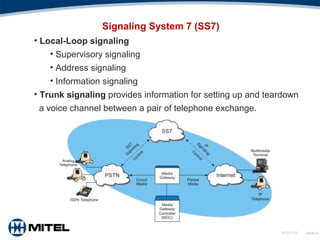
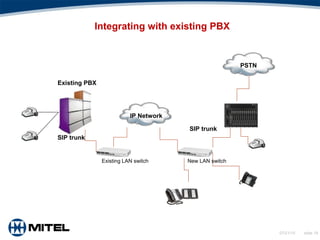
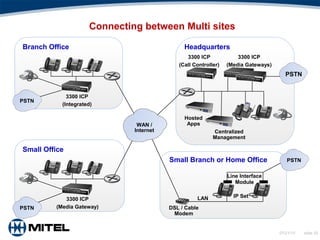
This document provides an overview of Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) technology. It discusses key components of VoIP including signaling protocols, audio codecs, echo elimination, advantages, applications, and considerations for deployment. The document contains slides that cover topics such as the public switched telephone network versus VoIP networks, signaling systems, audio codecs, quality of service factors, security threats, integrating VoIP with existing phone systems, and virtualized PBX solutions.