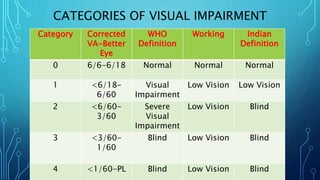
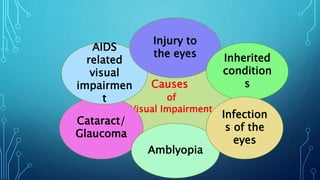
Visual impairment refers to limitations in vision including reduced visual acuity, visual field loss, photophobia, diplopia, and visual distortions. Legally blind is defined as visual acuity of 20/200 or less in the better eye with correction, or a visual field restricted to 20 degrees or less. Categories of visual impairment range from normal to blind based on corrected visual acuity and visual field. Causes include cataracts, glaucoma, infections, injuries, and inherited conditions. Visually impaired children can be identified through behaviors like headaches after close work, blinking, rubbing eyes, squinting, and difficulty seeing distant objects. Educational provisions for the visually impaired utilize remaining sight, magnification, Braille, recordings