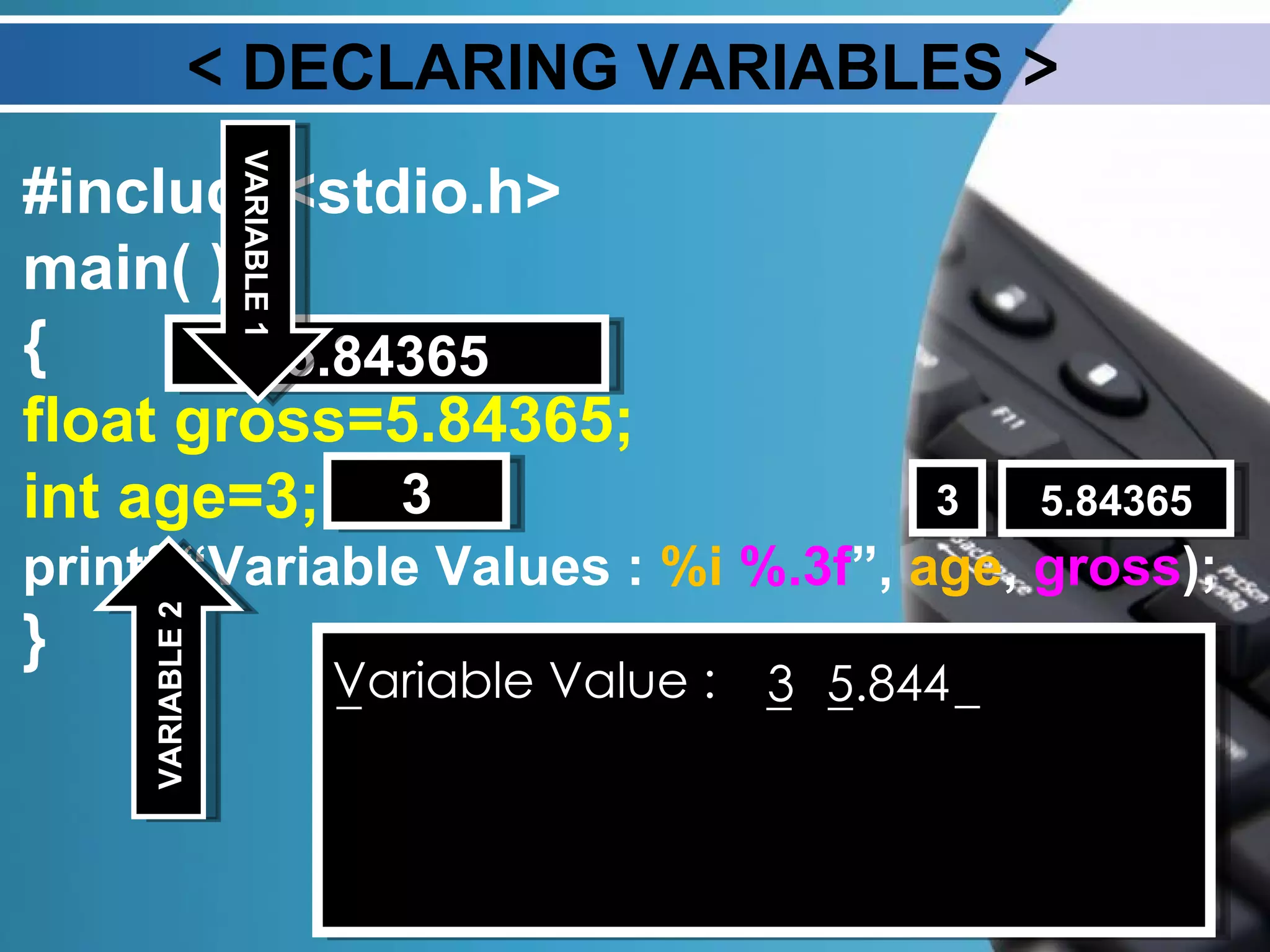
The document discusses data types and variable naming in Turbo-C. It describes the different data types like int, float, char, and long int. It explains the rules for naming variables, such as starting with a letter or underscore and not using keywords. It provides examples of declaring and assigning values to variables of different data types and using them in print statements.


![VARIABLE DECLARATION OF TURBO-C SYNTAX <data type> <variable name> char g ; int x , y , z ; float f=5.67 ; int x=10 ; char name[10] ;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/variabledeclaration-120130045034-phpapp01/75/Variable-declaration-3-2048.jpg)




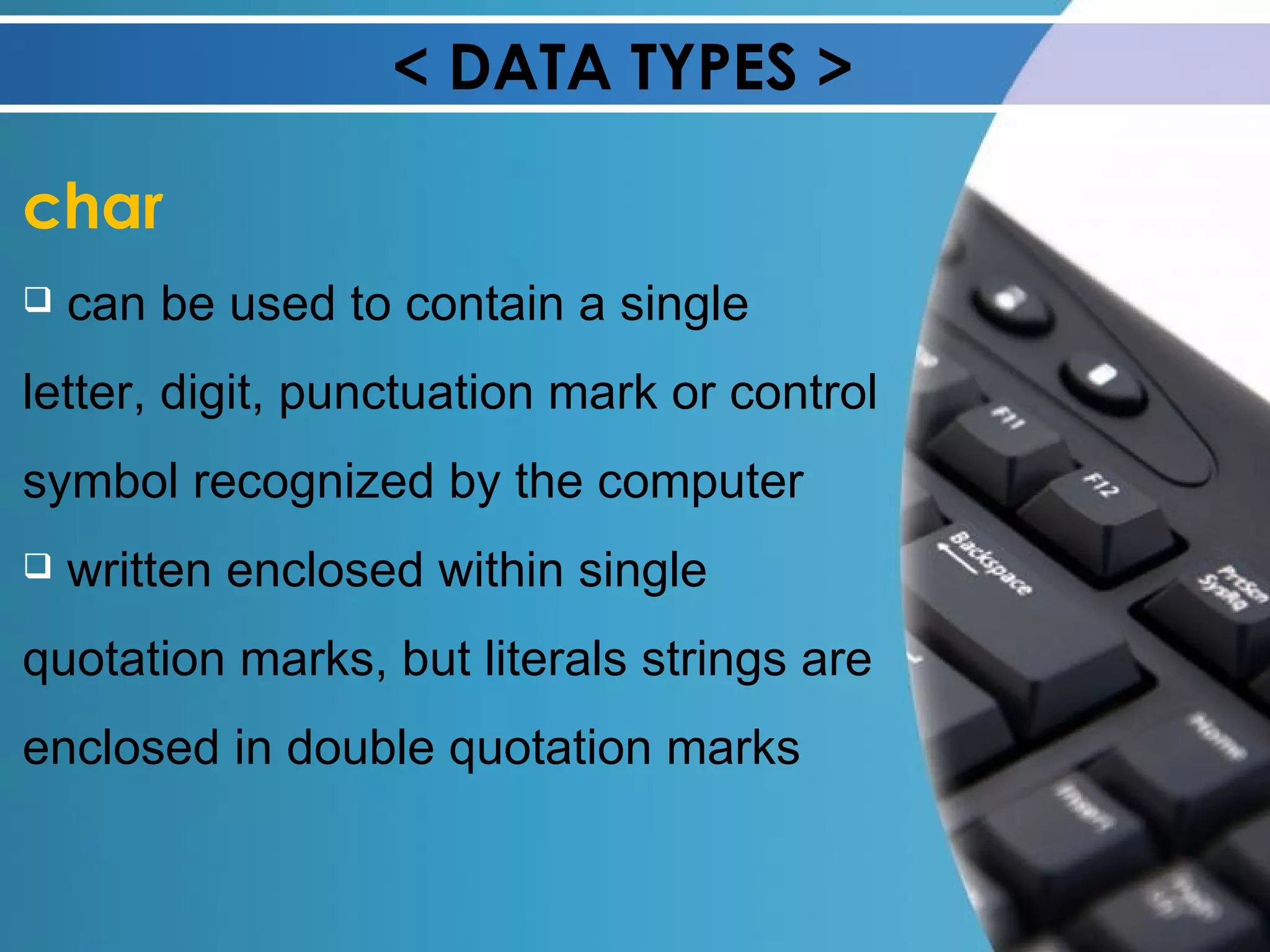
![< DATA TYPES > char a character may be assigned an integer value between –128 and +127 unsigned char data type may be assigned an integer value from 0 to 255 char c; char b = ‘*’; char a[30]; char a = “apple”;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/variabledeclaration-120130045034-phpapp01/75/Variable-declaration-9-2048.jpg)
![< VARIABLE NAME > arvin#030709 buendia_arvin : ] superman superman arvin25 [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/variabledeclaration-120130045034-phpapp01/75/Variable-declaration-10-2048.jpg)