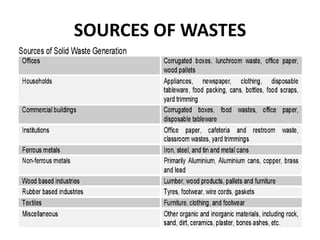
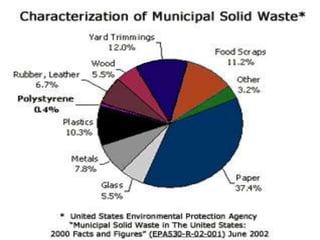
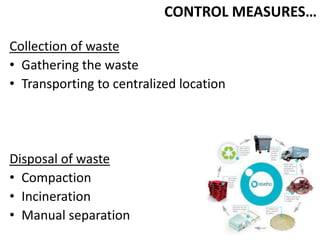
This document discusses the management of solid waste from municipalities. It defines solid waste and outlines its various sources such as municipal, industrial, and biomedical waste. The impacts of solid waste on health are described, including creating unhygienic conditions and spreading disease. Methods for solid waste management are proposed, including the "4Rs" of reduce, reuse, recycle, and refuse. The document recommends increasing public involvement, awareness, and the use of house-to-house collection to improve waste management efficiency.