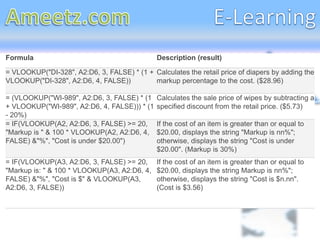
The document provides an overview of the VLOOKUP function in Excel, including its syntax and parameters such as lookup_value, table_array, col_index_num, and range_lookup. It explains how to use VLOOKUP to find data from a specific column based on a search value and provides examples for both approximate and exact matches. Additionally, it includes practical examples on calculating retail prices and displaying conditional strings based on item costs and markups.