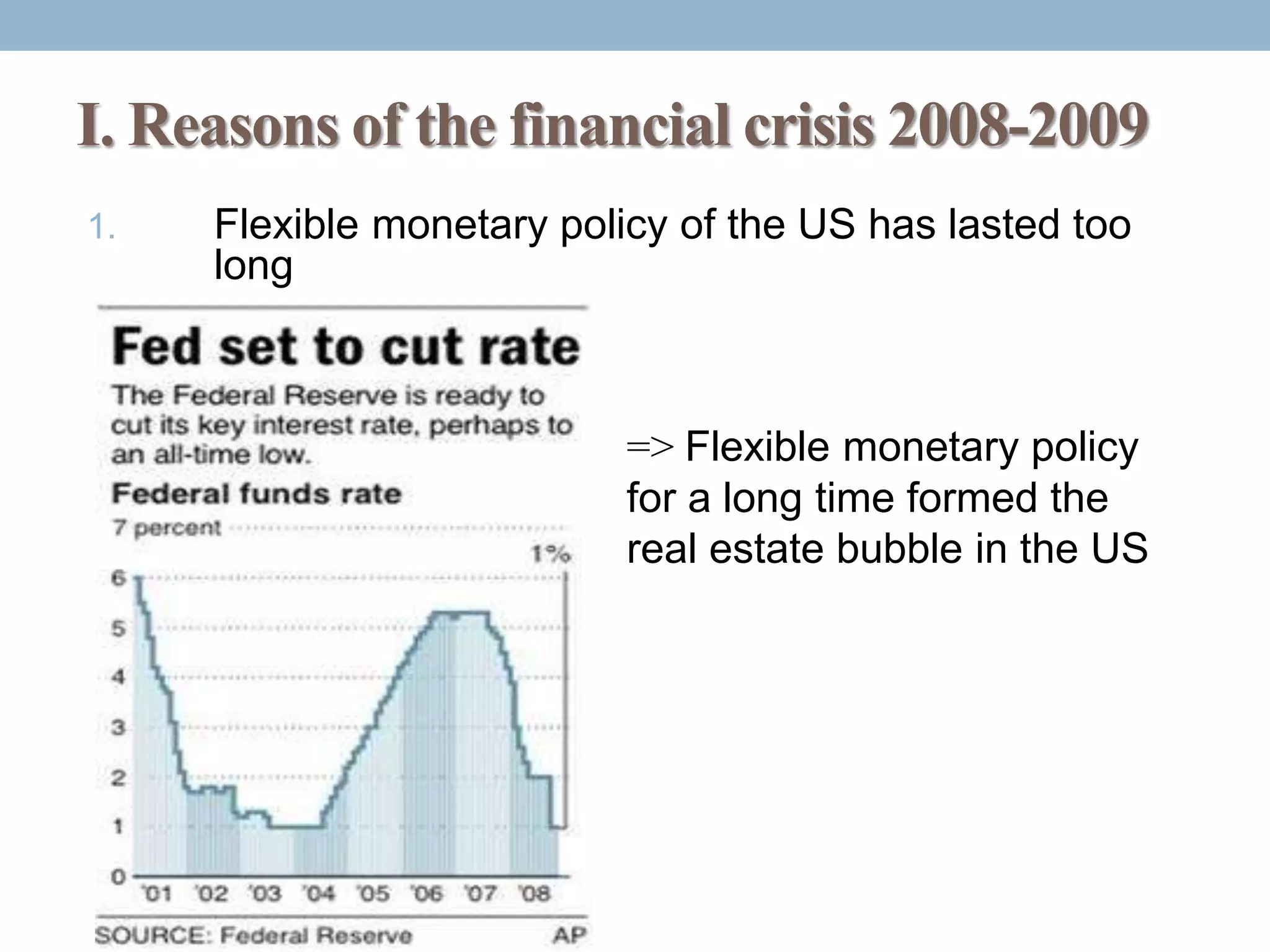
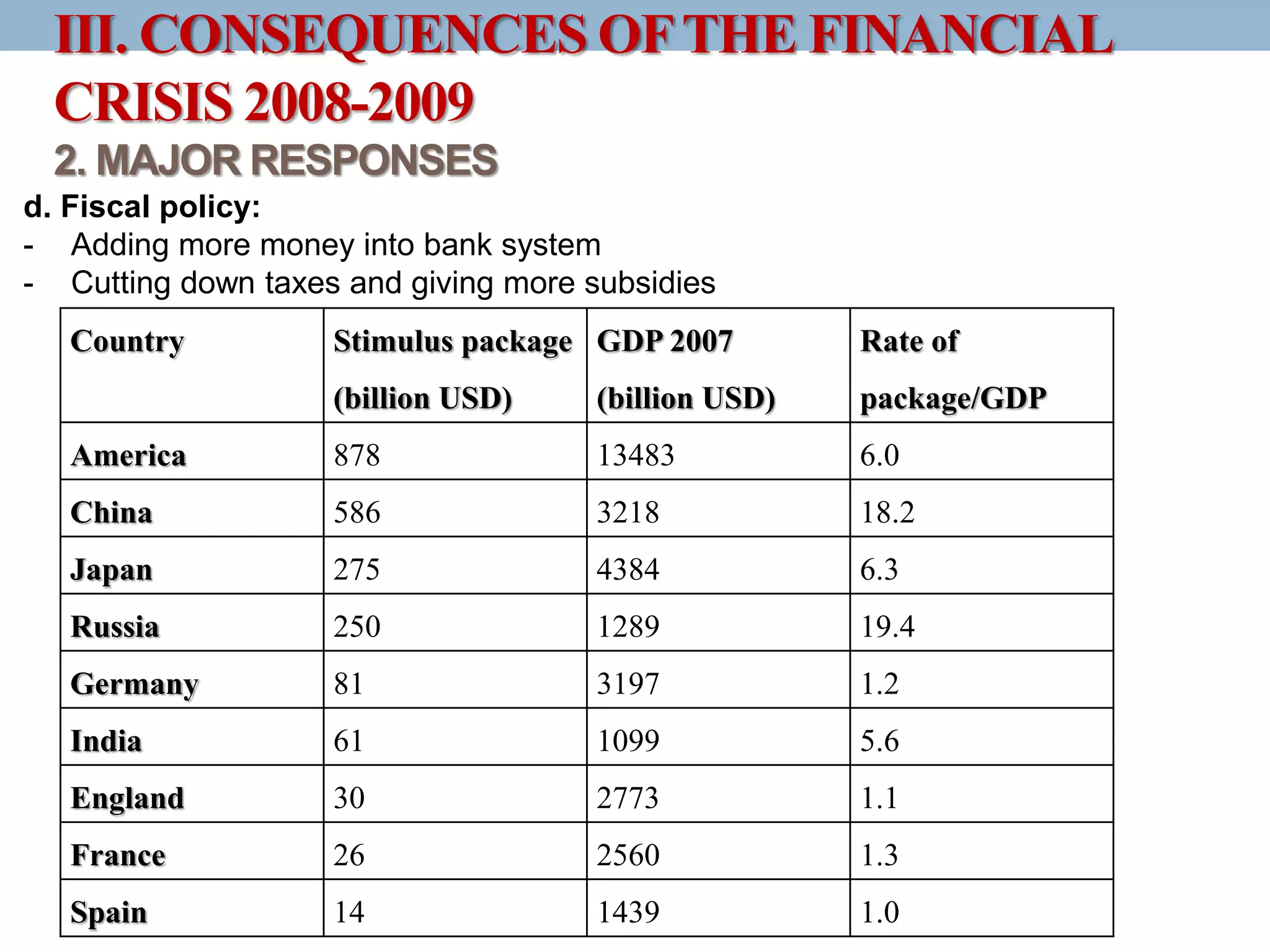
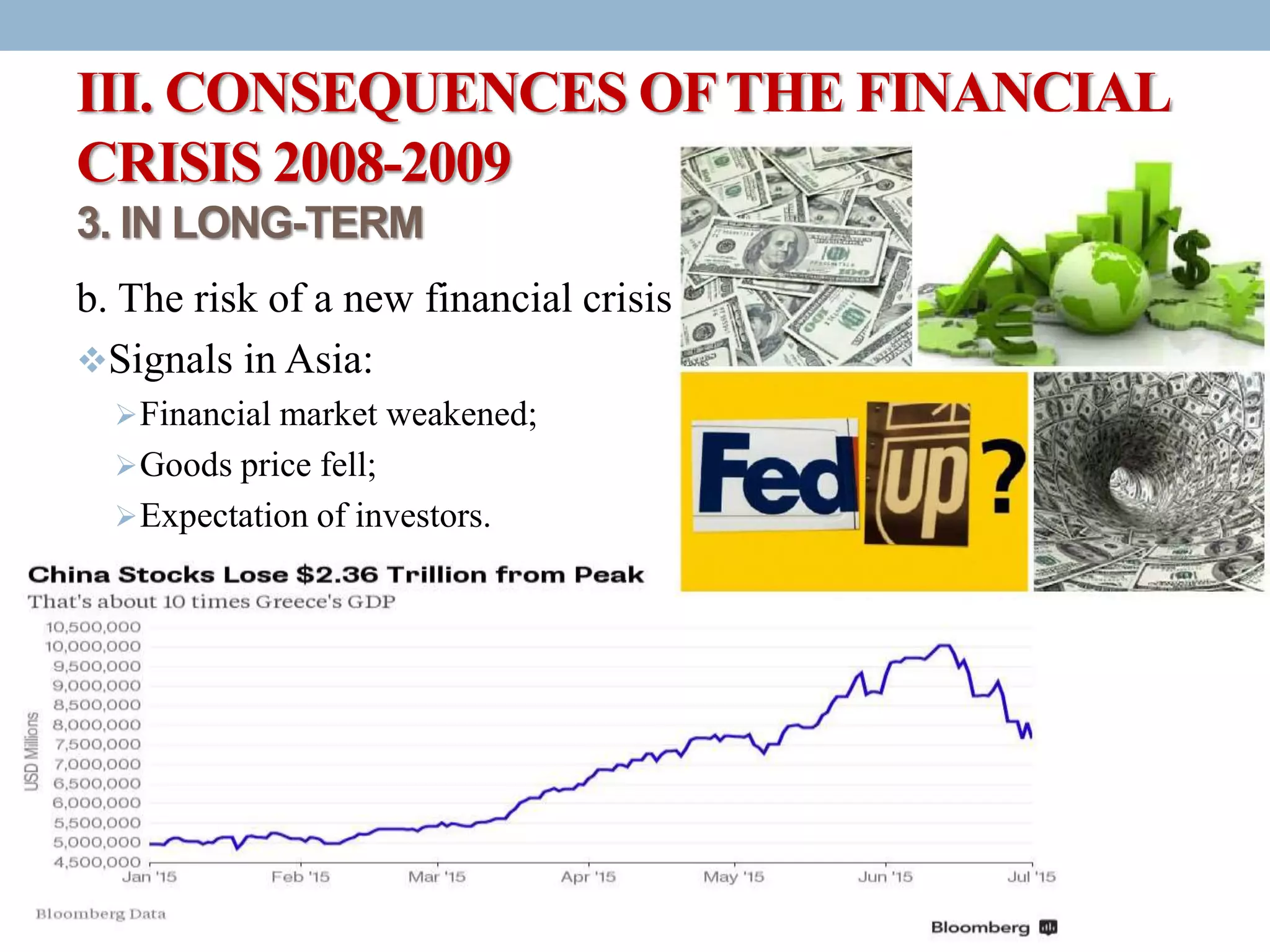
The document discusses the causes, developments, and consequences of the 2008-2009 financial crisis, highlighting factors like the US's long flexible monetary policy leading to a real estate bubble and subsequent collapse. It details major developments including bank bankruptcies and stock market declines, along with the responses from governments and international bodies to stabilize the economy. The long-term consequences include a risk of new financial crises, economic recession, and a backlash against globalization.