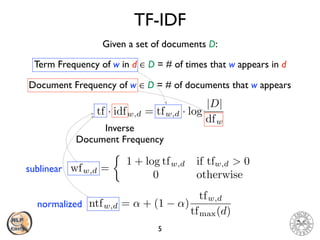
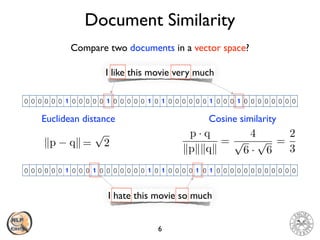
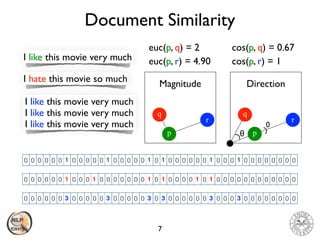
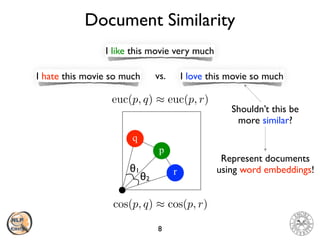
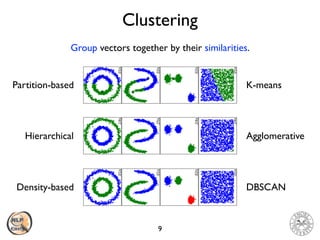
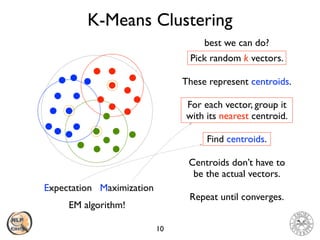
The document discusses vector space models and how they can be used to represent documents numerically. It introduces the bag-of-words model and TF-IDF weighting. It then discusses how cosine similarity and Euclidean distance can be used to calculate similarity between document vectors. Finally, it summarizes several clustering algorithms like k-means, k-means++, and hierarchical agglomerative clustering that can group similar document vectors.

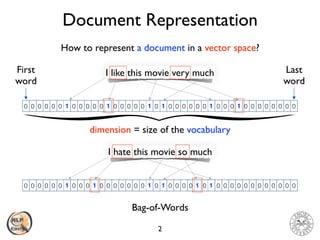


![K-Means++ Clustering
11
Introduce a random vector c as the first centroid.
Pick a random number r in (0, 1].
D(x) = min
8c
dist(x, c)
Choose xi as the next centroid s.t. C(xi 1) < r C(xi)
C(xi) =
iX
j=1
P(xj)C(x0) = 0
Measure the distance between every vertex x to its nearest centroid c.
Measure the distance probability for each vertex x.
Measure the cumulative probability for each vertex x.
P(x) =
D(x)2
P
8x D(x)2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vector-space-models-180404160851/85/Vector-Space-Models-11-320.jpg)