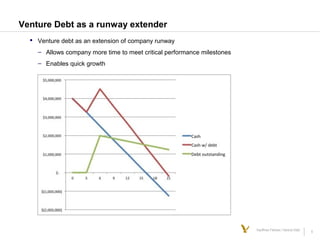
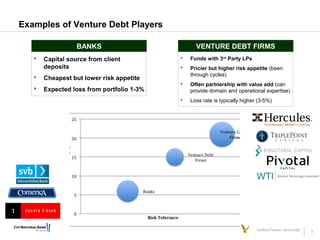
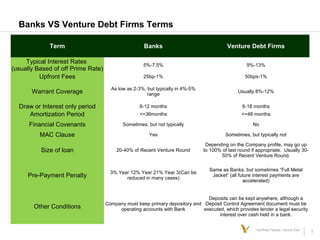
This document discusses various types of debt financing options for venture-backed startups, including venture debt, accounts receivable financing, recurring revenue financing, and mezzanine financing. It provides an overview of the key benefits and risks of taking on debt for startups. It also describes some of the key terms and considerations for different debt products, and provides examples of how venture debt and recurring revenue lines can extend a company's cash runway in a minimally dilutive way.