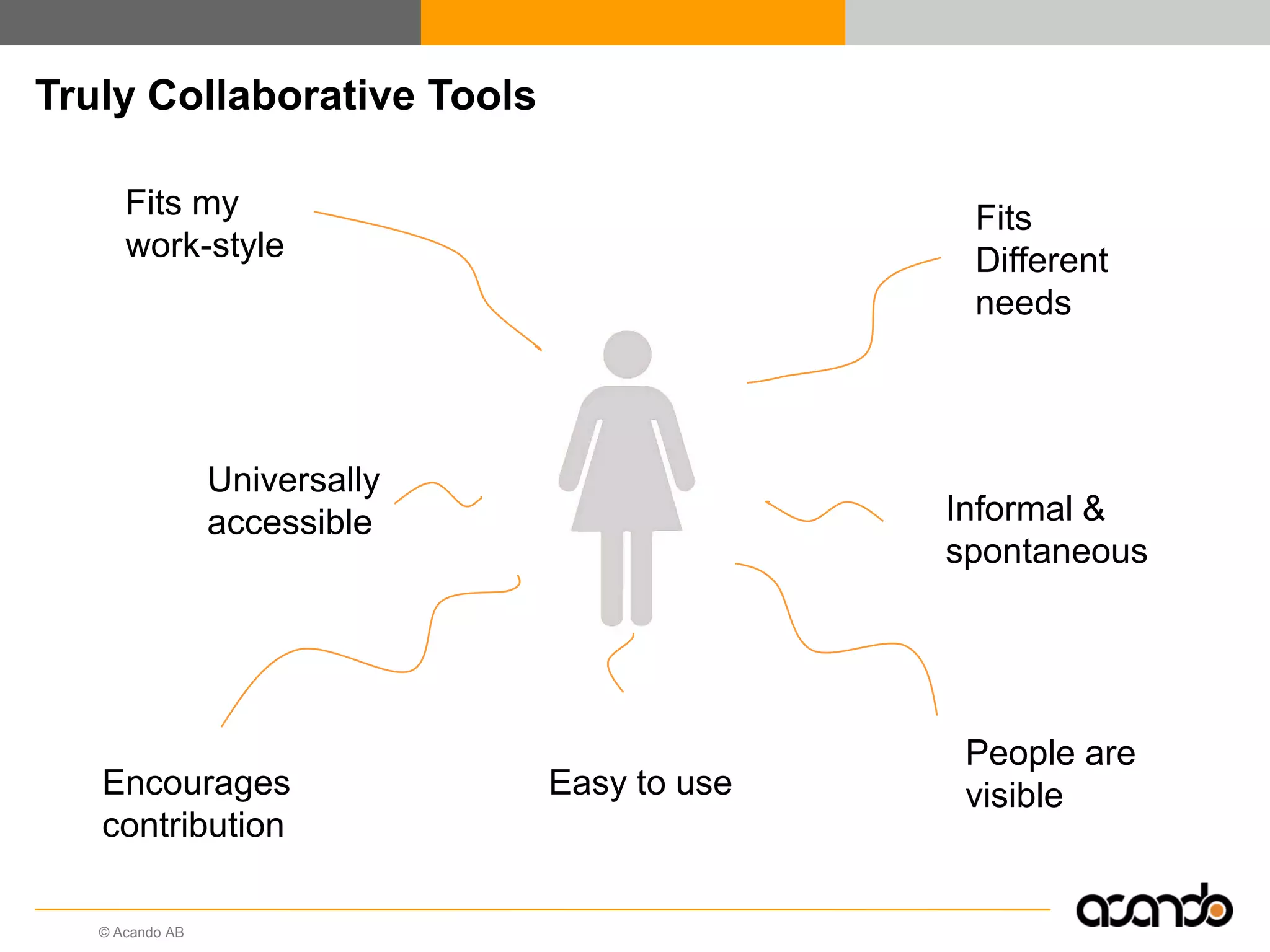
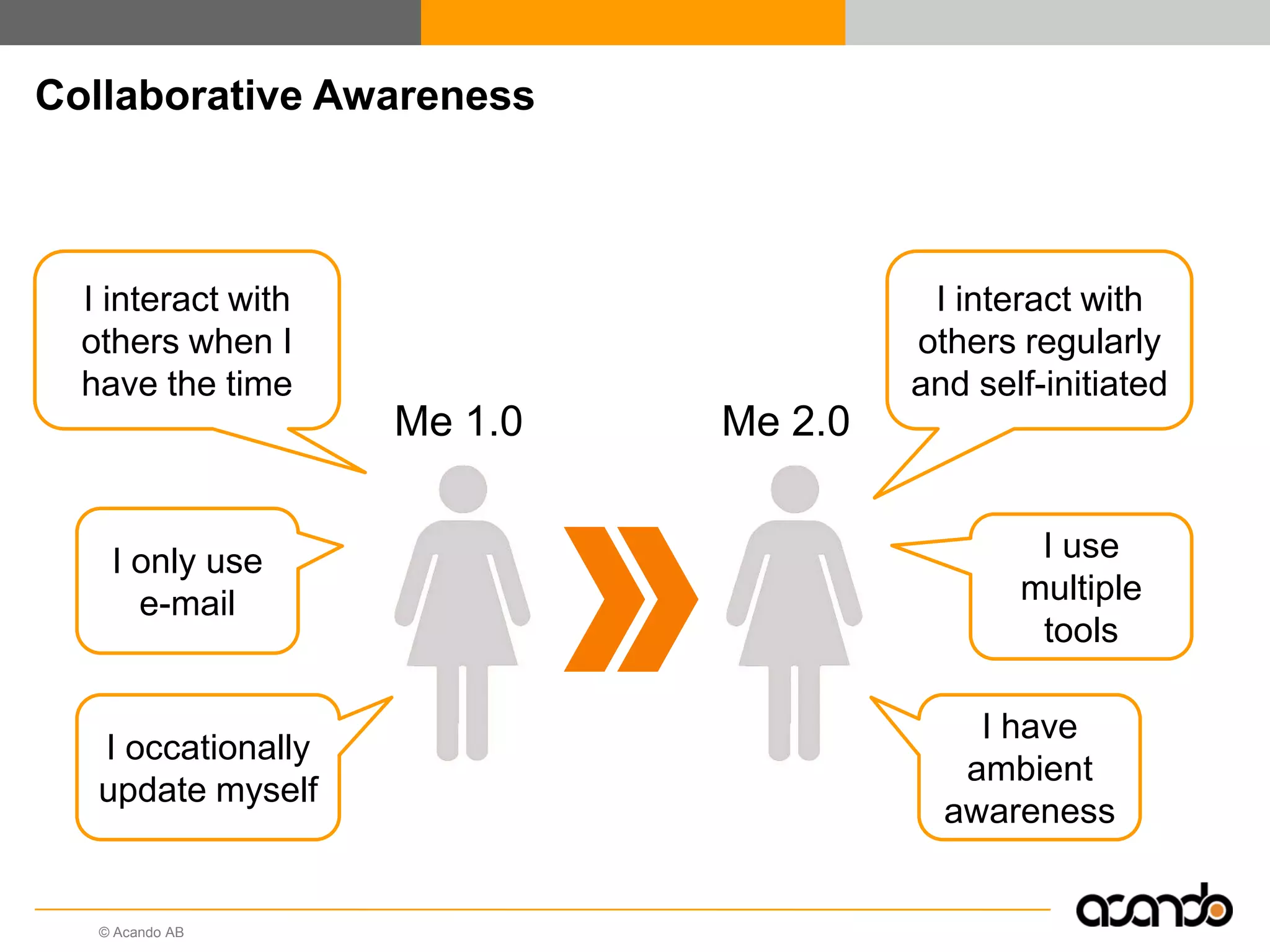
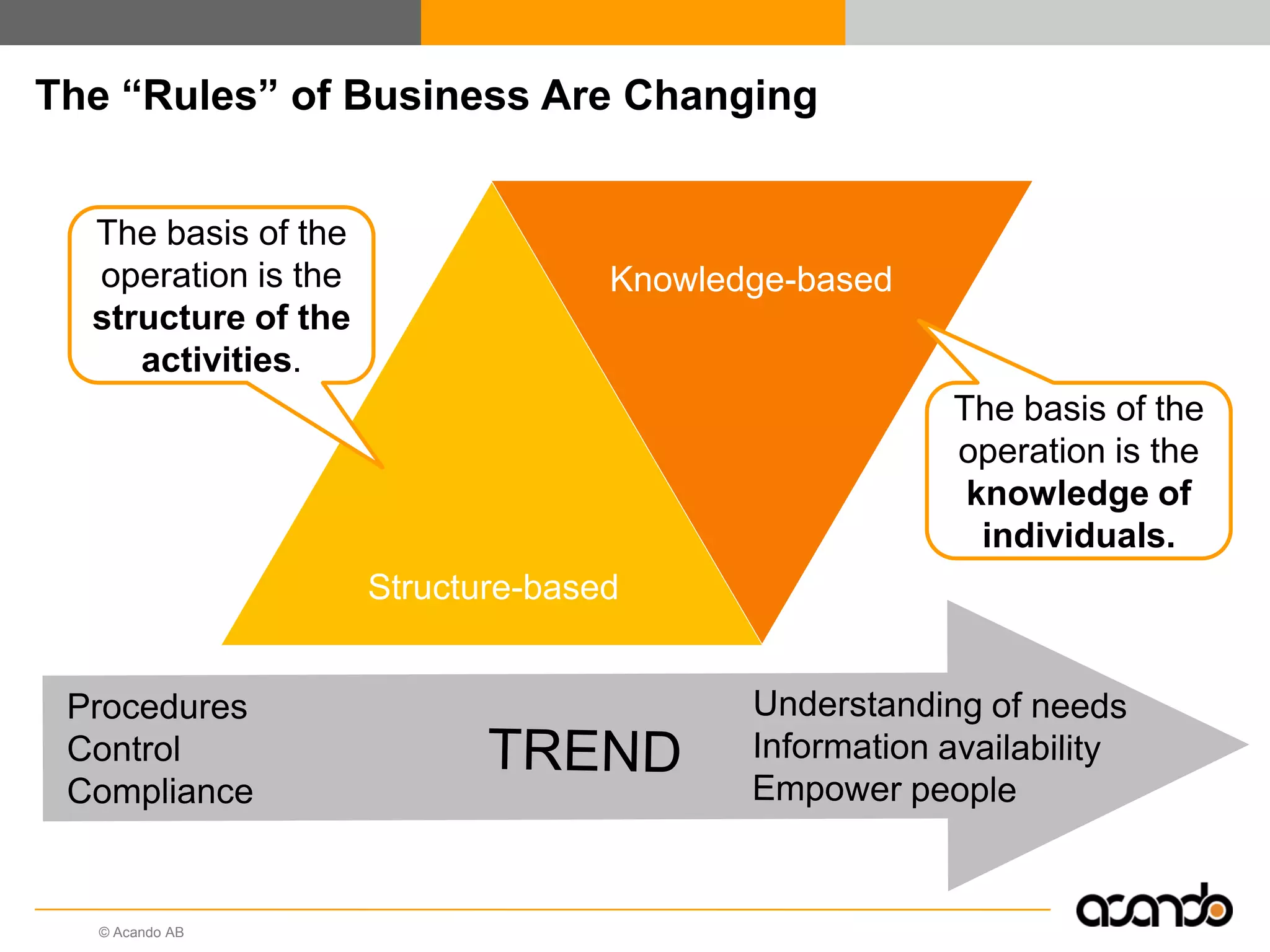
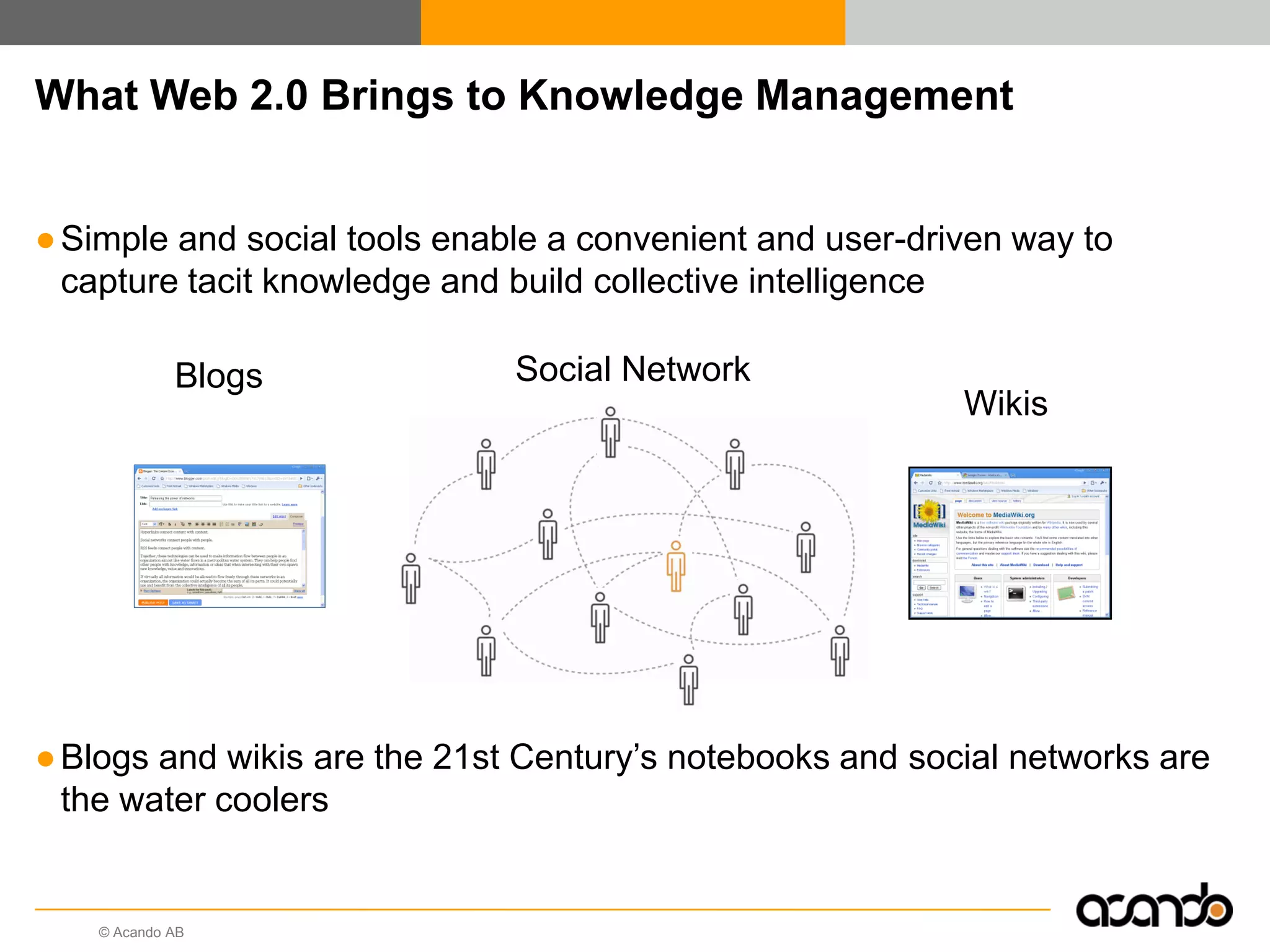
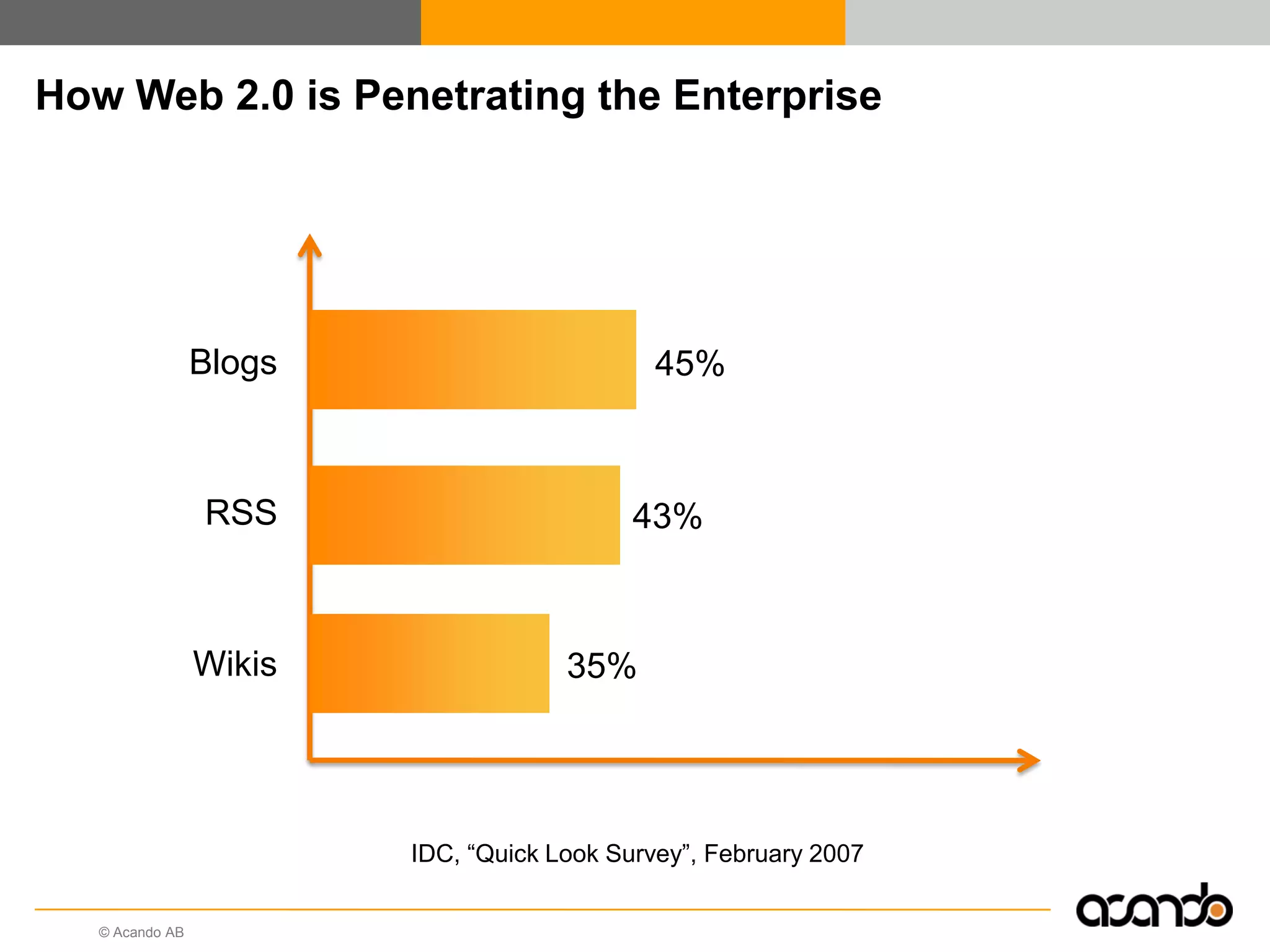
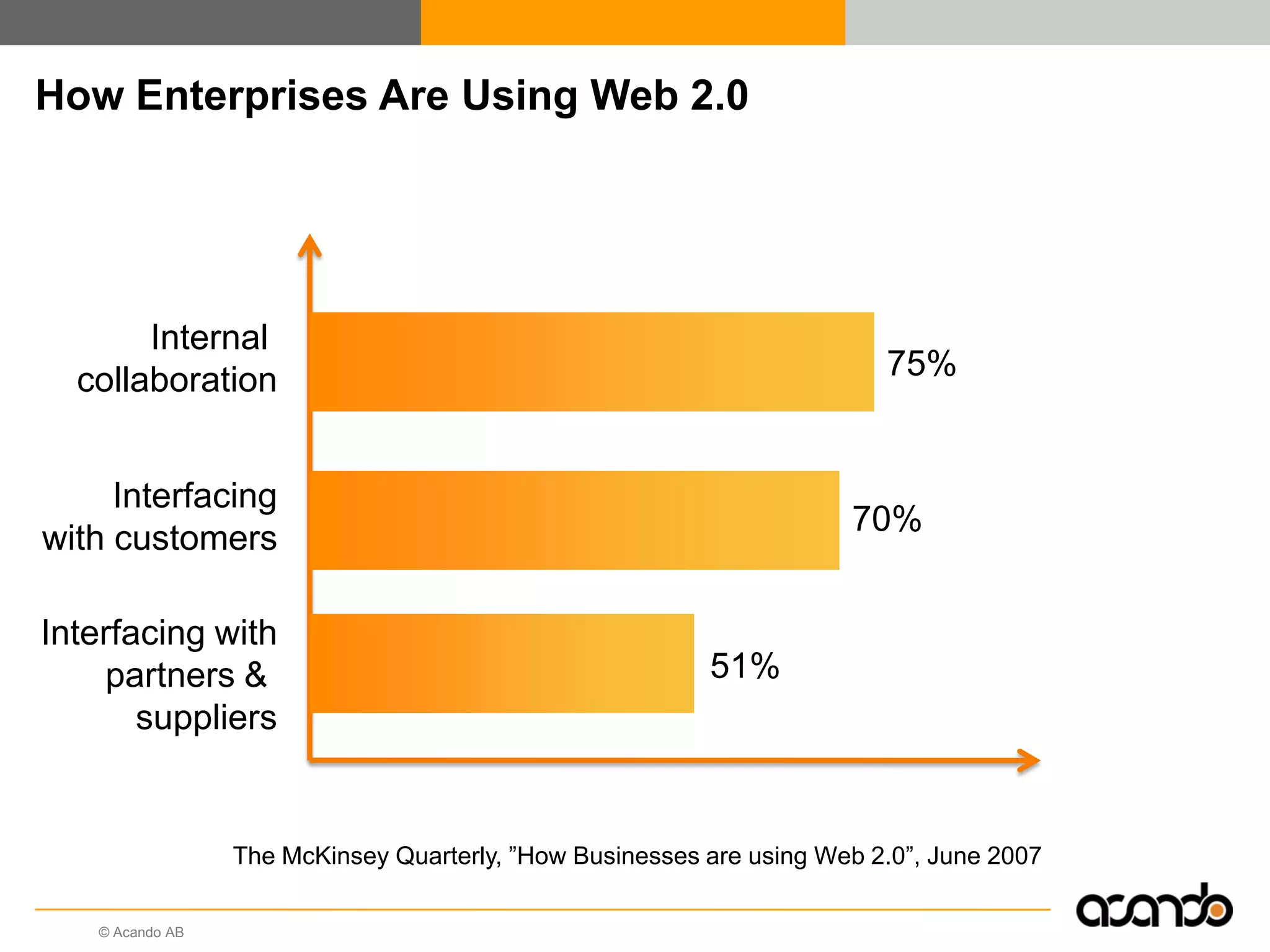
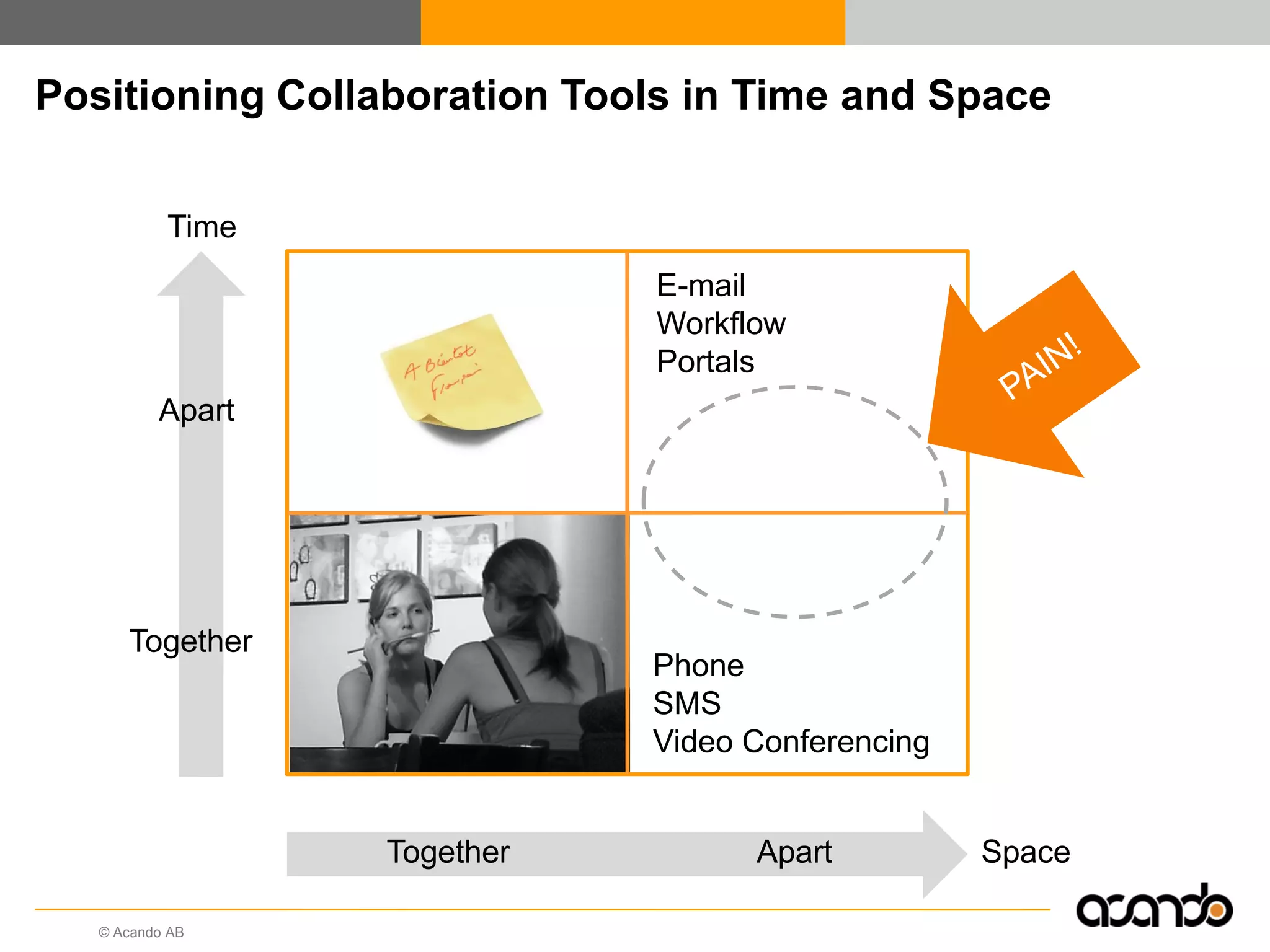
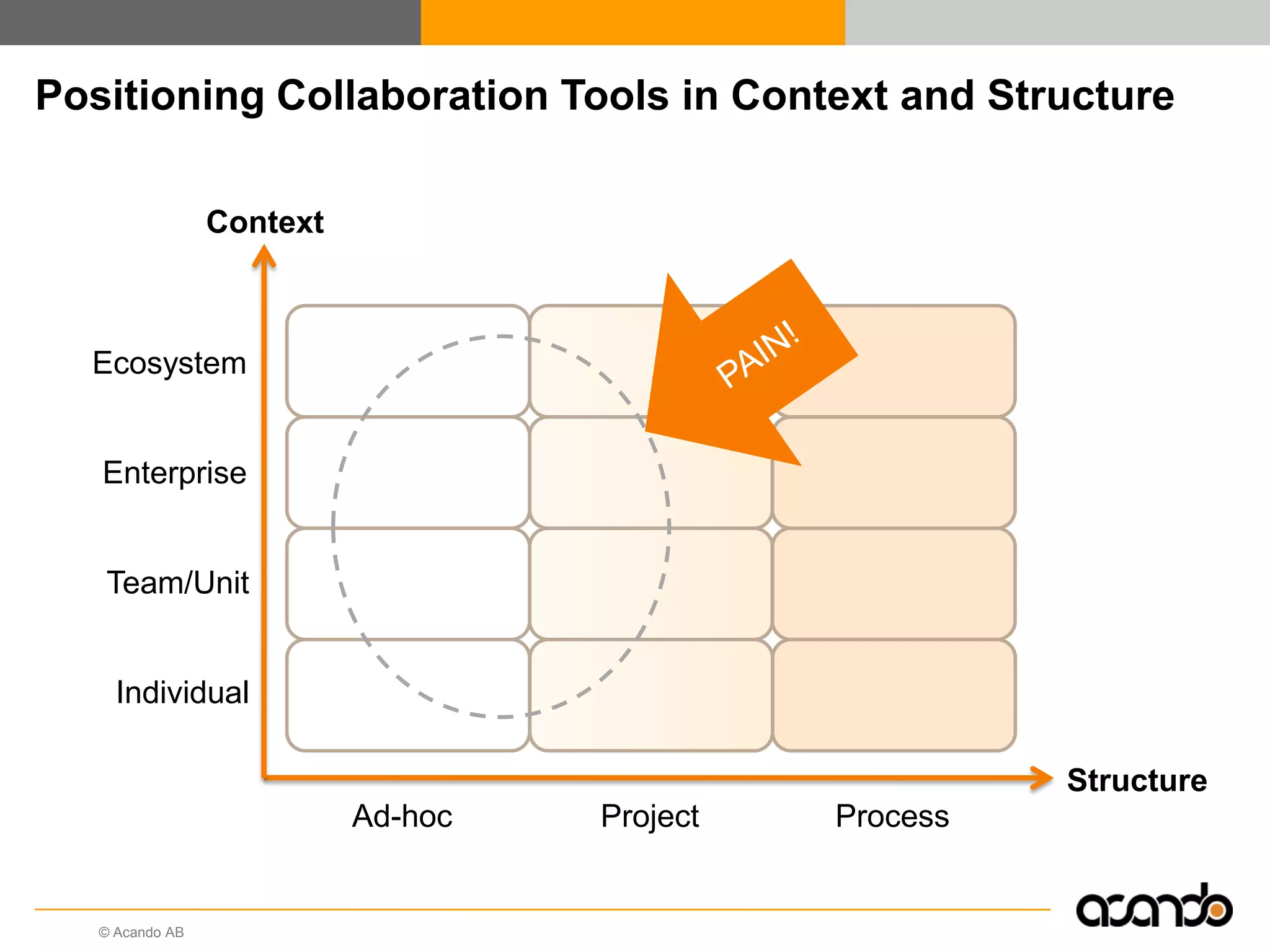
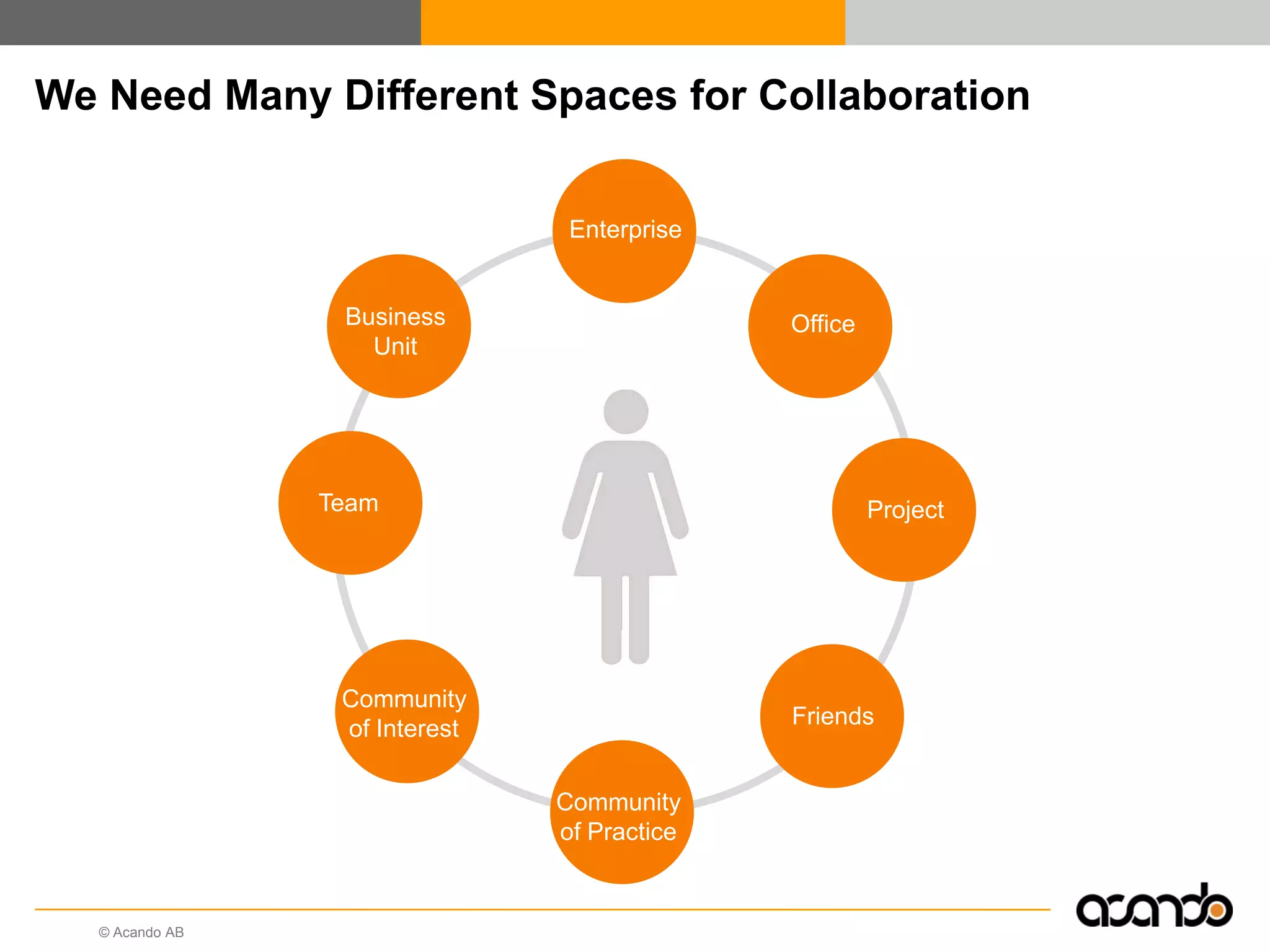
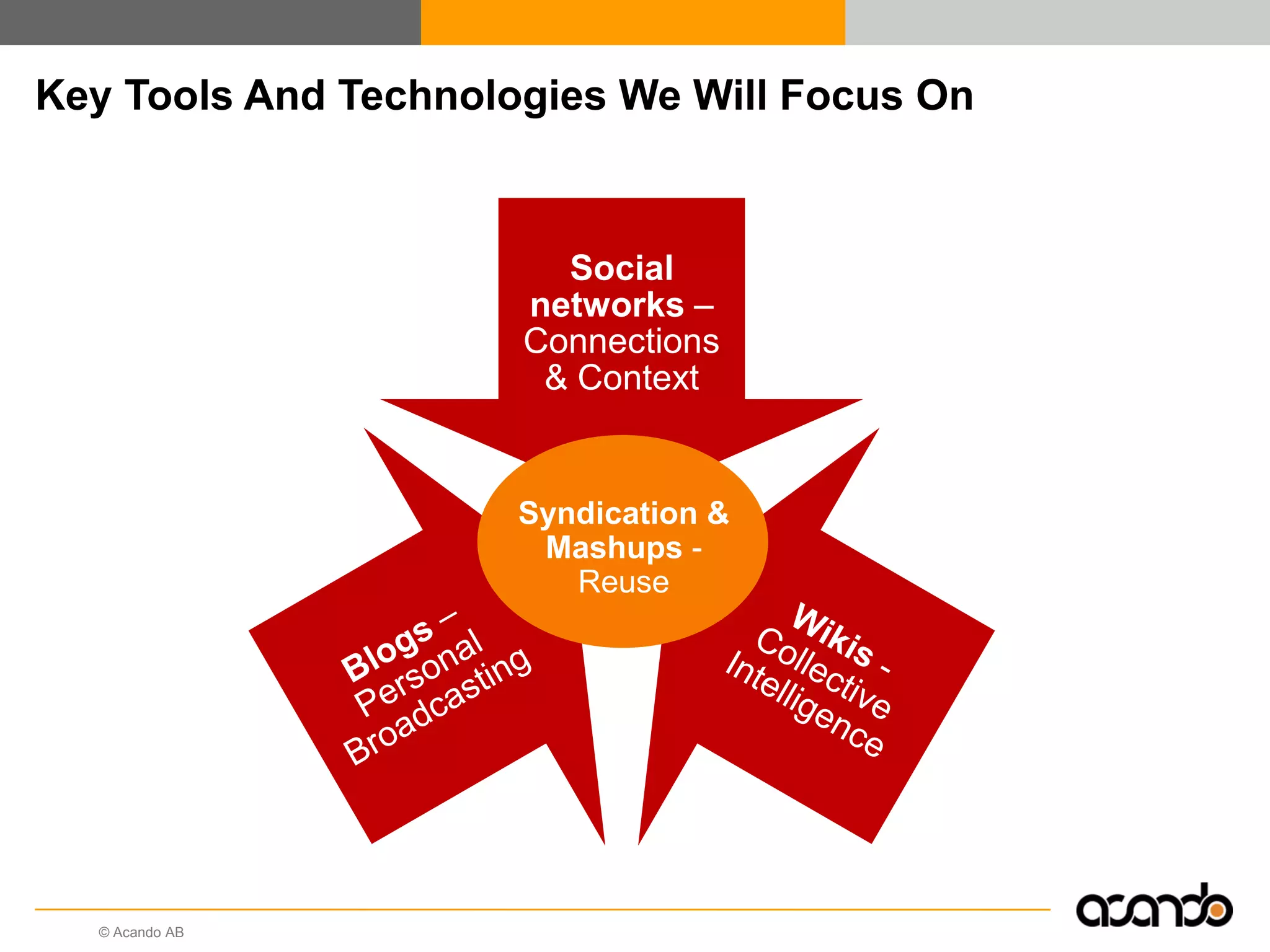
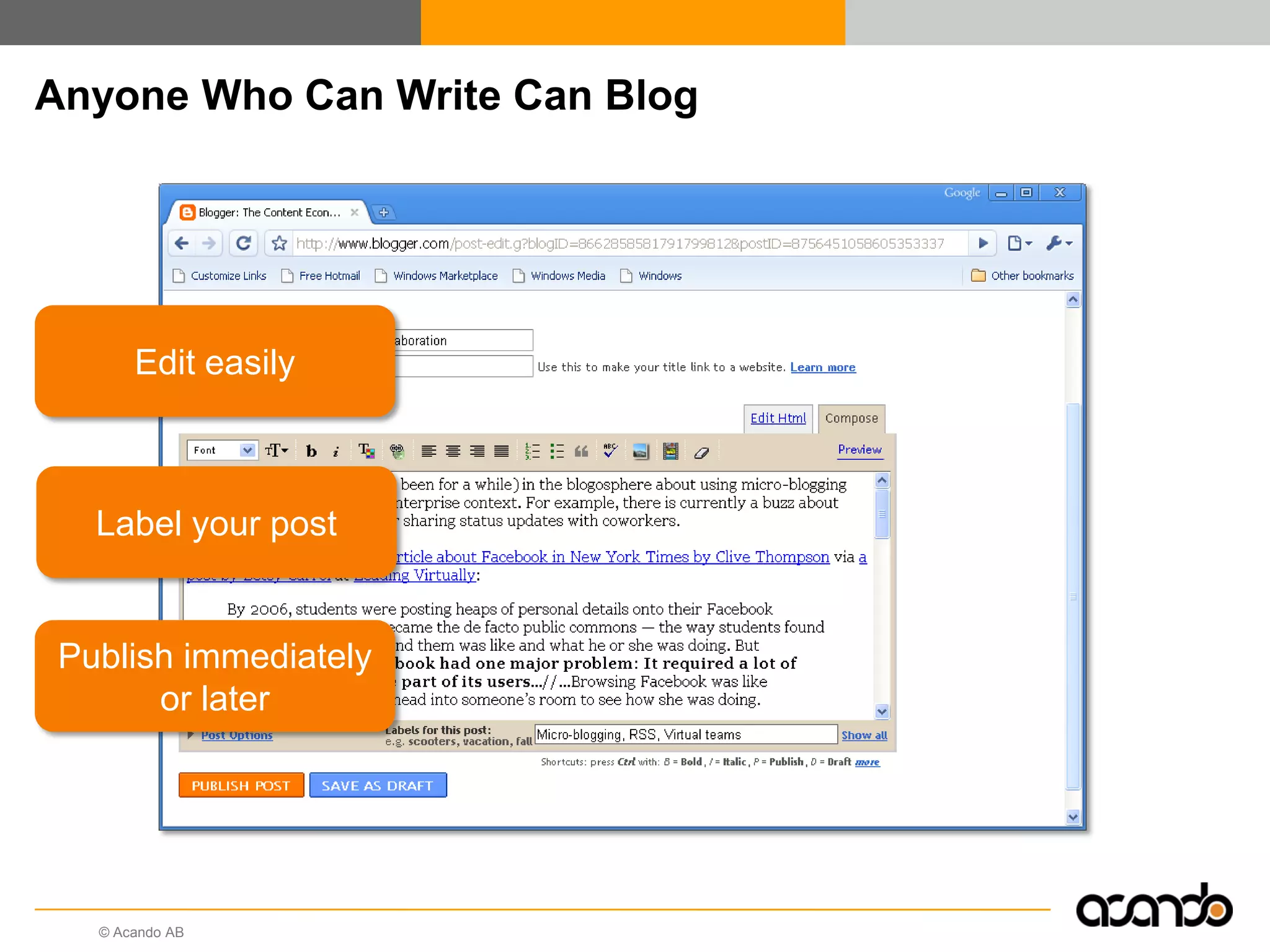
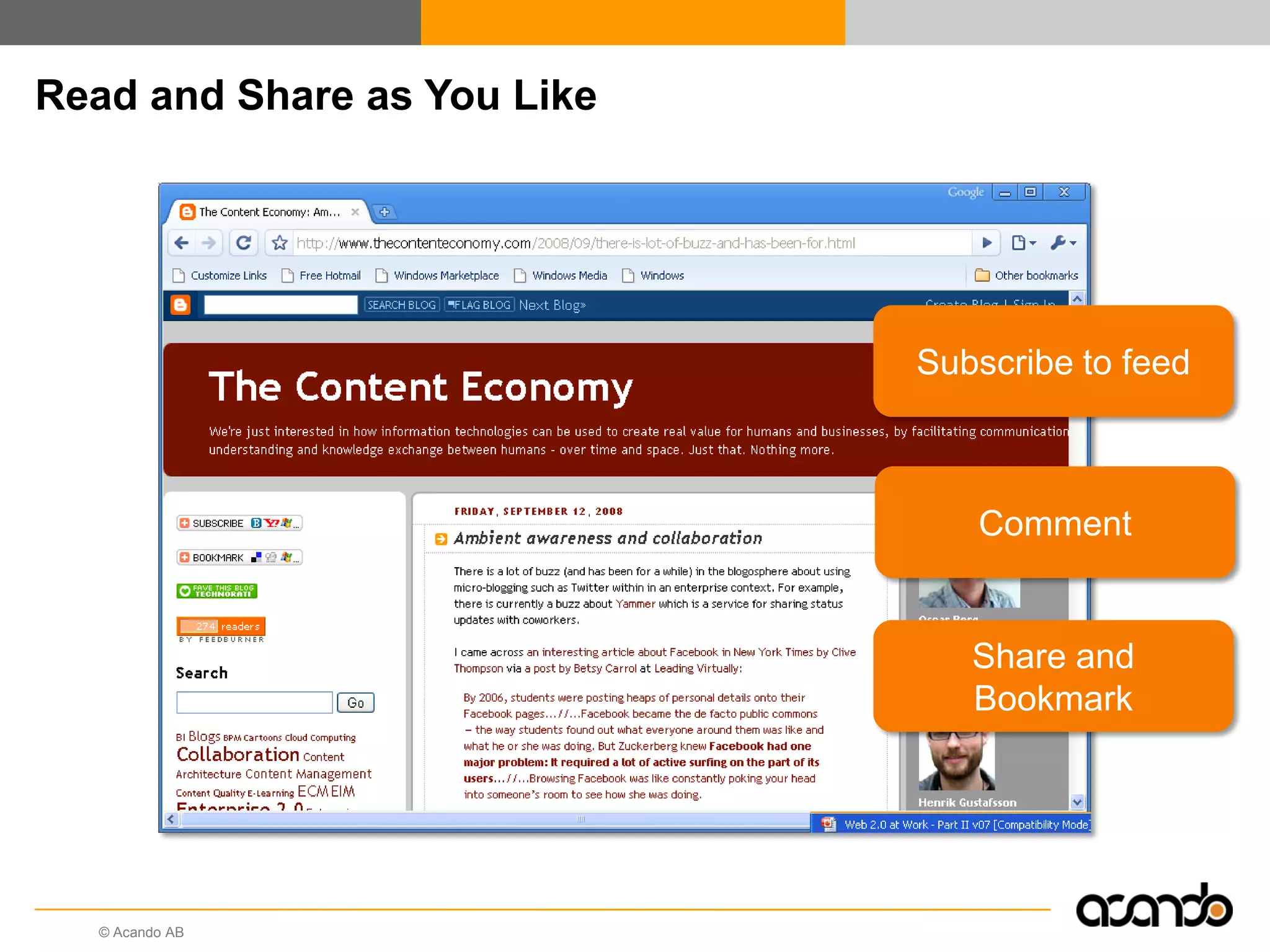
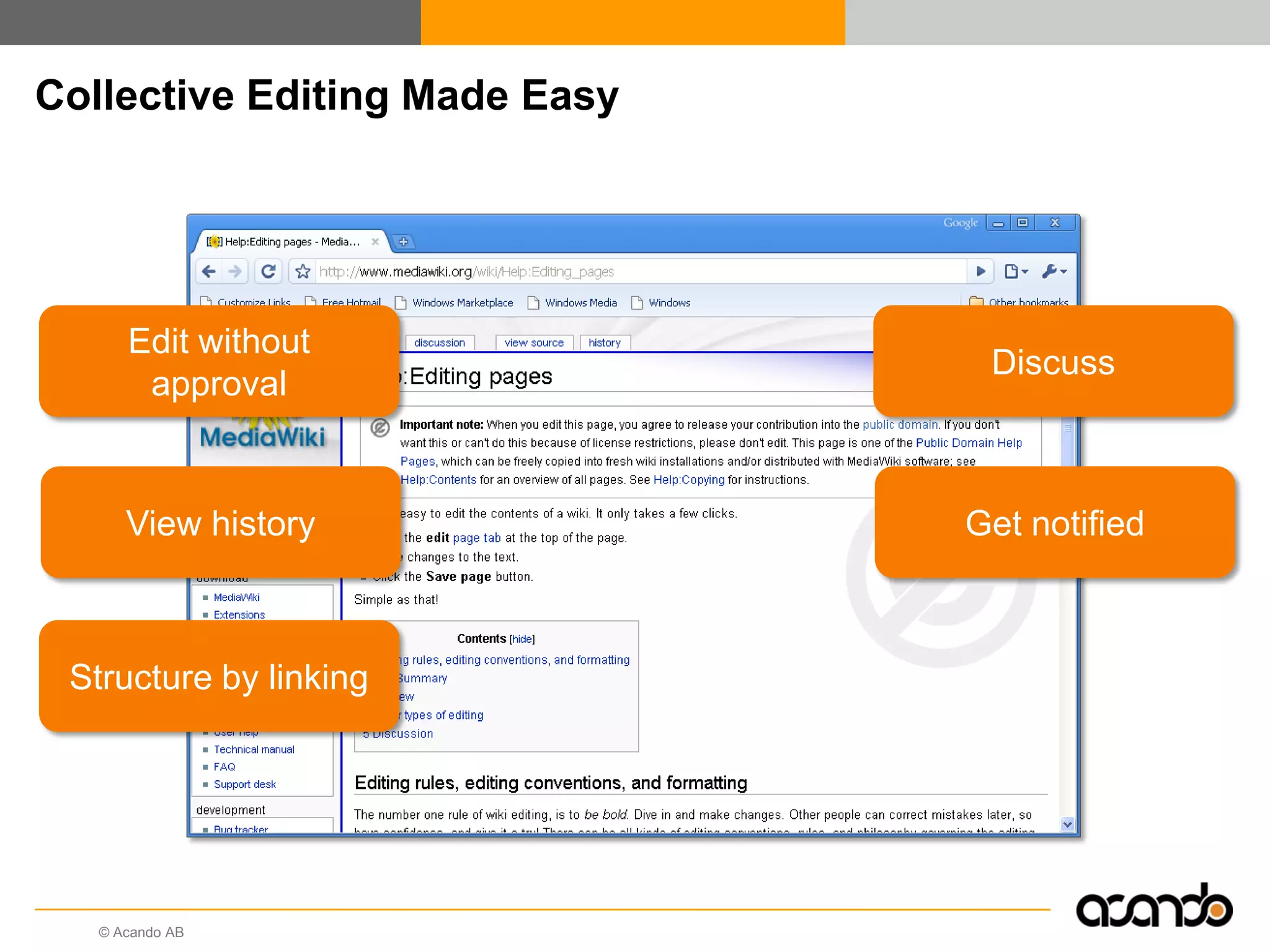
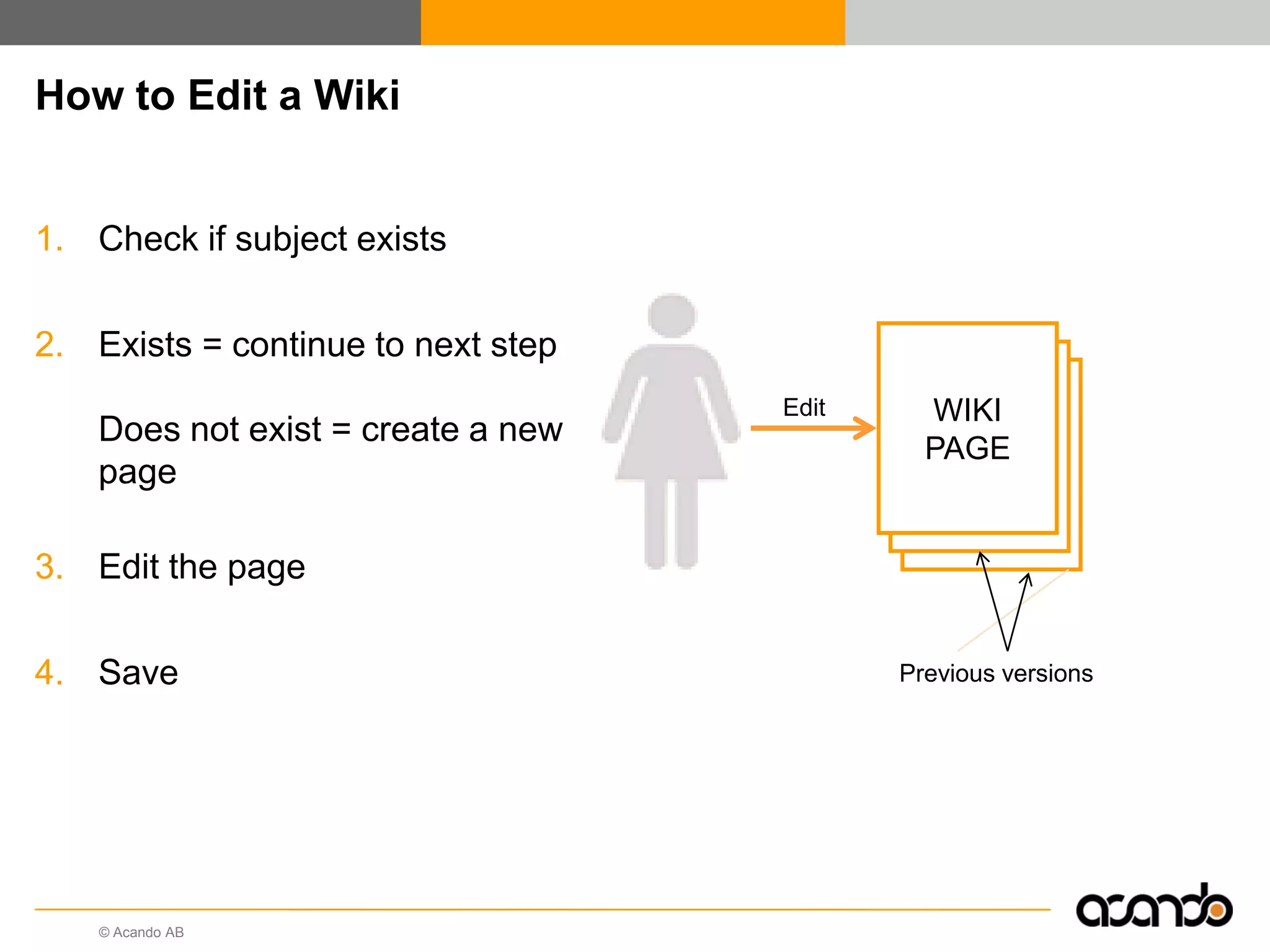
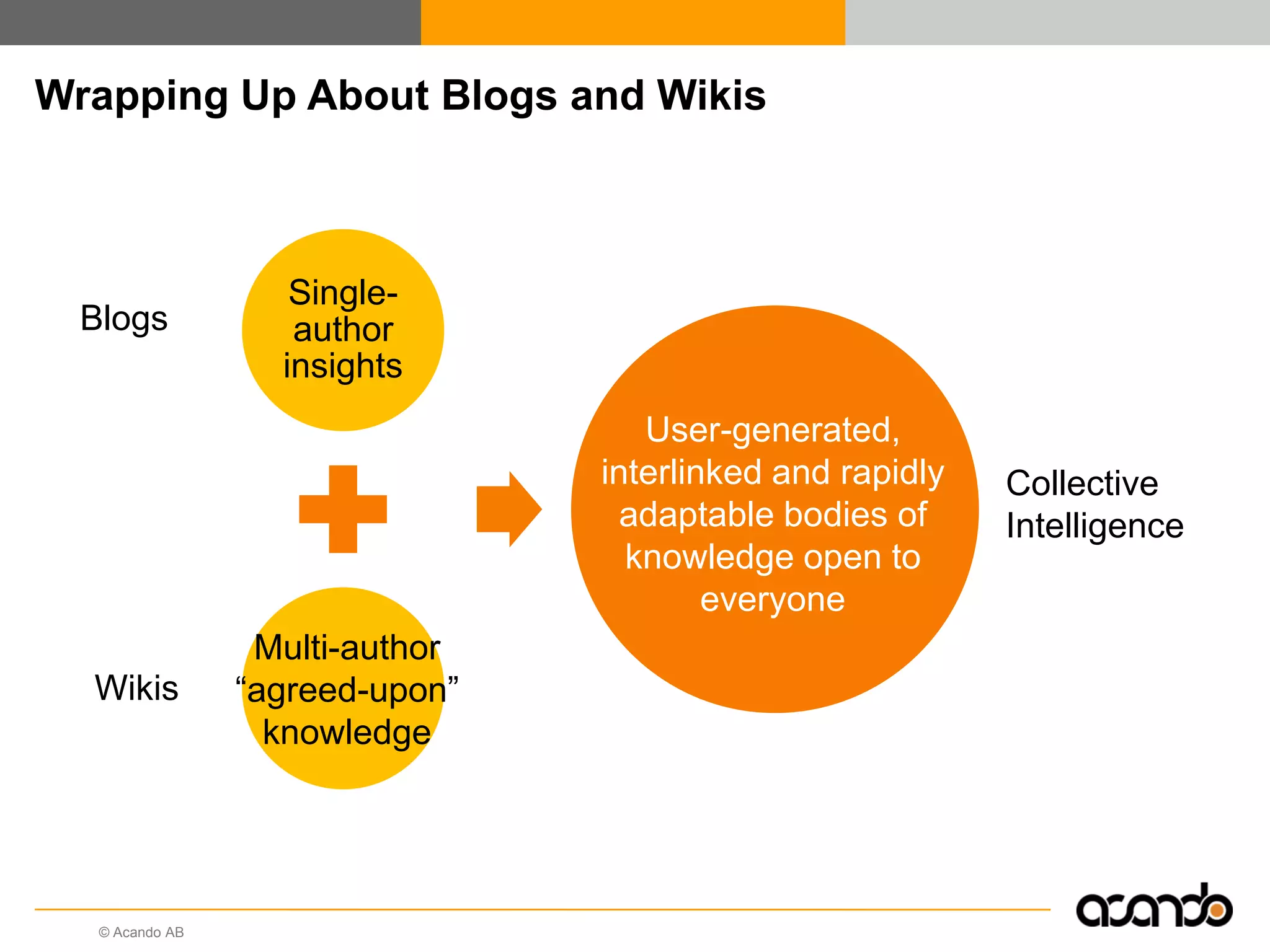
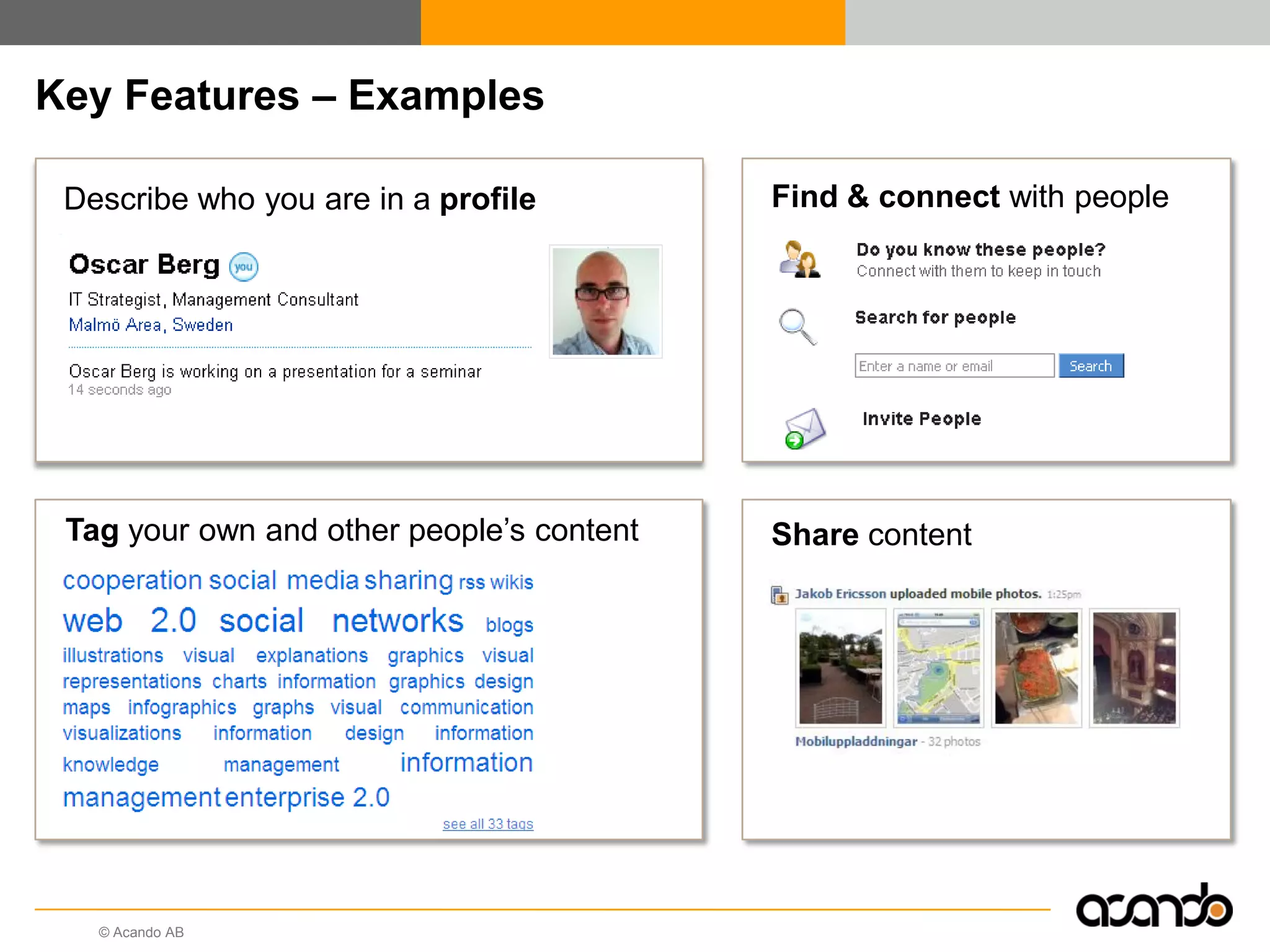
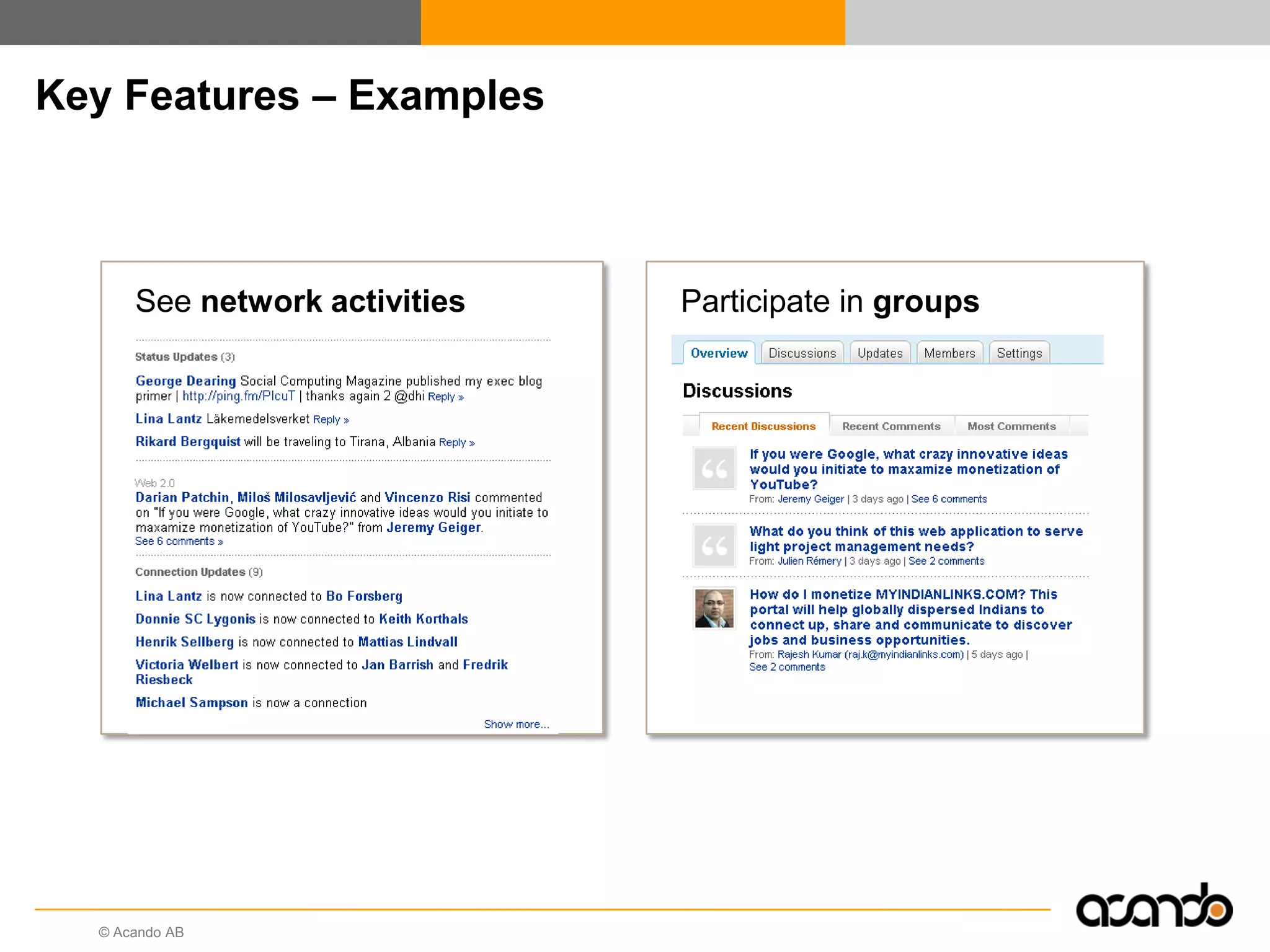
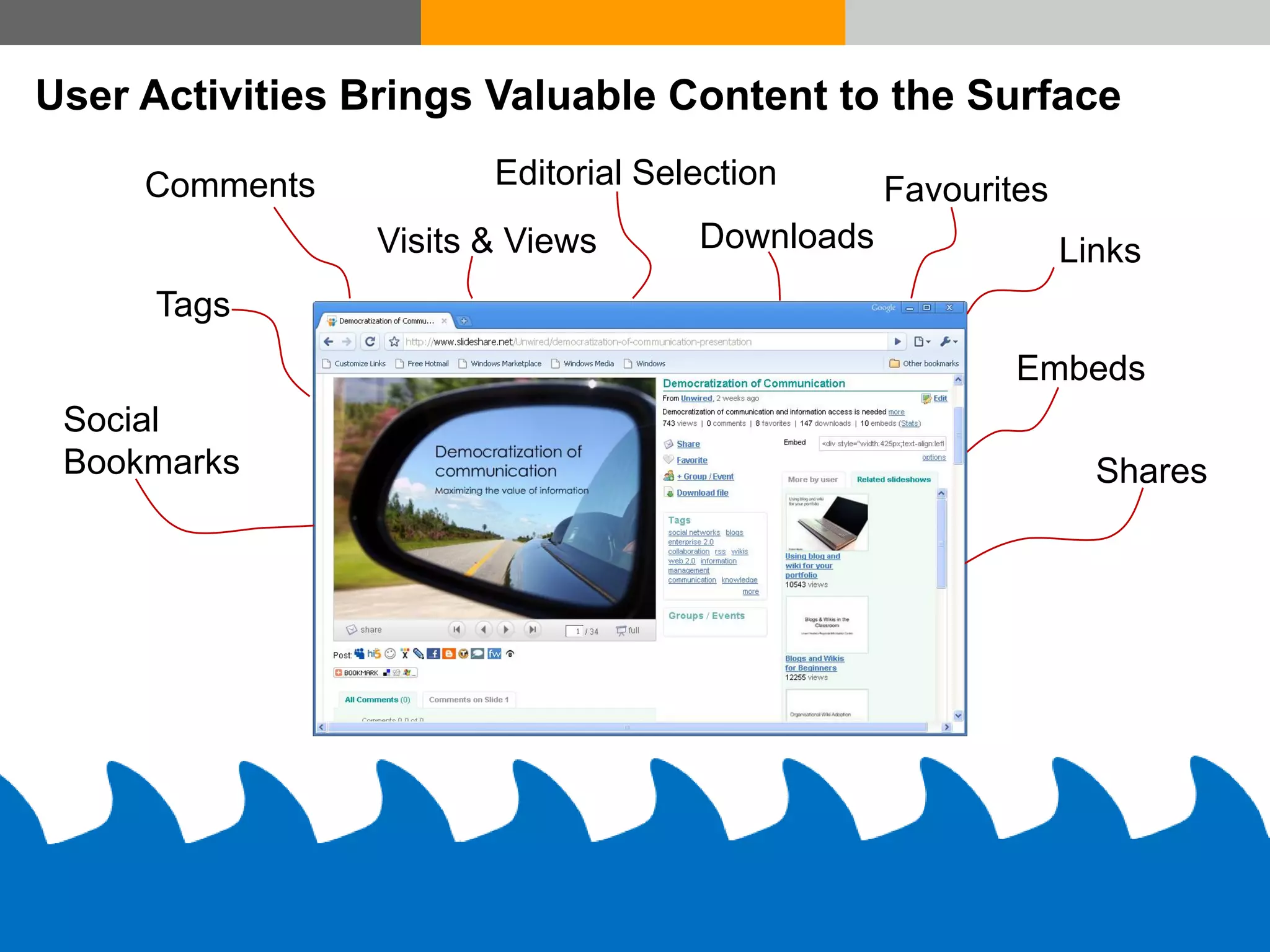
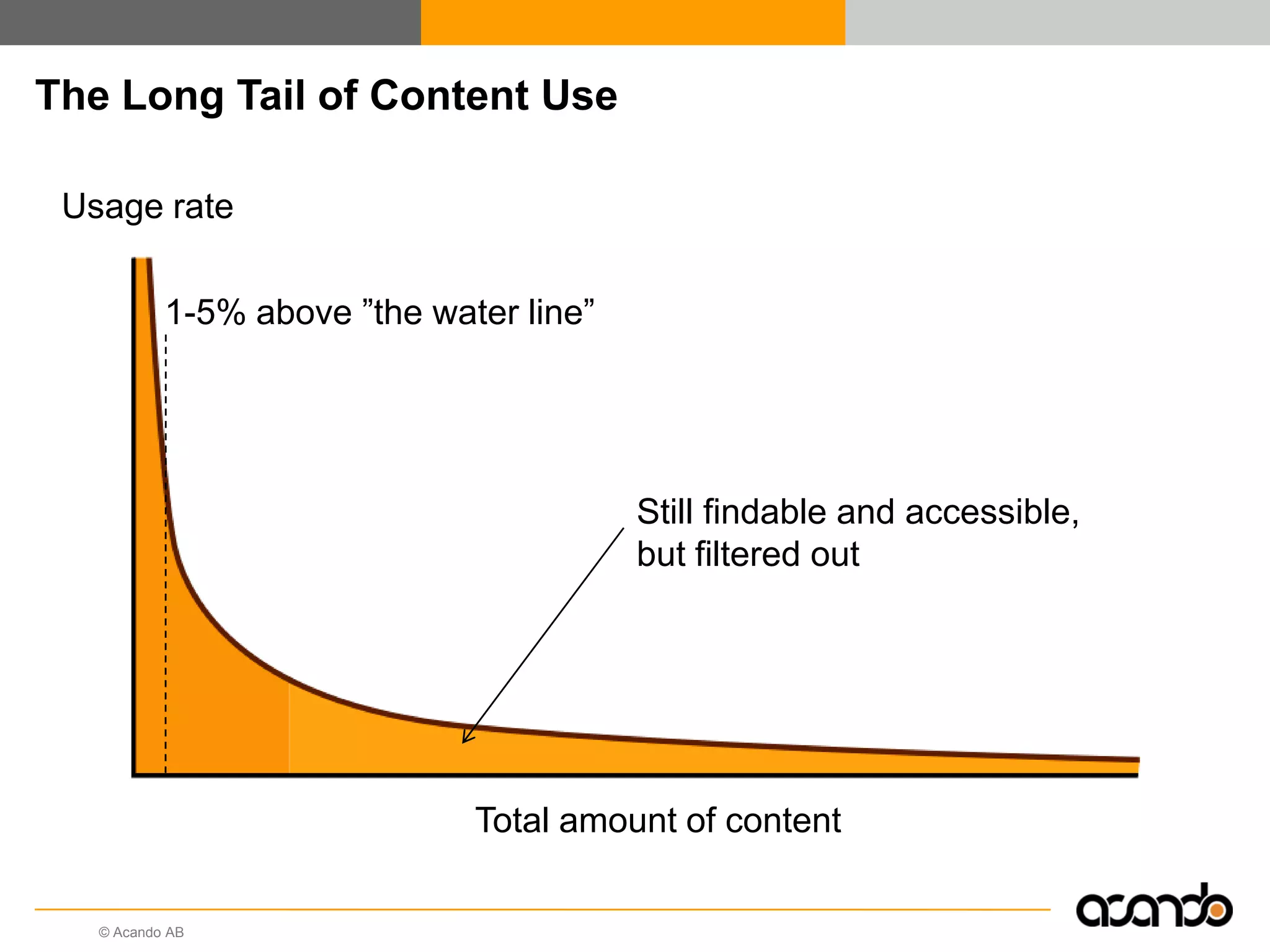
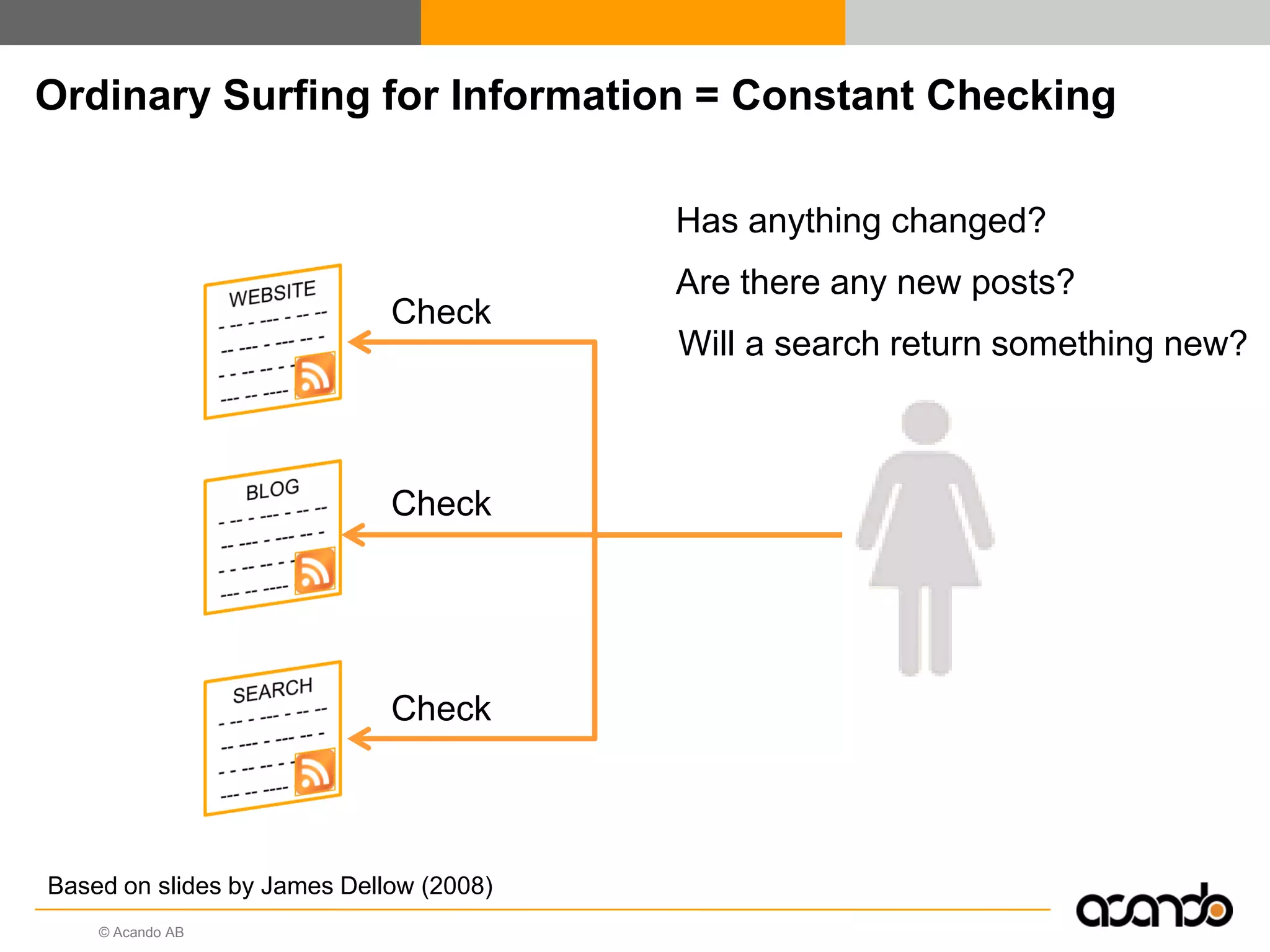
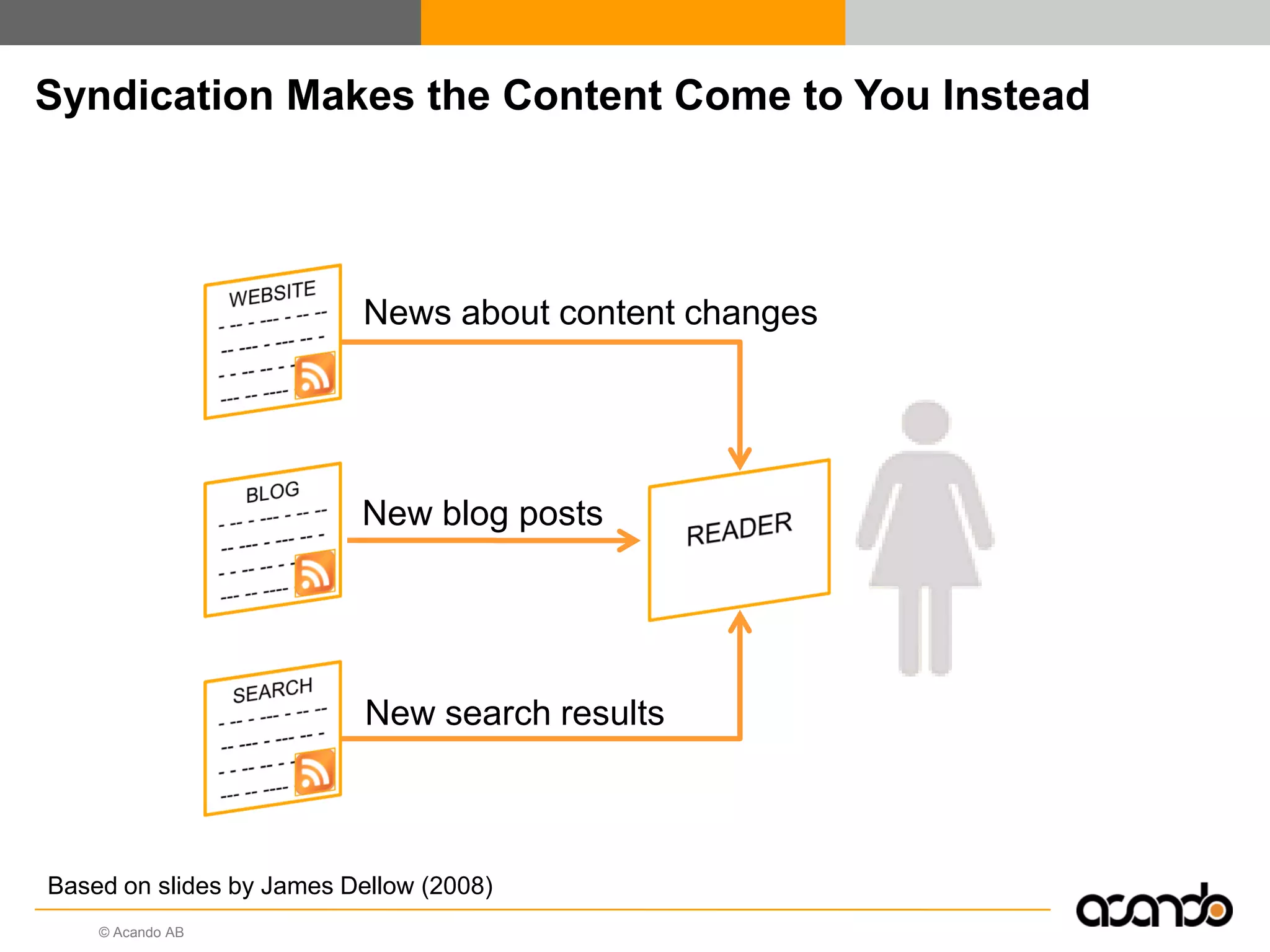
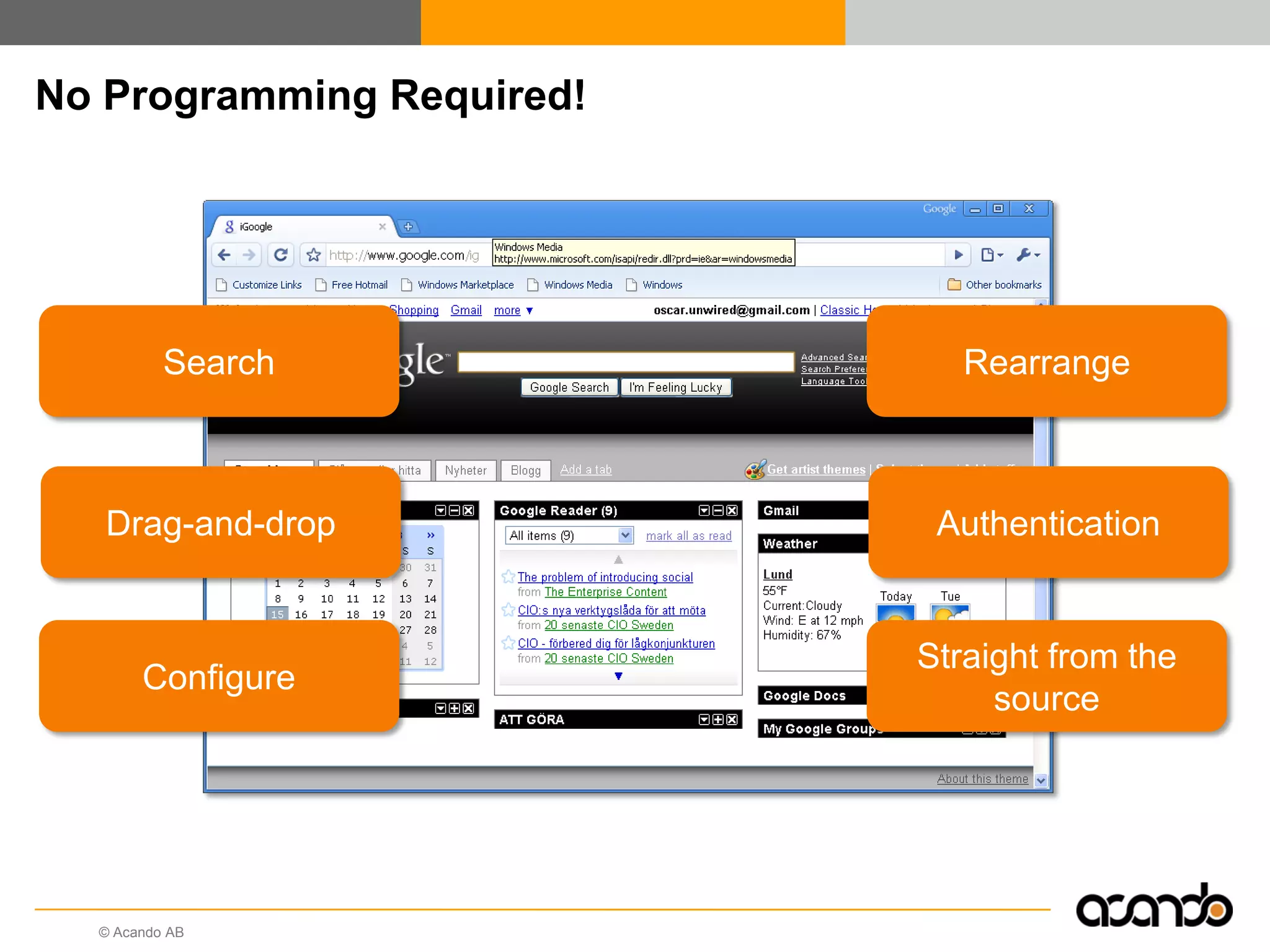
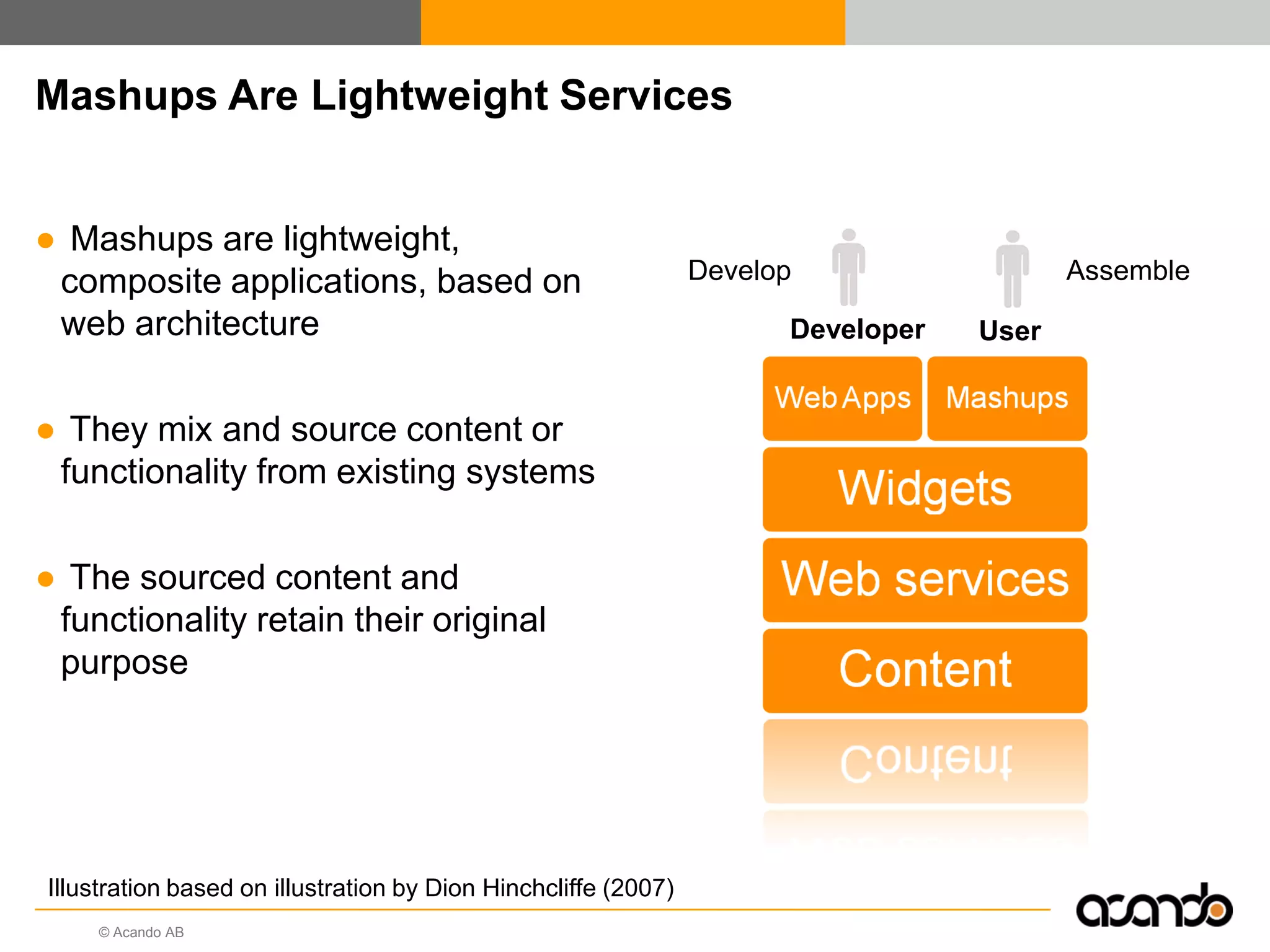
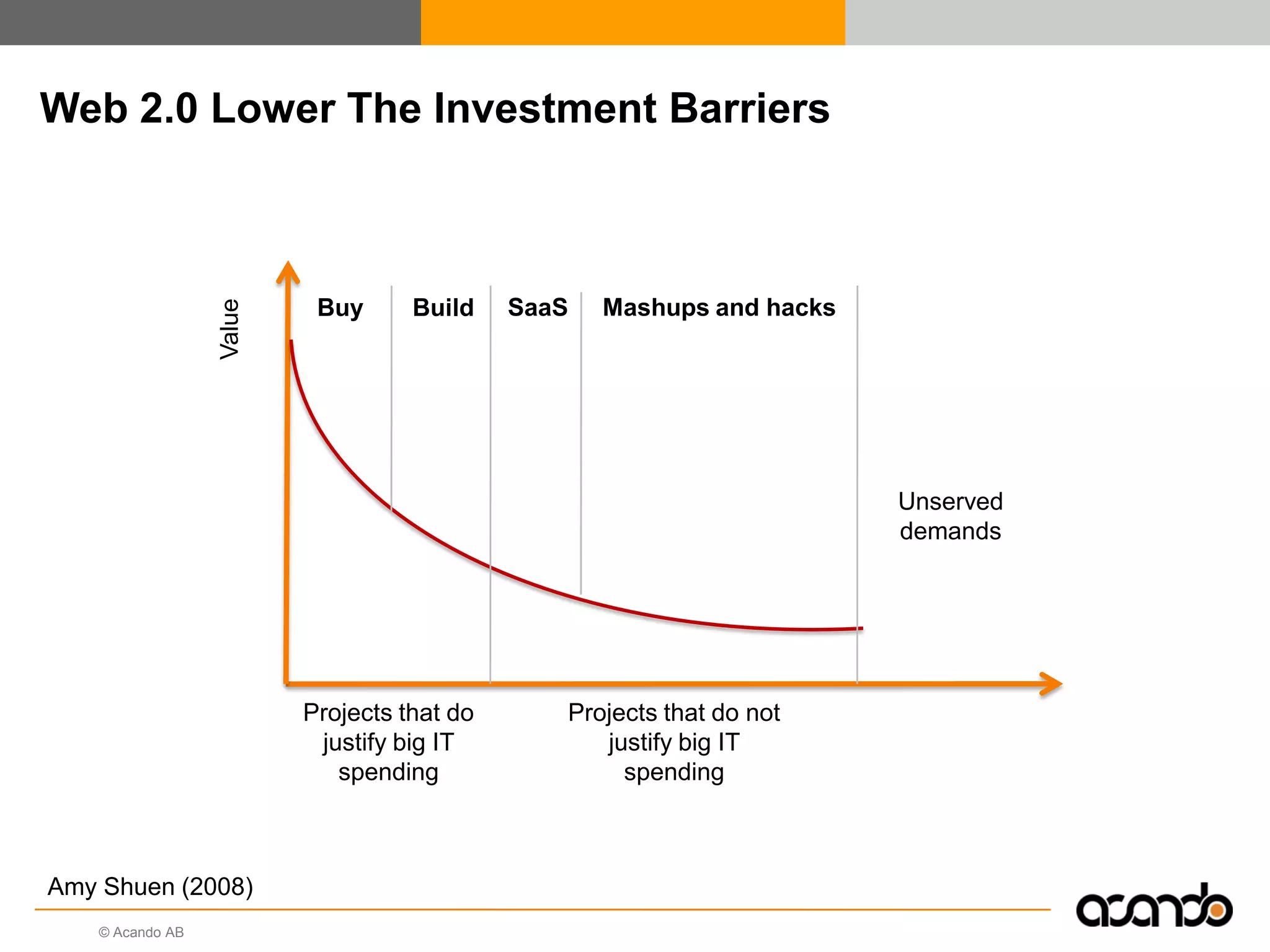
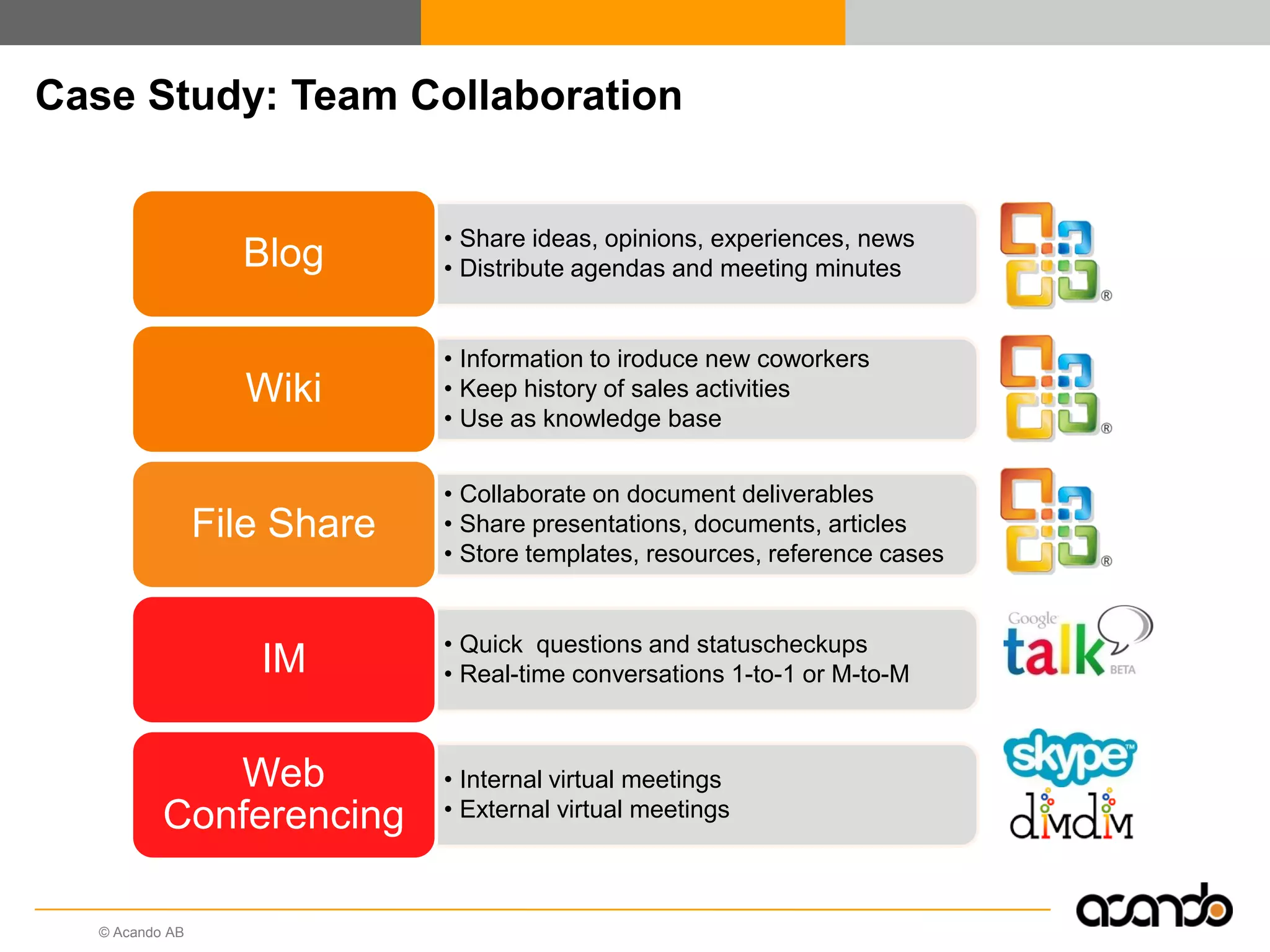
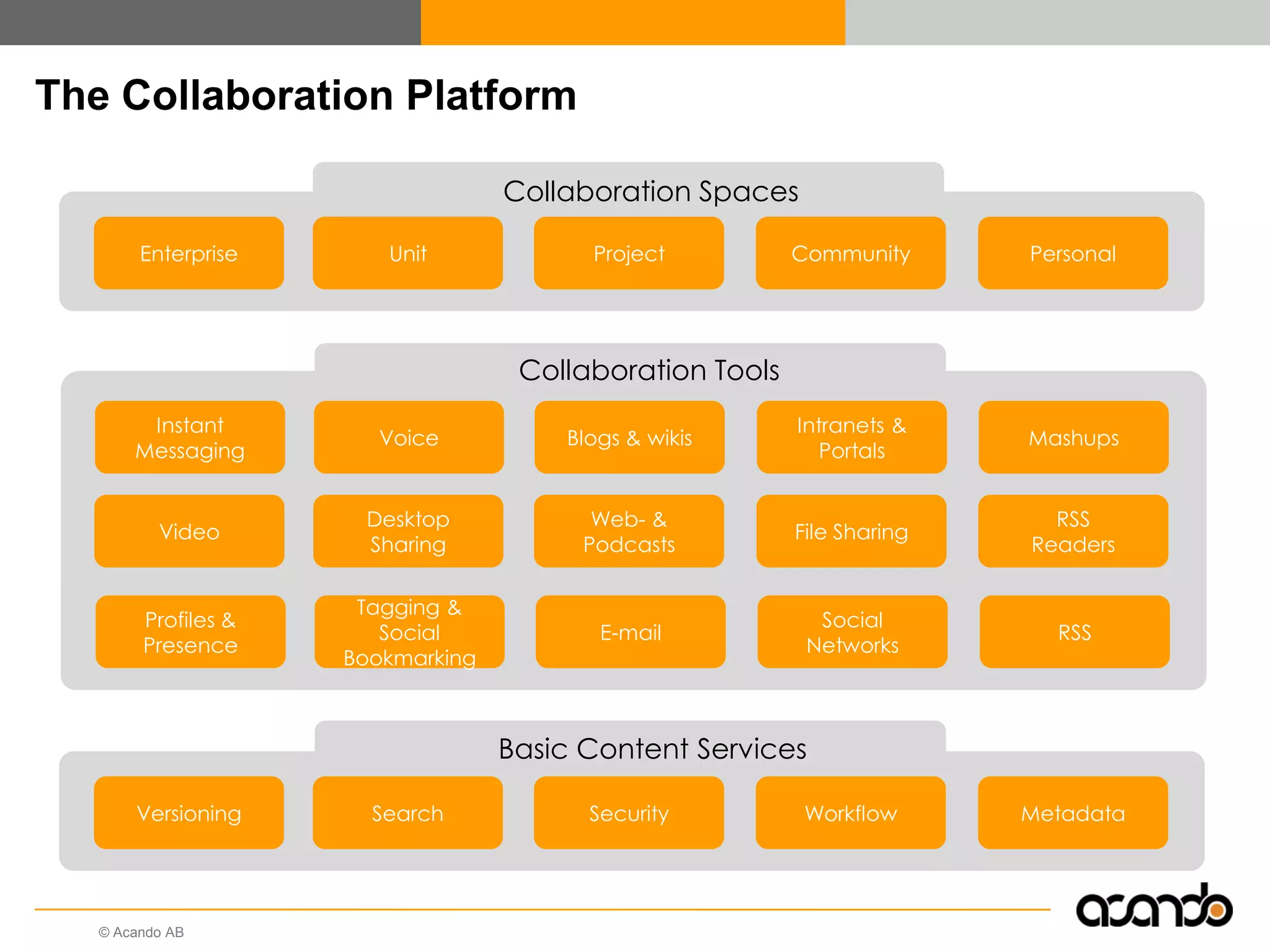
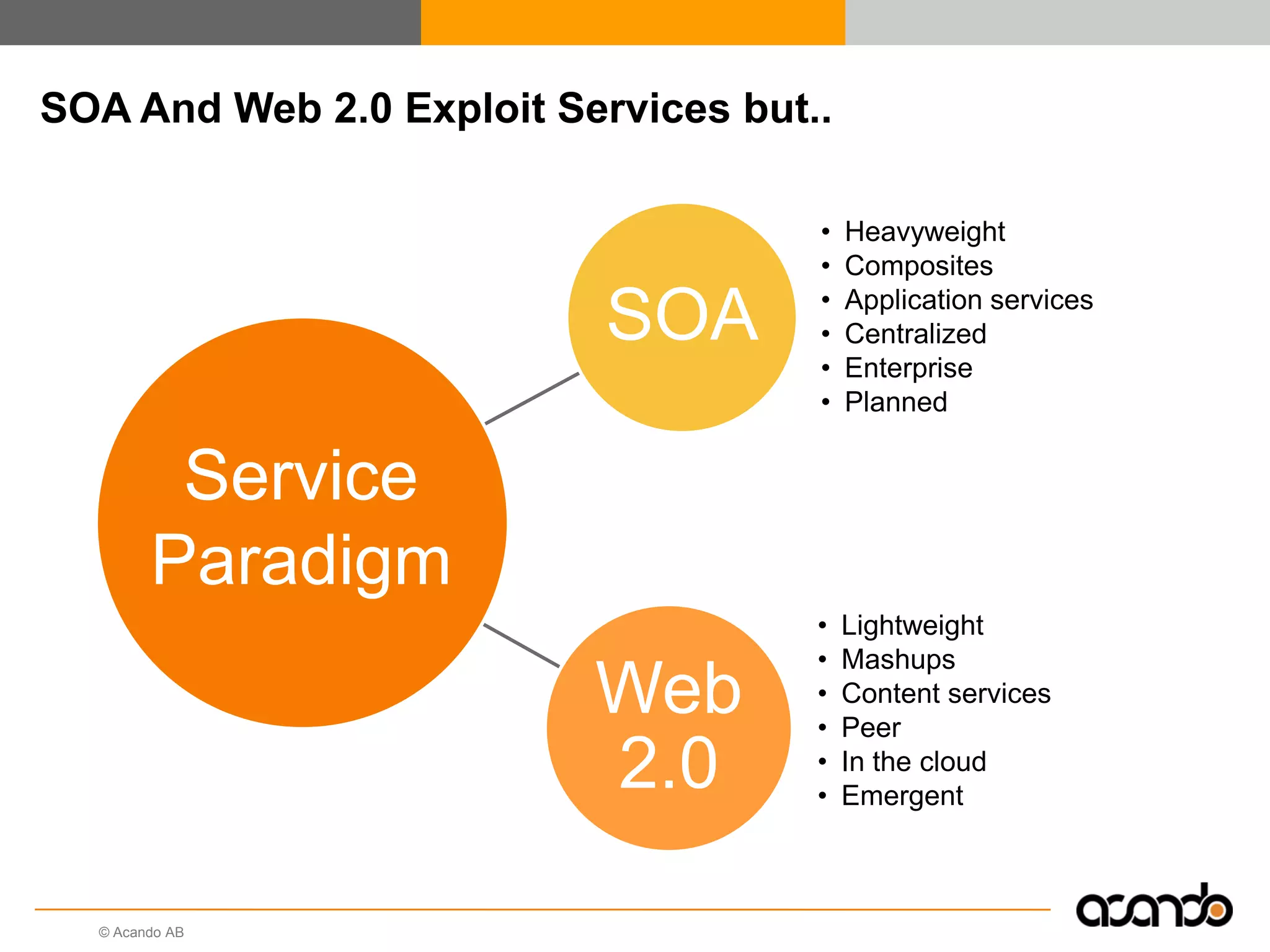
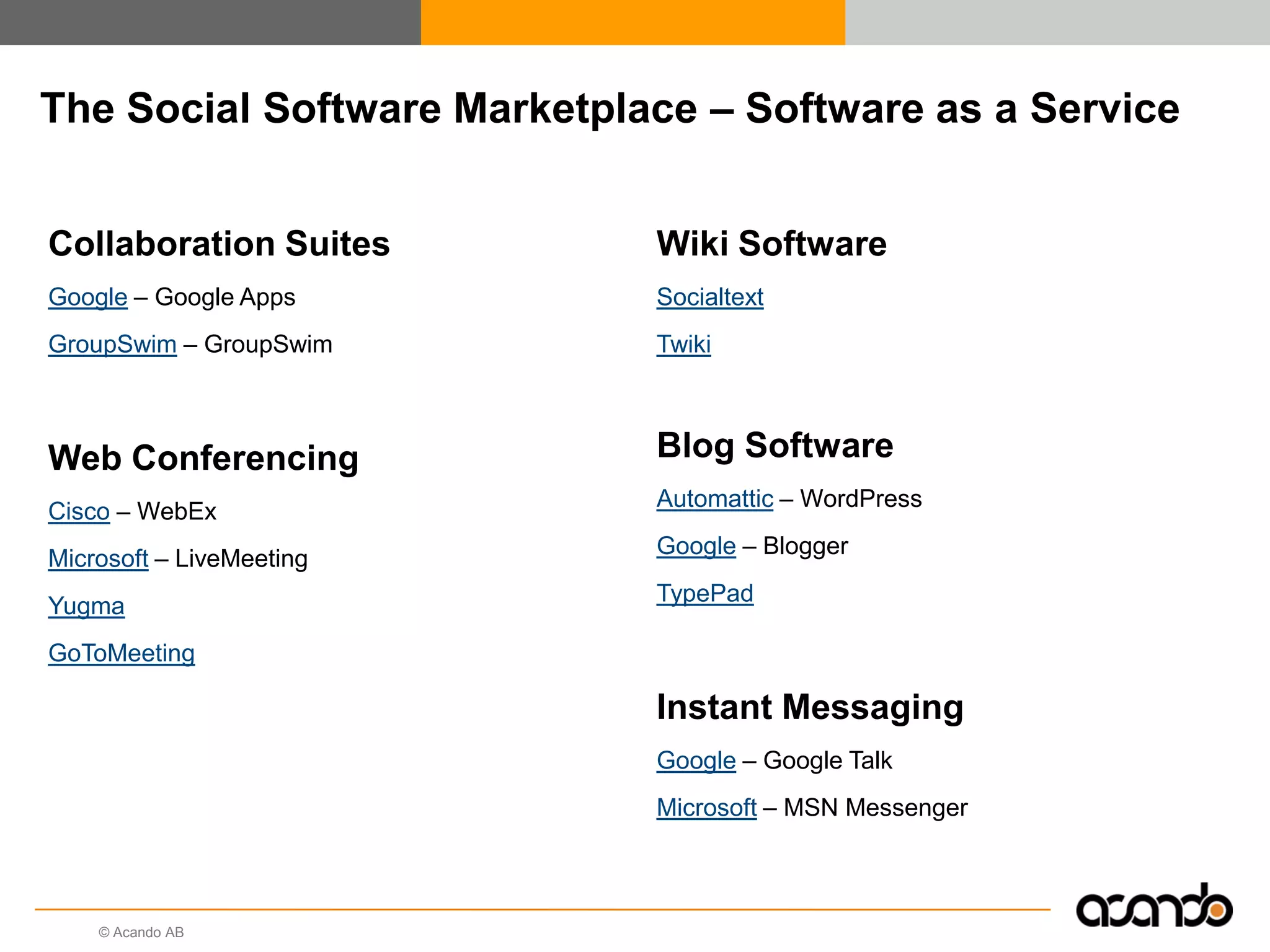
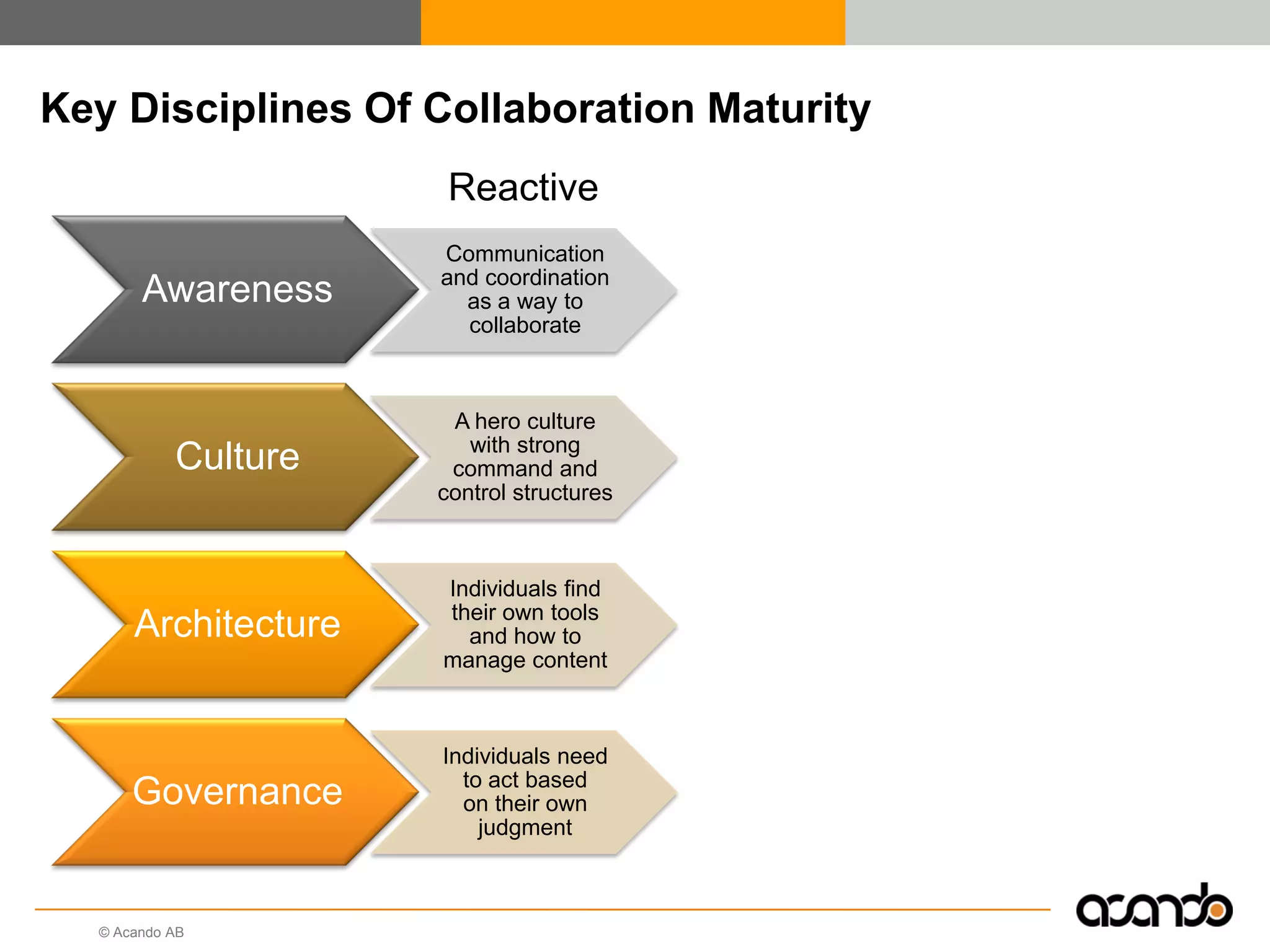
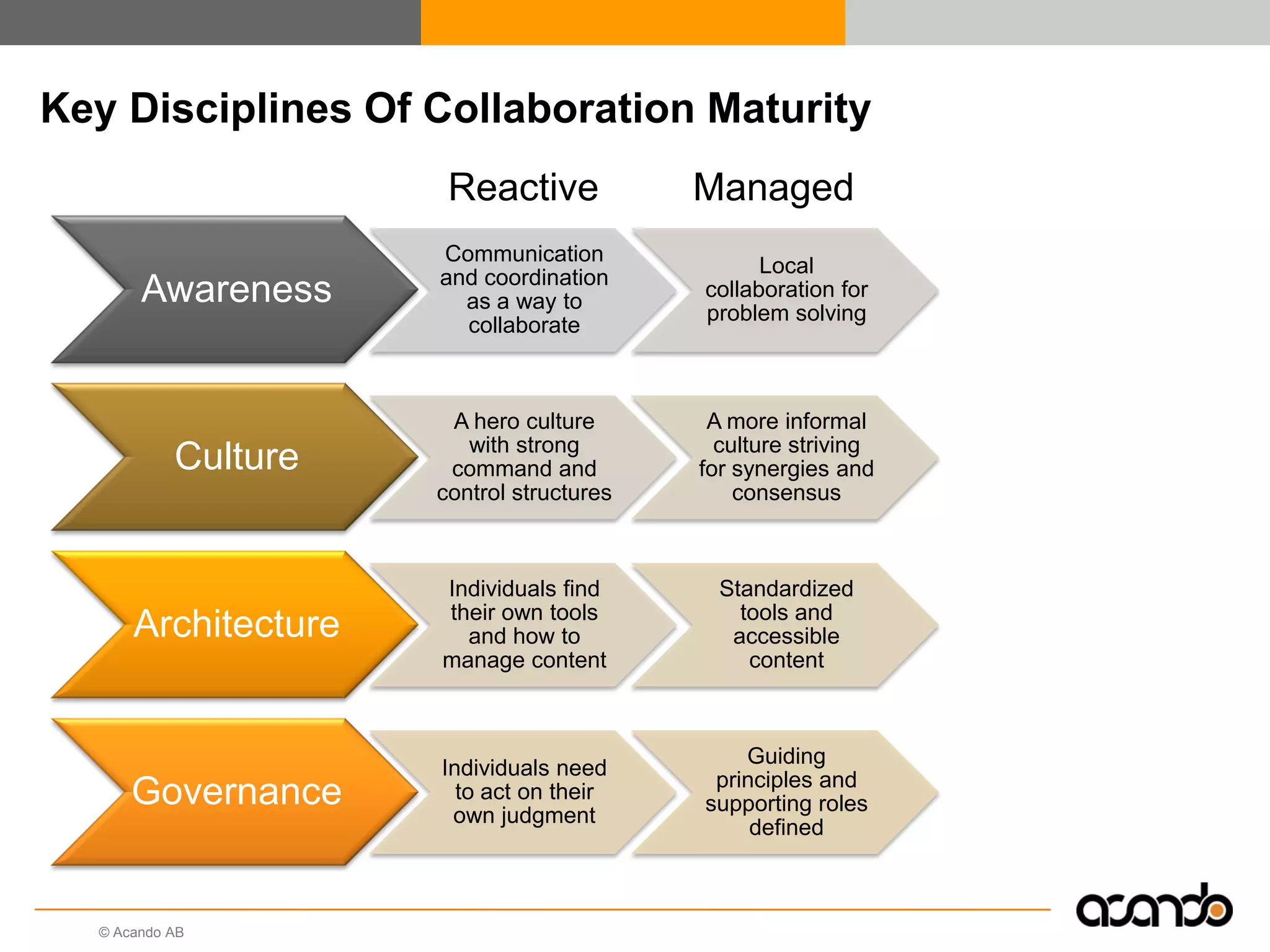
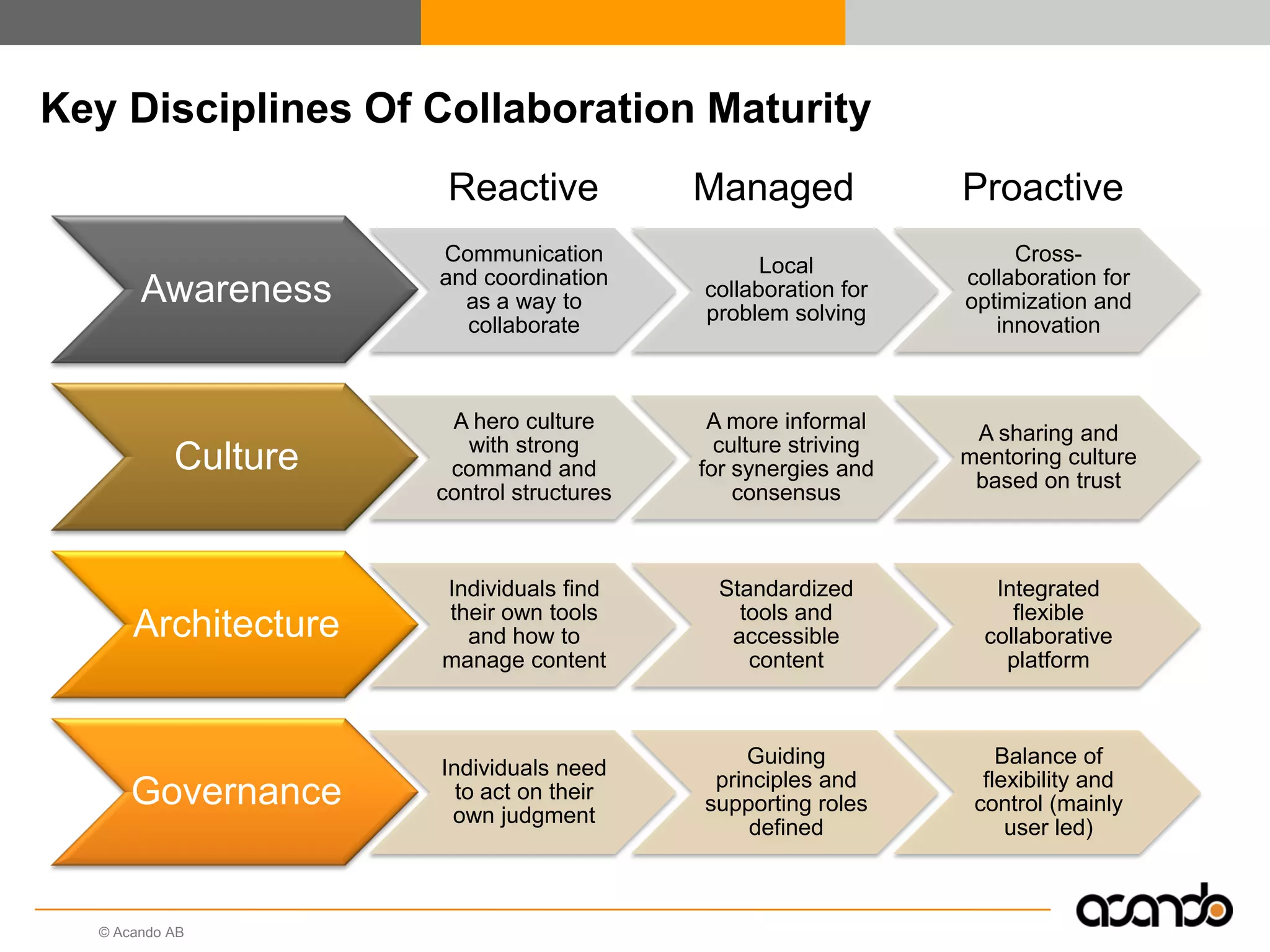
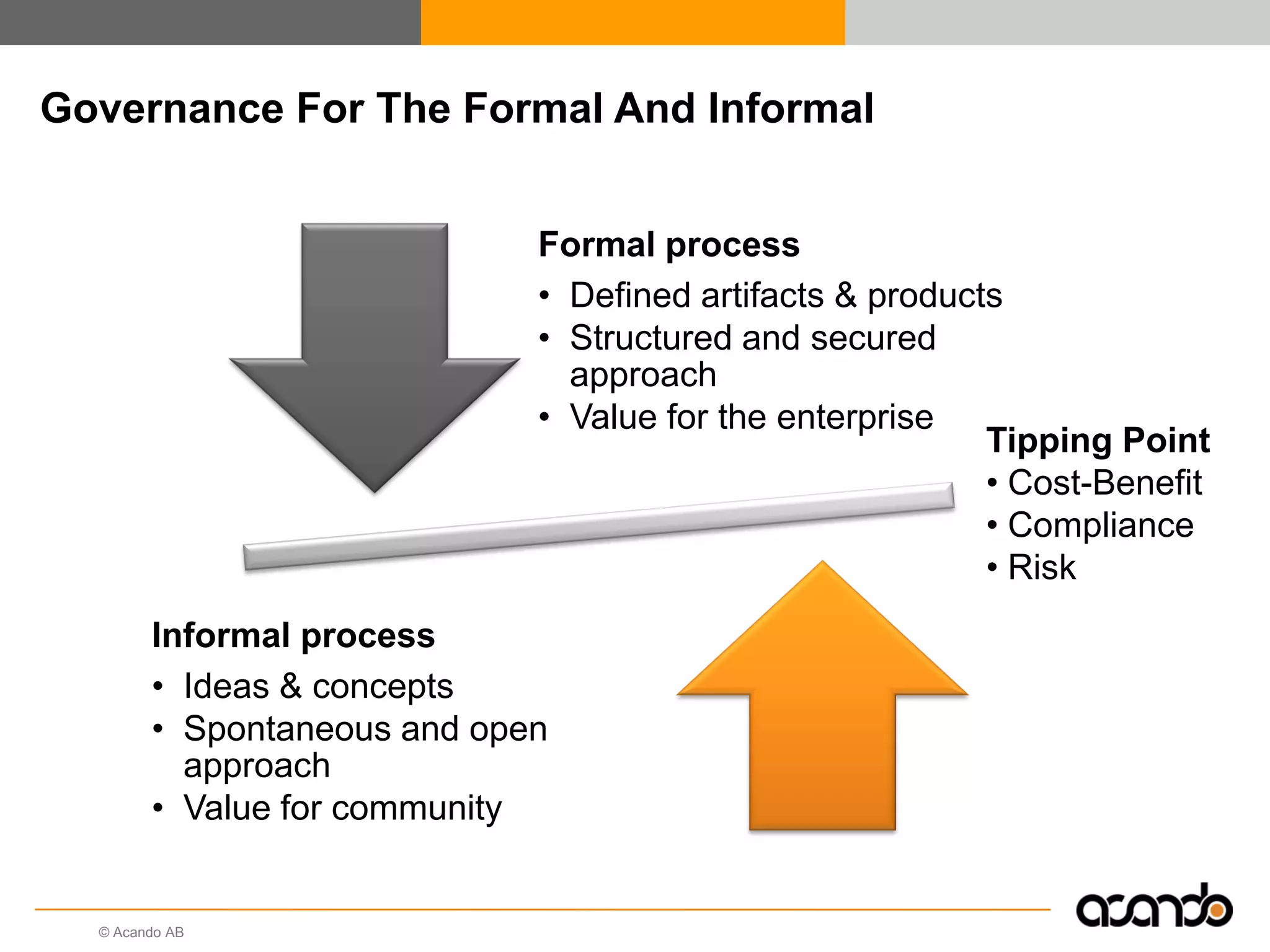
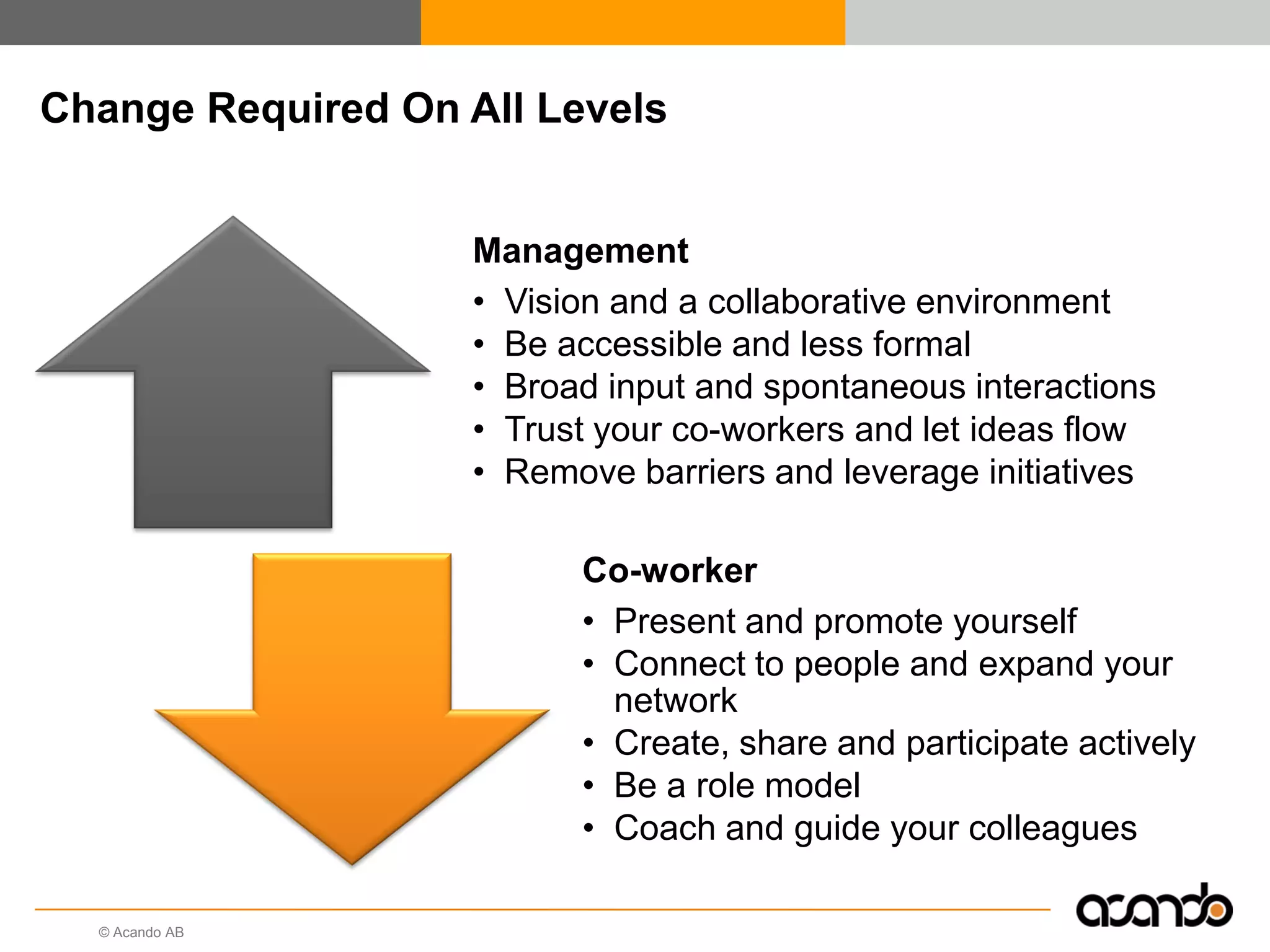
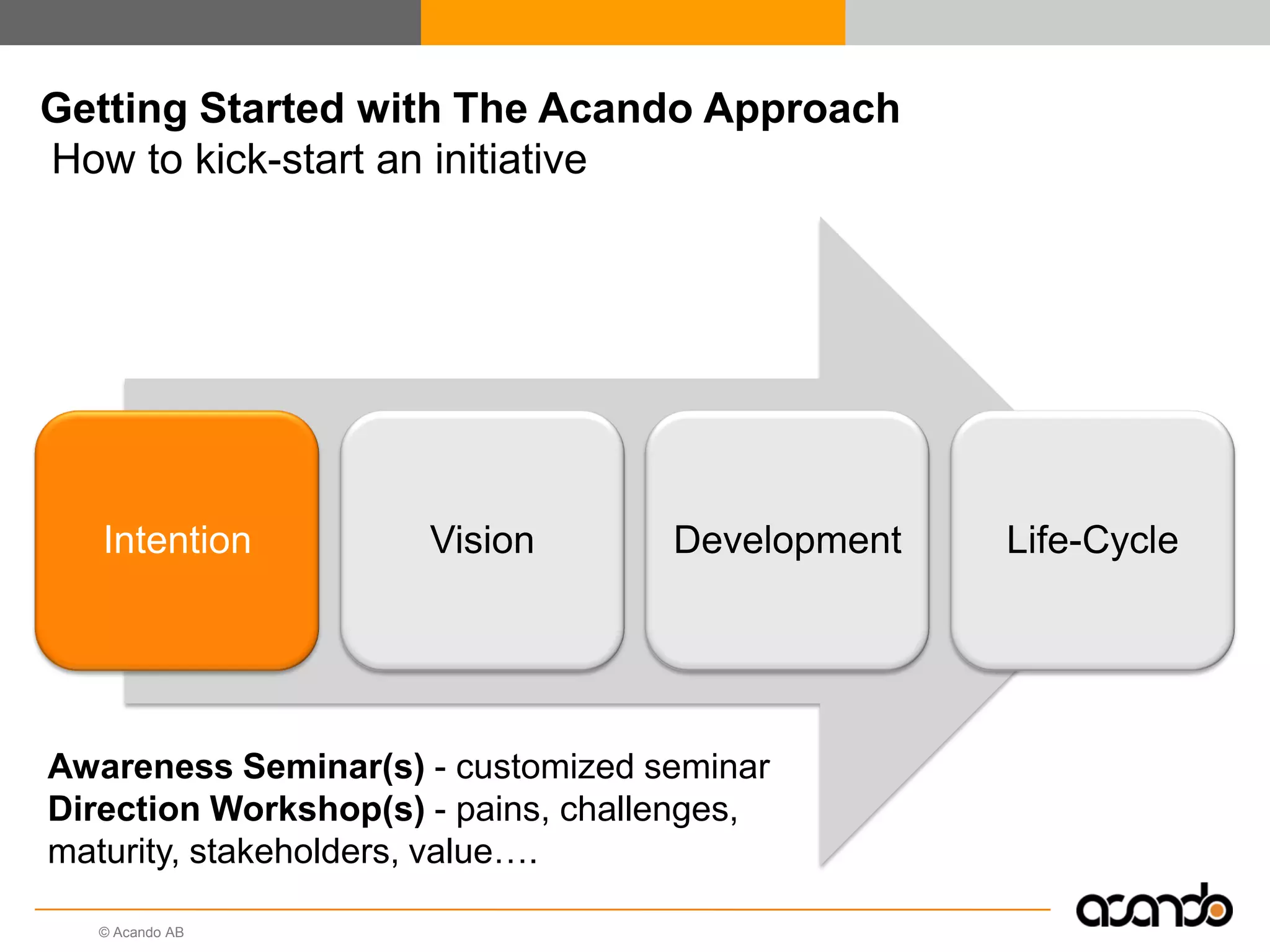
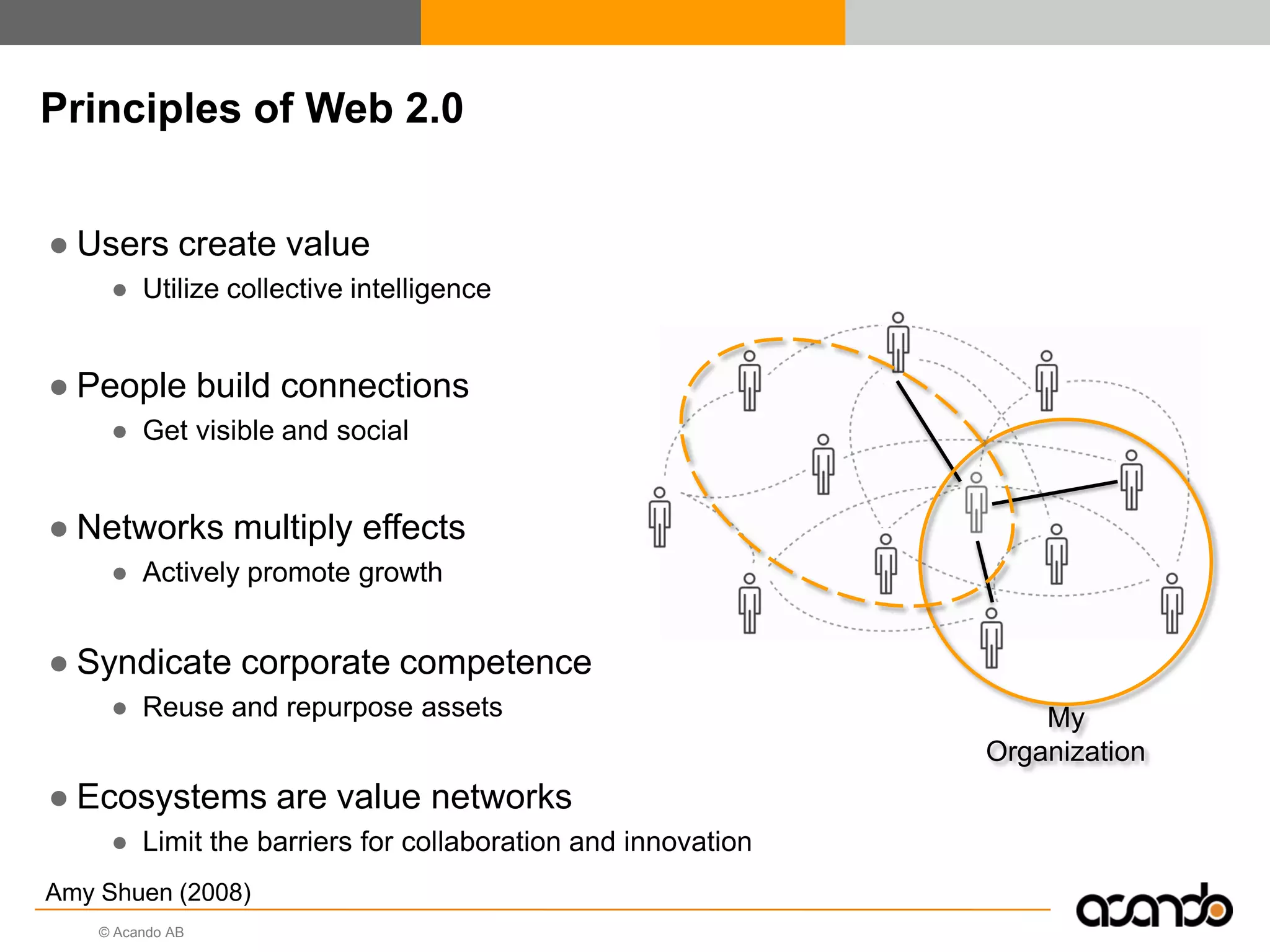
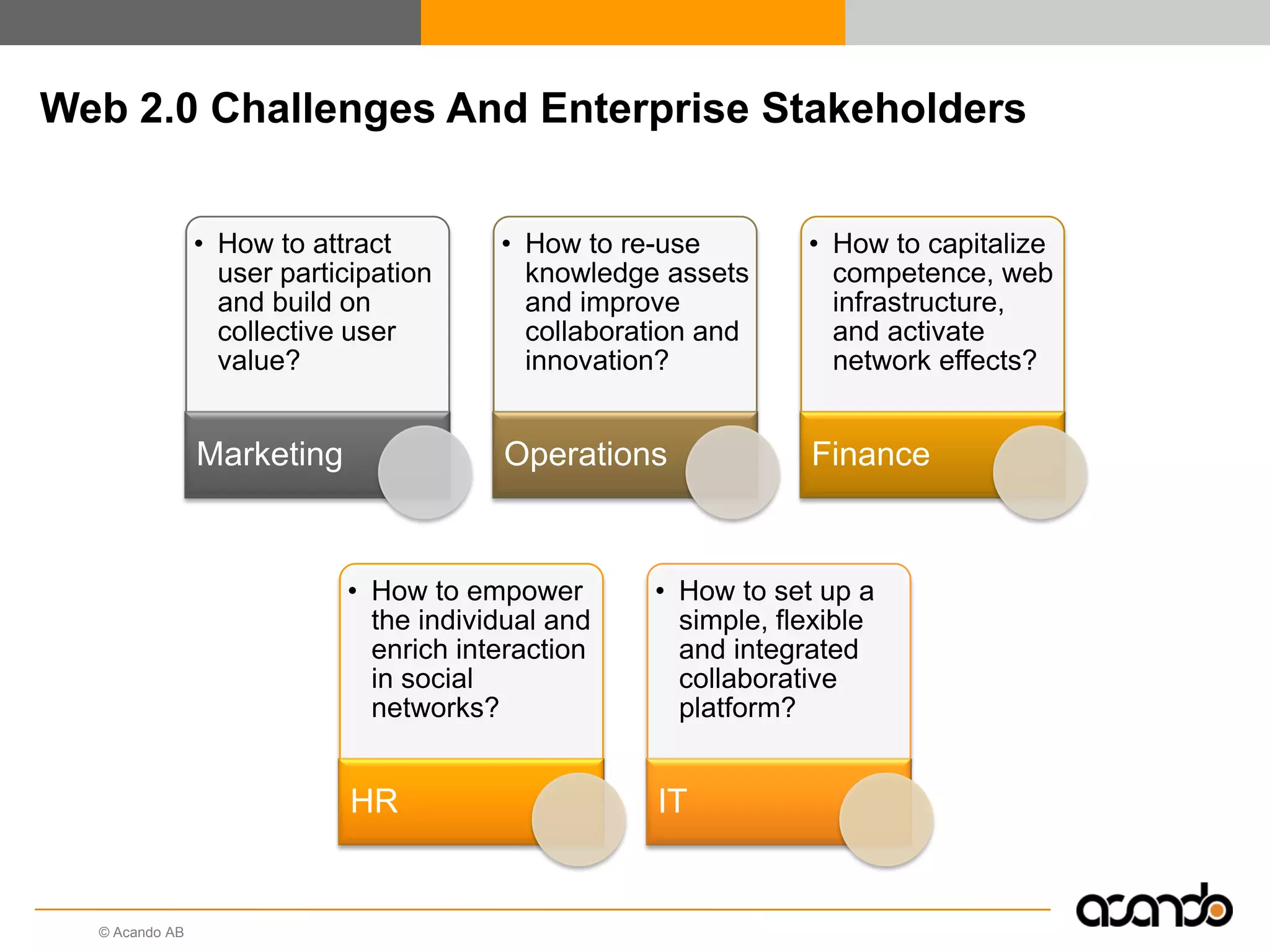
This document discusses how various Web 2.0 tools can be used to improve internal collaboration in organizations. It begins by providing background on how communication technologies and the web have evolved, enabling more open sharing of information. It then addresses trends challenging traditional collaboration like globalization and the consumerization of IT. Various Web 2.0 tools are presented for internal collaboration, including blogs to share insights, wikis for collective knowledge bases, social networks to find and connect with people, syndication to receive customized information, and mashups to integrate multiple data sources. The document concludes with a case study of using blogs, wikis and social networks to improve team collaboration.