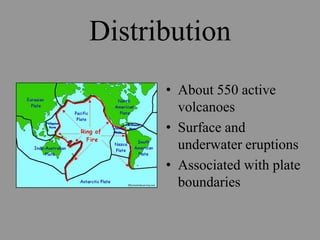
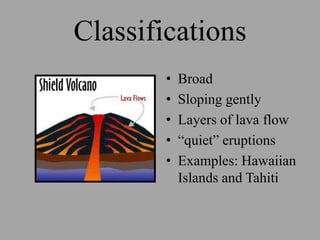
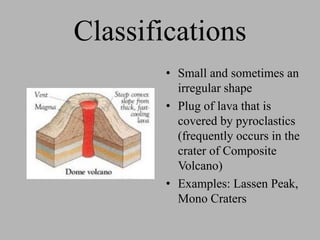
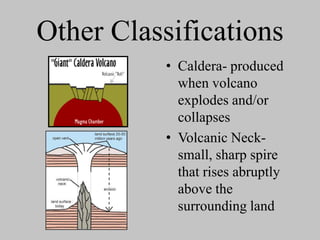
Volcanoes are openings in the Earth's crust where magma and gases escape. They are found at boundaries where tectonic plates are diverging or converging. When magma reaches the surface it is called lava, and eruptions produce lava, rock fragments, ashes, dust, and gases. There are over 550 active volcanoes distributed around plate boundaries on land and undersea. The type of eruption depends on factors like the crust's strength, pressure, and magma composition. Volcanoes are classified based on their shape, eruptive behavior, and deposits. Major hazards include lava flows, eruption columns, pyroclastic flows, and volcanic mudflows.