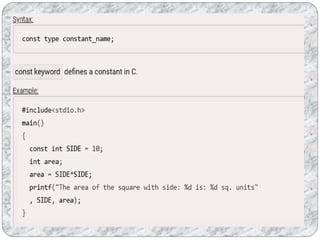
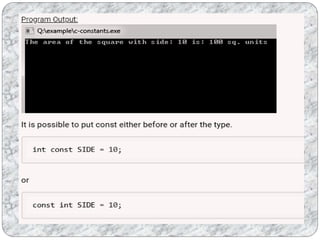
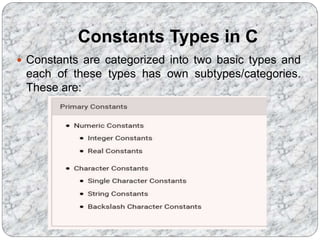
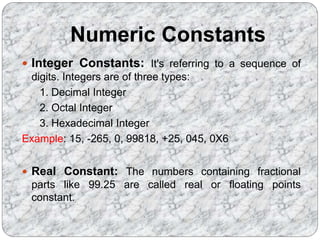
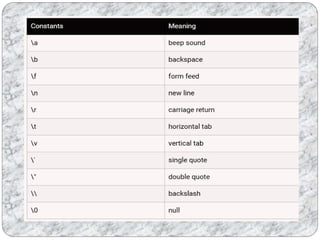
C programs are composed of the smallest units called tokens, which can be individual words or punctuation. Identifiers are names given to entities like variables and functions, and they must follow certain naming conventions. Constants are fixed values that do not change during program execution, and there are different types of constants including numeric, character, and string constants. Keywords are reserved words that cannot be used as identifiers.