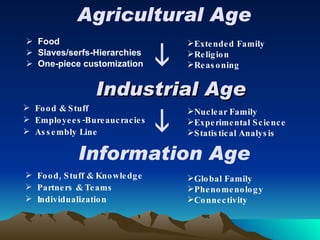
The document discusses various visions and predictions for the future of technology in education. It envisions a shift towards more individualized, collaborative, and self-directed learning as technology becomes more advanced and ubiquitous. Key aspects of the future vision include more flexible, adaptive, and networked models of learning; greater emphasis on lifelong learning and skills development; and stronger partnerships between education institutions and businesses.




















![Future Software “… software will someday get intelligent enough to give individualized tutoring that is much better than the typical classroom experience.” Kahn, Ken. "Re: Future of Learning." 26 February 2002. Online Posting. [IFETS-DISCUSSION:2895] . Retrieved 27 February 2003 <http://ifets.gmd.de/archiv/0685.html>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vision-1272057451-phpapp01/85/Vision-of-Education-23-320.jpg)


![Future Collaboration Instructional design is moving, and will continue to do so rapidly, to involve the learner more and more. Collaboration (synchronous and asynchronous) will become more important elements in our courses and participation will probably be an important factor for certified courses. Multi-user simulation exercises and games is probably the coming trend... and it is a trend that can fundamentally enhance the learner experience. Kiran Bhandari Brainvisa Technologies Ltd. From: "Kiran Bhandari" <kiran@brainvisa.com> Subject: [IFETS-DISCUSSION:3403] RE: future trends Date: Thu, 2 May 2002 16:23:52 +0530](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vision-1272057451-phpapp01/85/Vision-of-Education-26-320.jpg)

