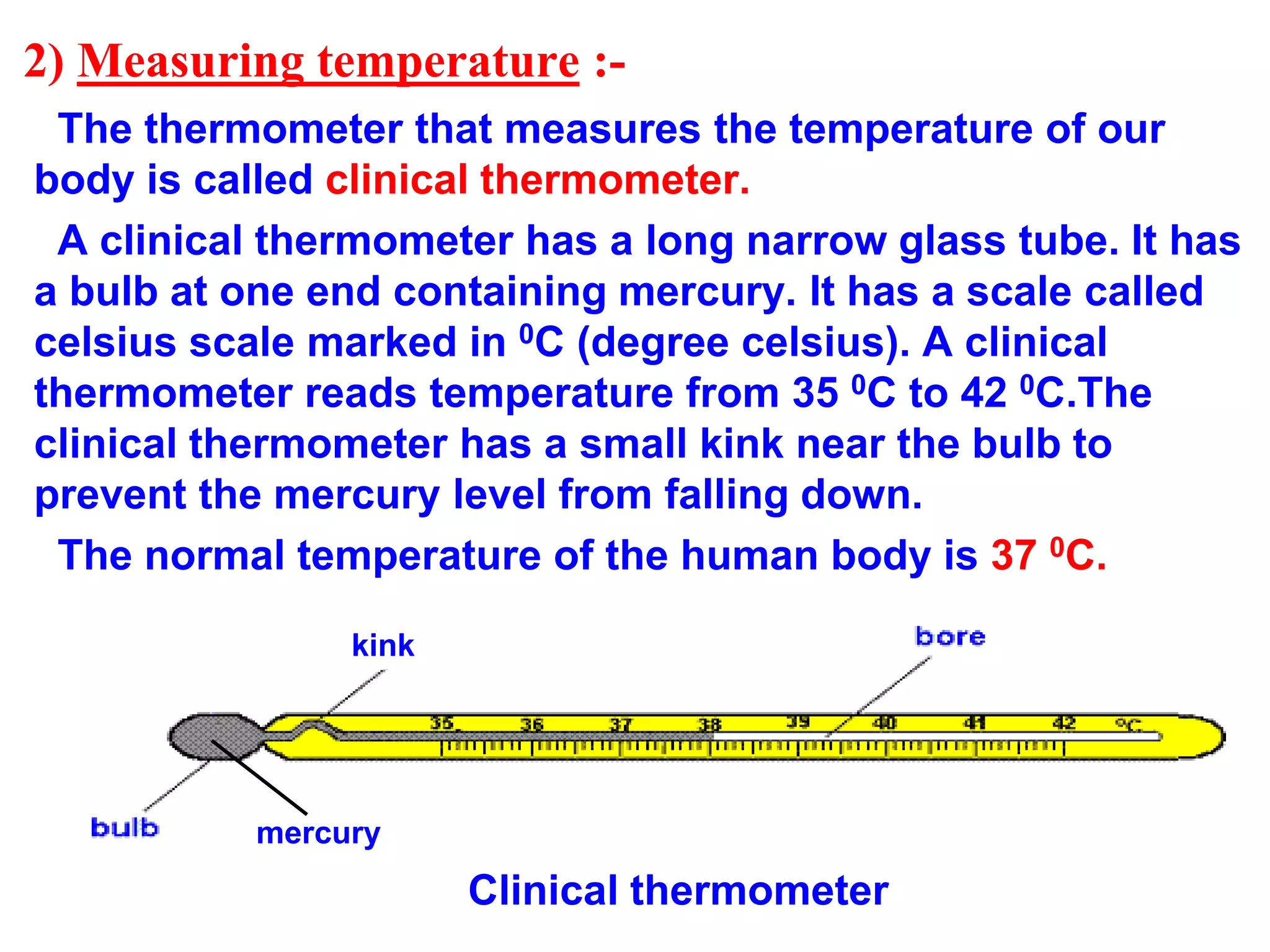
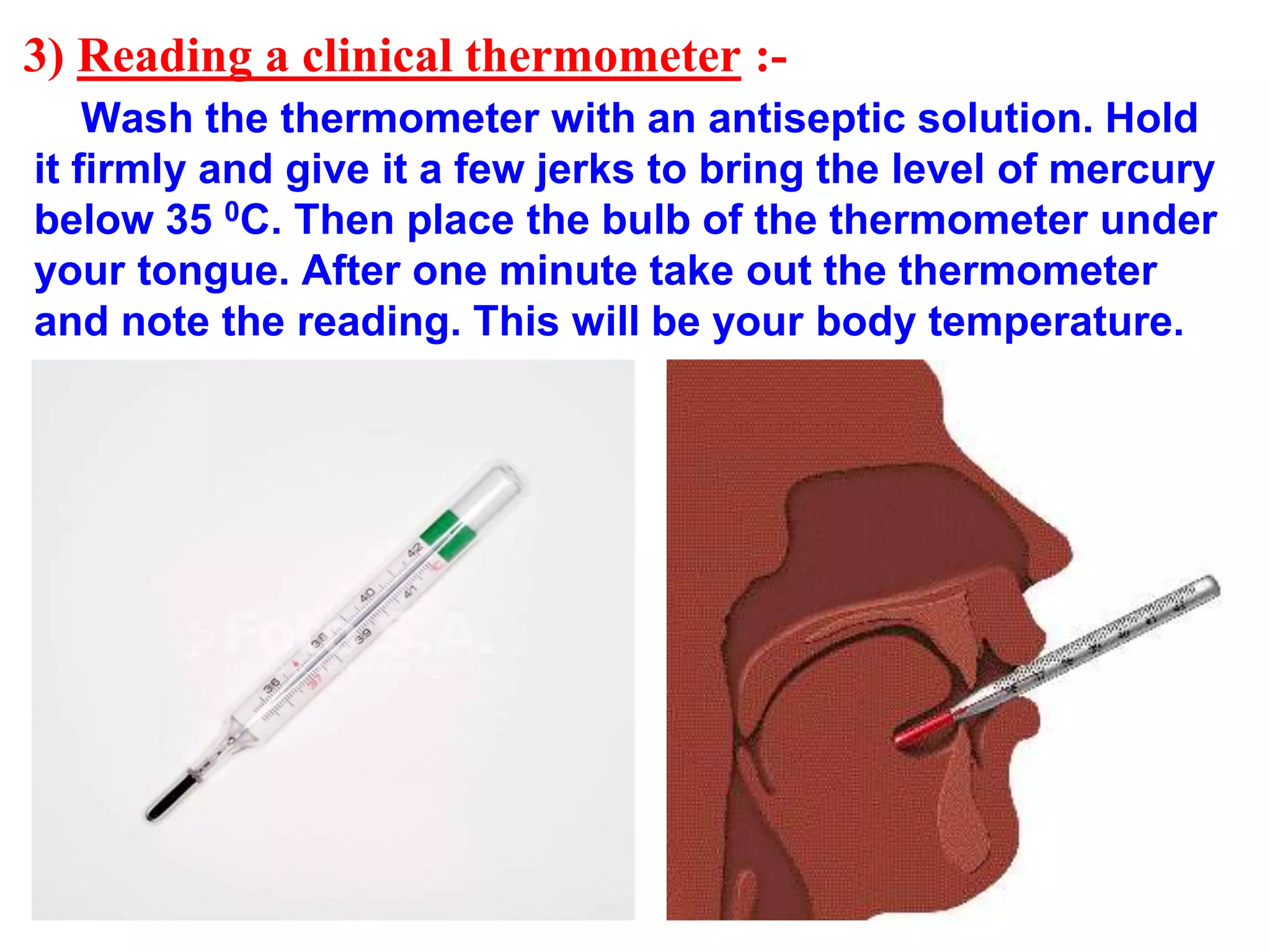
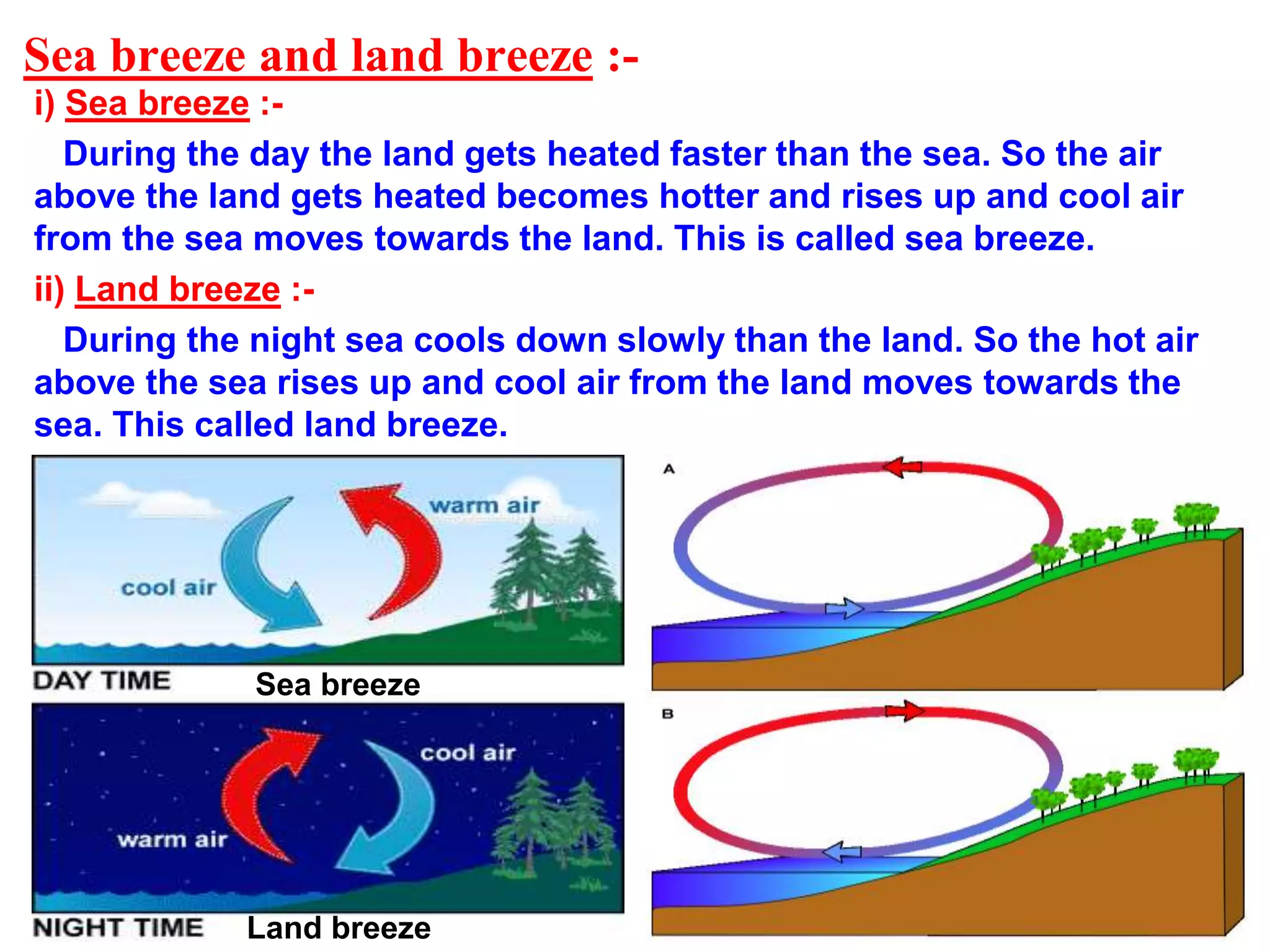
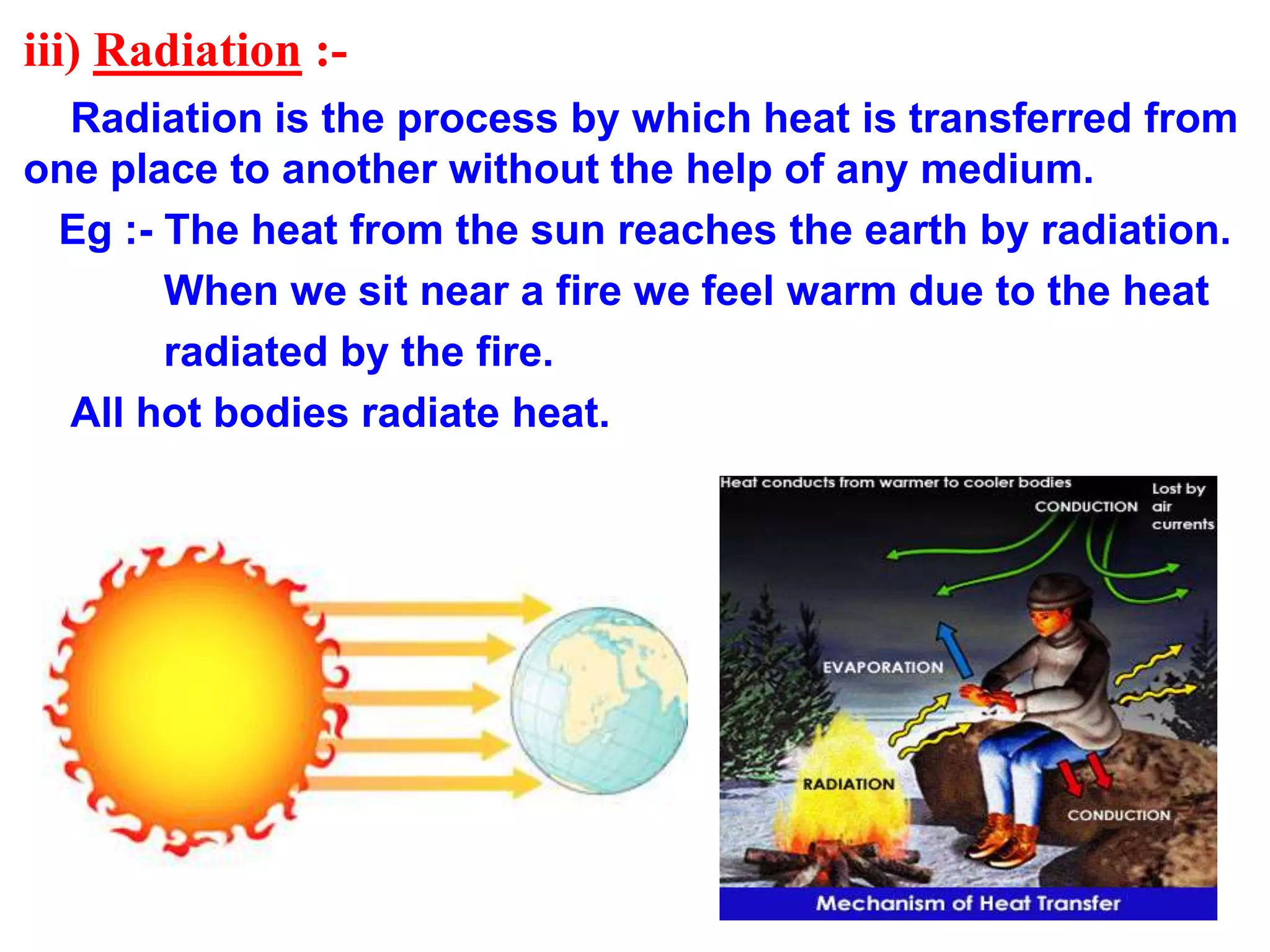
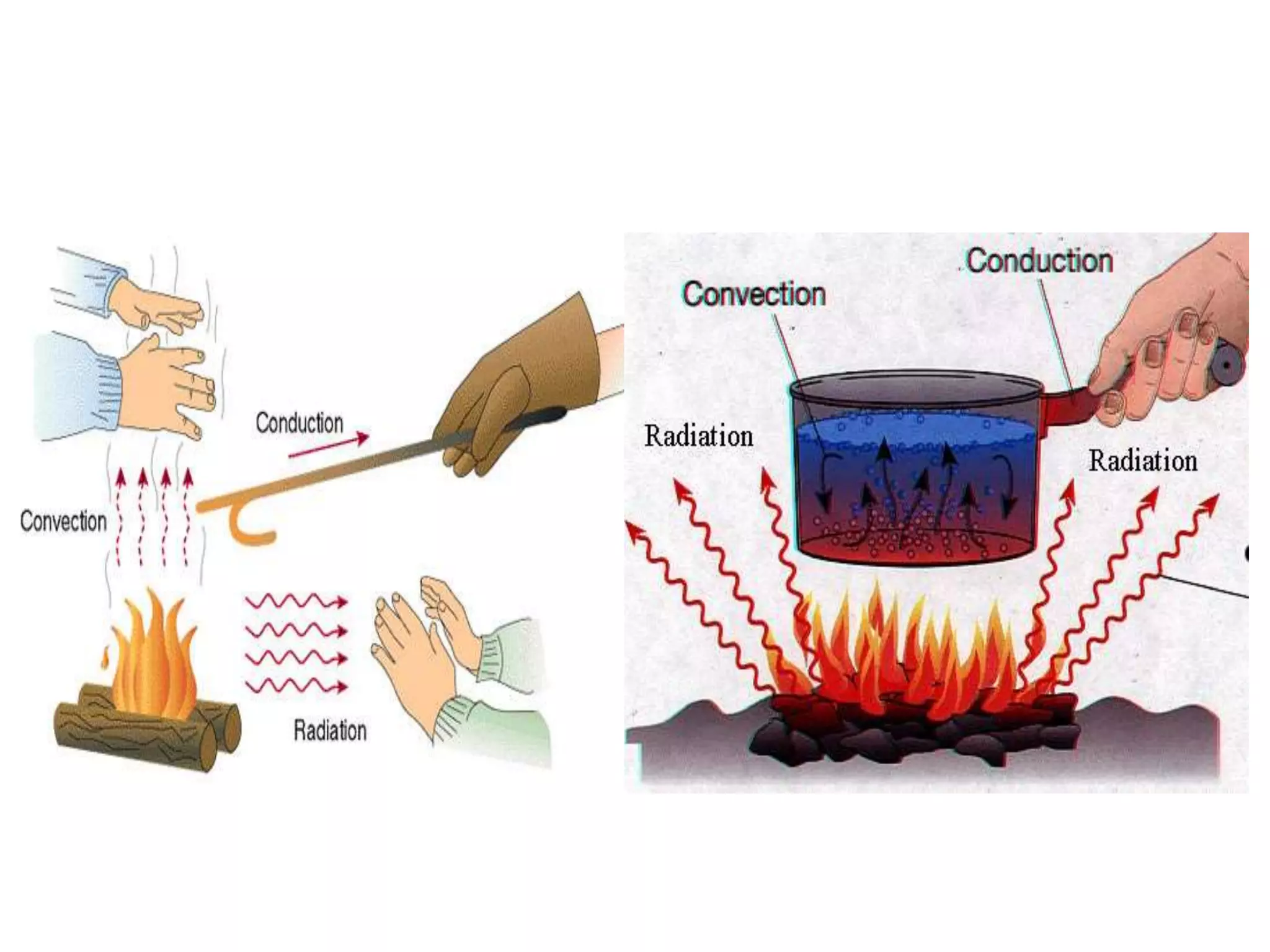
This document discusses heat and temperature. It explains that temperature is a measure of how hot or cold an object is, and is measured using a thermometer. It describes clinical thermometers and laboratory thermometers, and how to take temperatures using each. It also discusses the different ways heat is transferred - through conduction, convection, and radiation. Conduction occurs through direct contact in solids, convection through liquids and gases as hotter parts rise and cooler parts sink, and radiation through electromagnetic waves without a medium. The document concludes by explaining why we wear different colored clothes in summer versus winter based on how colors absorb and radiate heat.