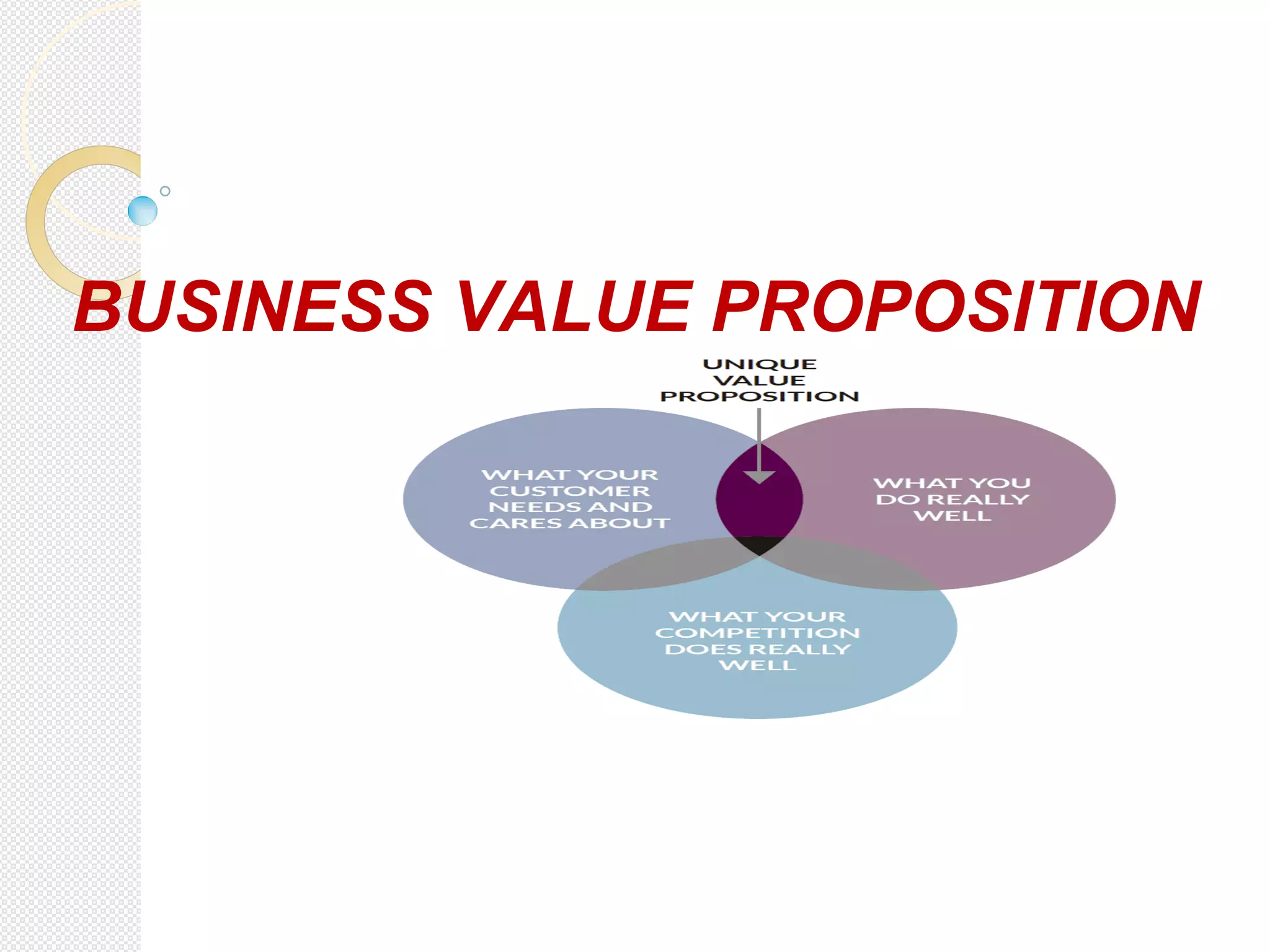
This document provides guidance on creating an effective value proposition in 3 steps:
1. Understand the customer by determining their needs, problems, values through research.
2. Analyze your product or service to show how it specifically solves customer problems and creates value through features and benefits. Use numbers to quantify value.
3. Compare your solution to competitors to show how it creates more value.
The value proposition statement should complete the sentence "I want to buy this because it will..." from the customer's perspective, highlighting the most important benefits and differentiators that address what the customer values most.