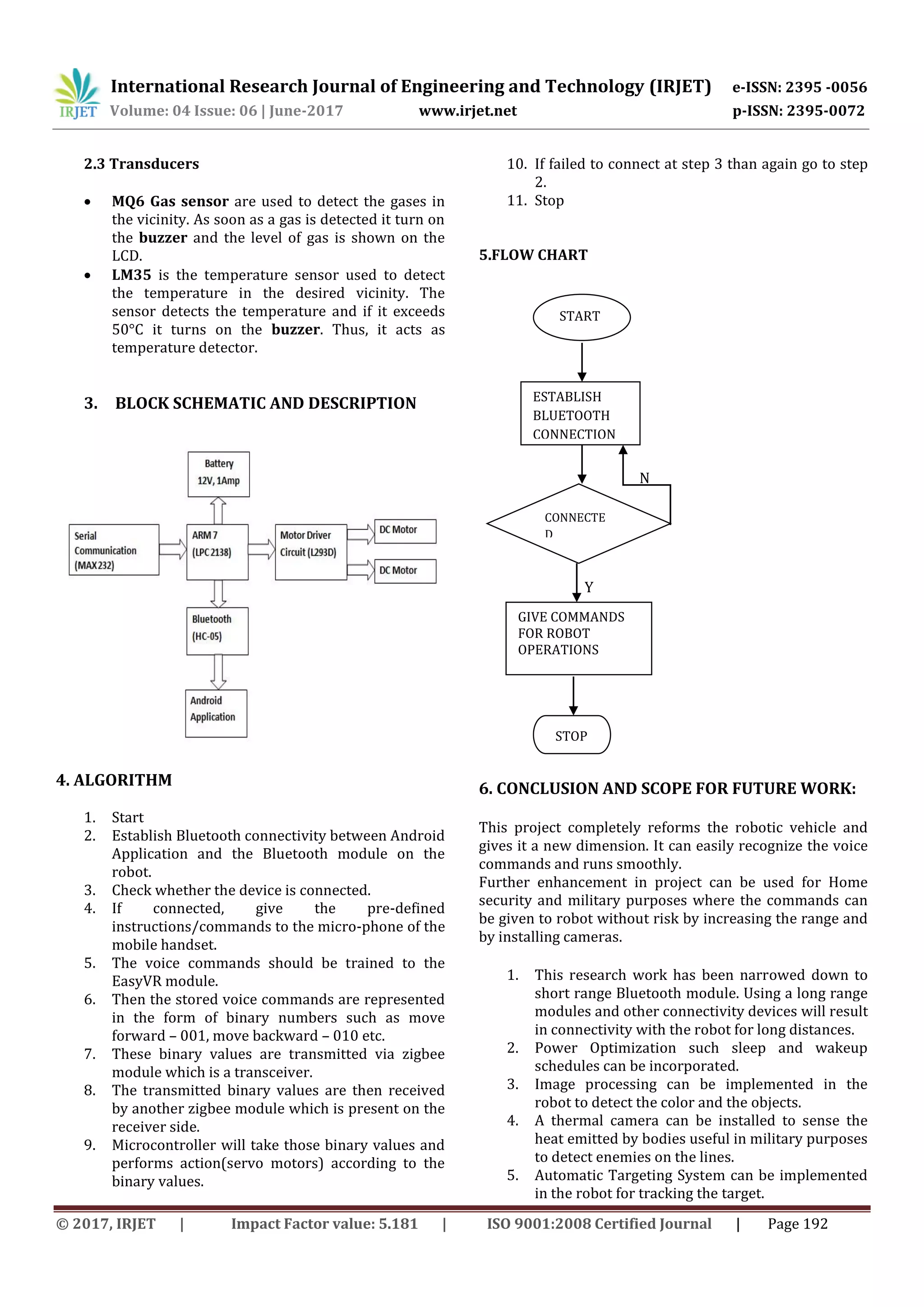
This document describes a voice-controlled robotic vehicle that can be operated remotely through voice commands on an Android application connected via Bluetooth. The robotic vehicle uses an ARM microcontroller and Bluetooth module to receive voice commands from the Android application and translate them to control two DC servo motors that move the vehicle. The system is trained to understand the user's voice commands, which are converted to encoded digital data and transmitted up to 100 meters via the Bluetooth connection to the robotic vehicle. This allows for remote voice control of the robotic vehicle over long distances compared to other wireless technologies. The project could later be expanded to use Internet of Things technology for global control of the robot from anywhere in the world.