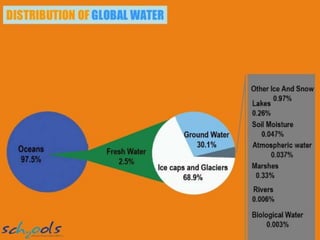
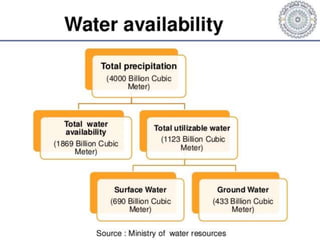
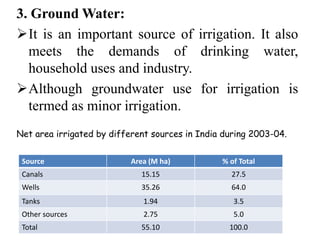
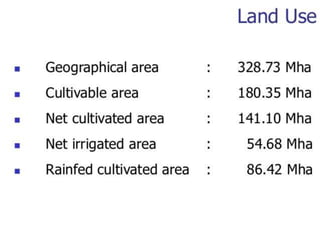
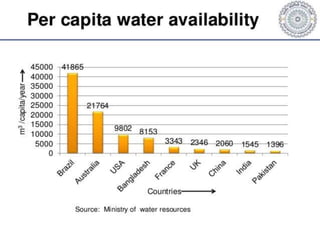
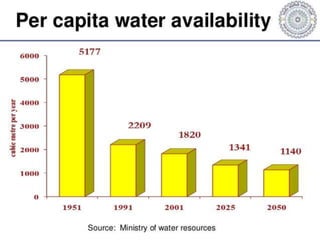
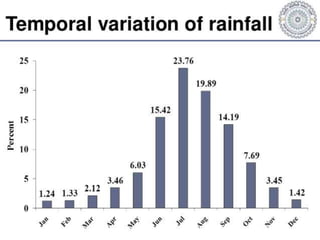
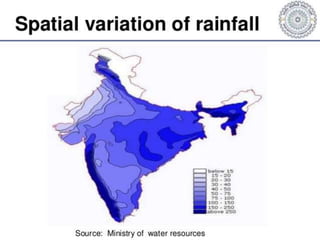
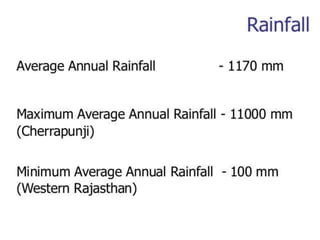
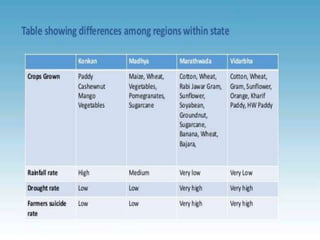
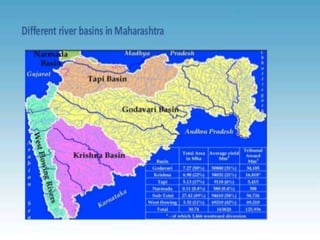
This document summarizes water resources in India. It discusses that India receives adequate annual rainfall on average but experiences water scarcity due to uneven rainfall distribution and lack of conservation efforts. The major sources of water are rainwater, surface water from rivers, and groundwater. India's major river systems include the Ganga-Brahmaputra-Meghna system which has the largest catchment area. Groundwater meets irrigation, drinking, and other domestic needs. Wells irrigate over 60% of India's total irrigated area. The document then provides specifics on water resources in the state of Maharashtra, noting its semi-arid climate and sources of irrigation including wells and micro-irrigation systems.