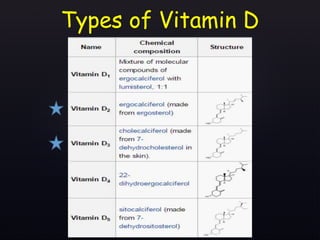
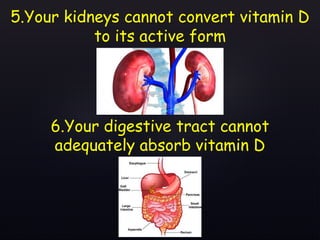
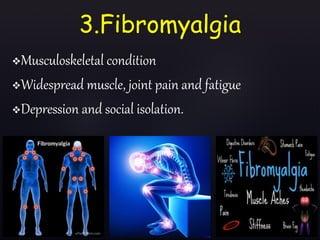
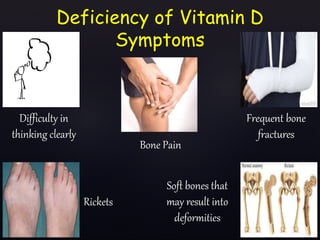
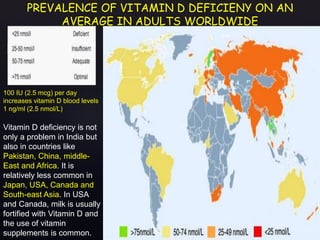
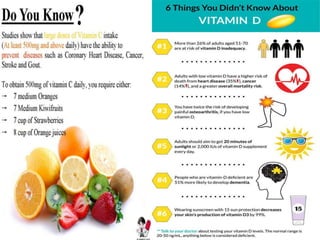
The document discusses vitamin D, its importance for various bodily functions, sources, and types, as well as the causes and prevalence of vitamin D deficiency, particularly in India. It highlights the role of vitamin D in maintaining bone health, supporting the immune system, and its association with various medical conditions. Additionally, it notes that a significant portion of the population has vitamin D deficiency and examines factors contributing to this issue.