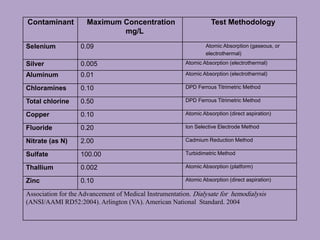
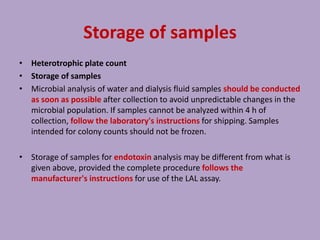
This document discusses water treatment for hemodialysis units. It notes that water quality significantly impacts patient outcomes. The summary is as follows:
1. Proper water treatment is essential for hemodialysis patients who are exposed to large volumes of water each week through dialysis.
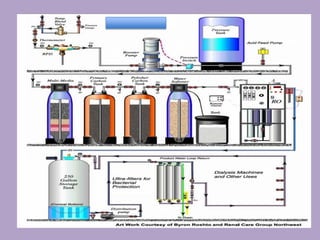
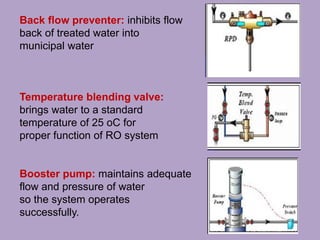
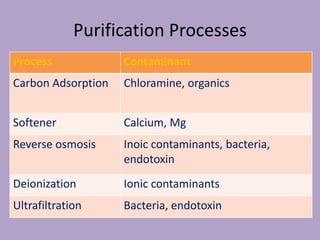
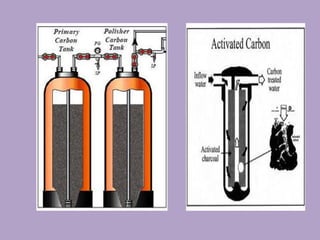
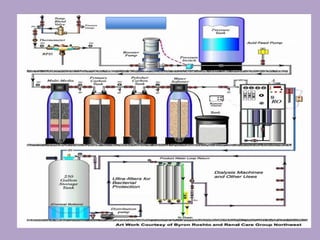
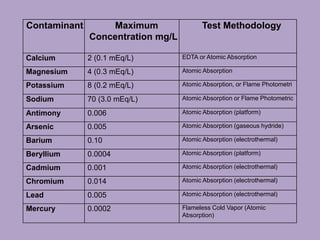
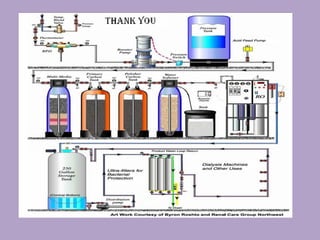
2. The water treatment system uses various processes like carbon filtration, softening, reverse osmosis, and deionization to remove contaminants.
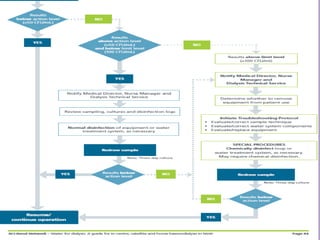
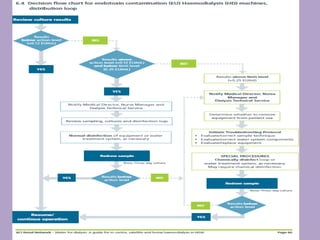
3. Strict policies, documentation, and staff education are needed to ensure the water treatment system operates safely and provides water that meets quality standards.