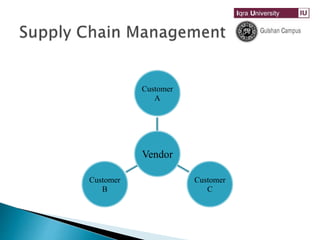
Vendor Managed Inventory (VMI) is an approach where the manufacturer or vendor monitors and manages the inventory levels at the distributor or retailer. The key aspects of VMI are:
1. The vendor has access to the customer's inventory data and is responsible for maintaining the required inventory levels.
2. It optimizes supply chain performance by pushing decision making responsibility upstream to the vendor.
3. Benefits include lower inventory costs, fewer stockouts, improved information sharing and customer satisfaction.