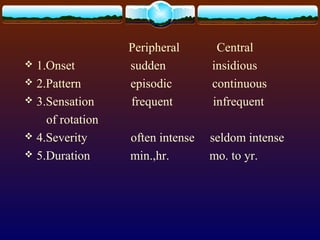
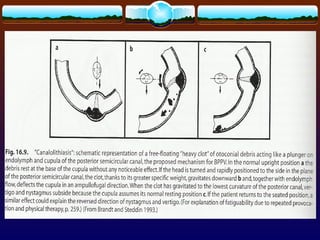
Vertigo refers to illusions of movement and is caused by problems in the vestibular system. Common causes of vertigo include BPPV, Meniere's disease, sudden hearing loss, vestibular neuritis, and labyrinthitis. Peripheral vertigo tends to be episodic with intense but brief symptoms, while central vertigo is often continuous with less intense symptoms. Treatment depends on the underlying cause but may include medications, repositioning maneuvers, physical therapy, or surgery.