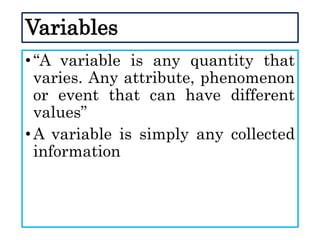
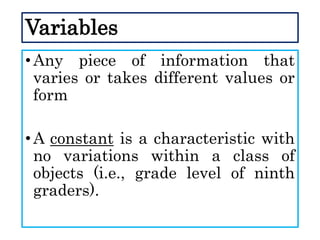
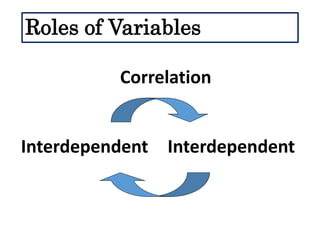
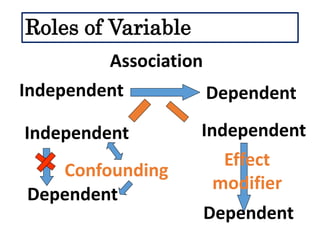
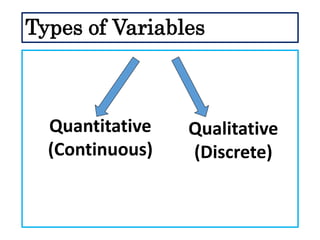
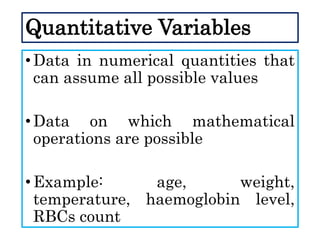
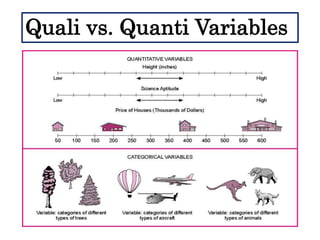
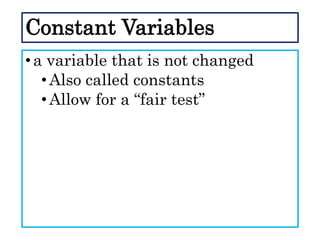
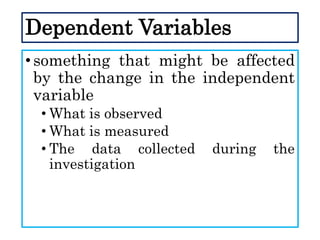
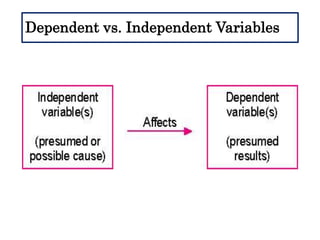
This document defines and describes different types of scientific variables. It begins by defining a variable as any quantity that can take on different values. It then distinguishes between independent and dependent variables, with the independent variable being what is manipulated or tested, and the dependent variable being what is observed and measured. The document outlines quantitative and qualitative variables and provides examples. It also discusses specifying variables, their roles in relationships, and examples of using variables in experiments with controls.