This document discusses several models of consumer behavior:
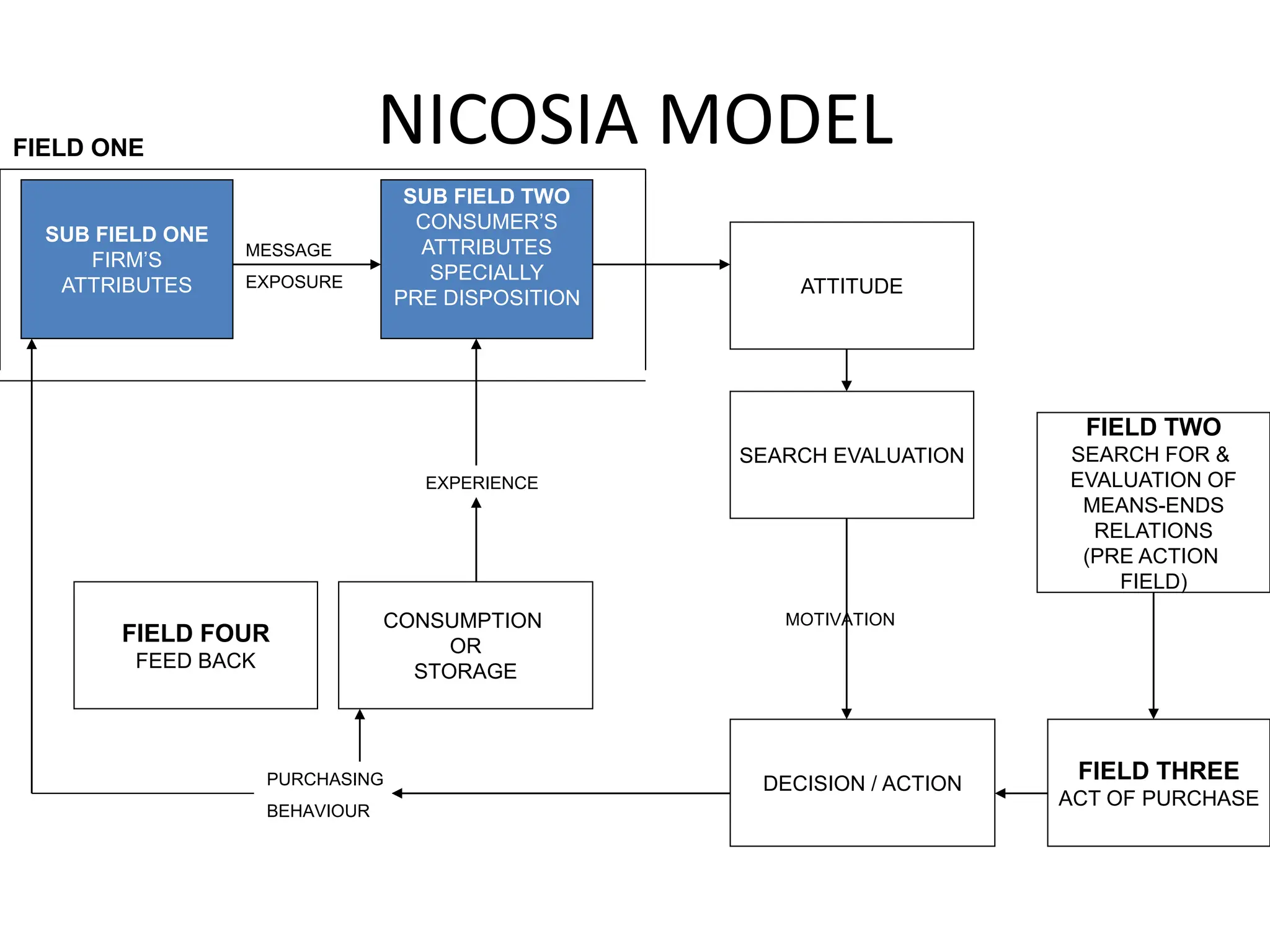
1) The Nicosia Model which shows the relationship between a firm's attributes, a consumer's attributes, and the consumer's decision making process.
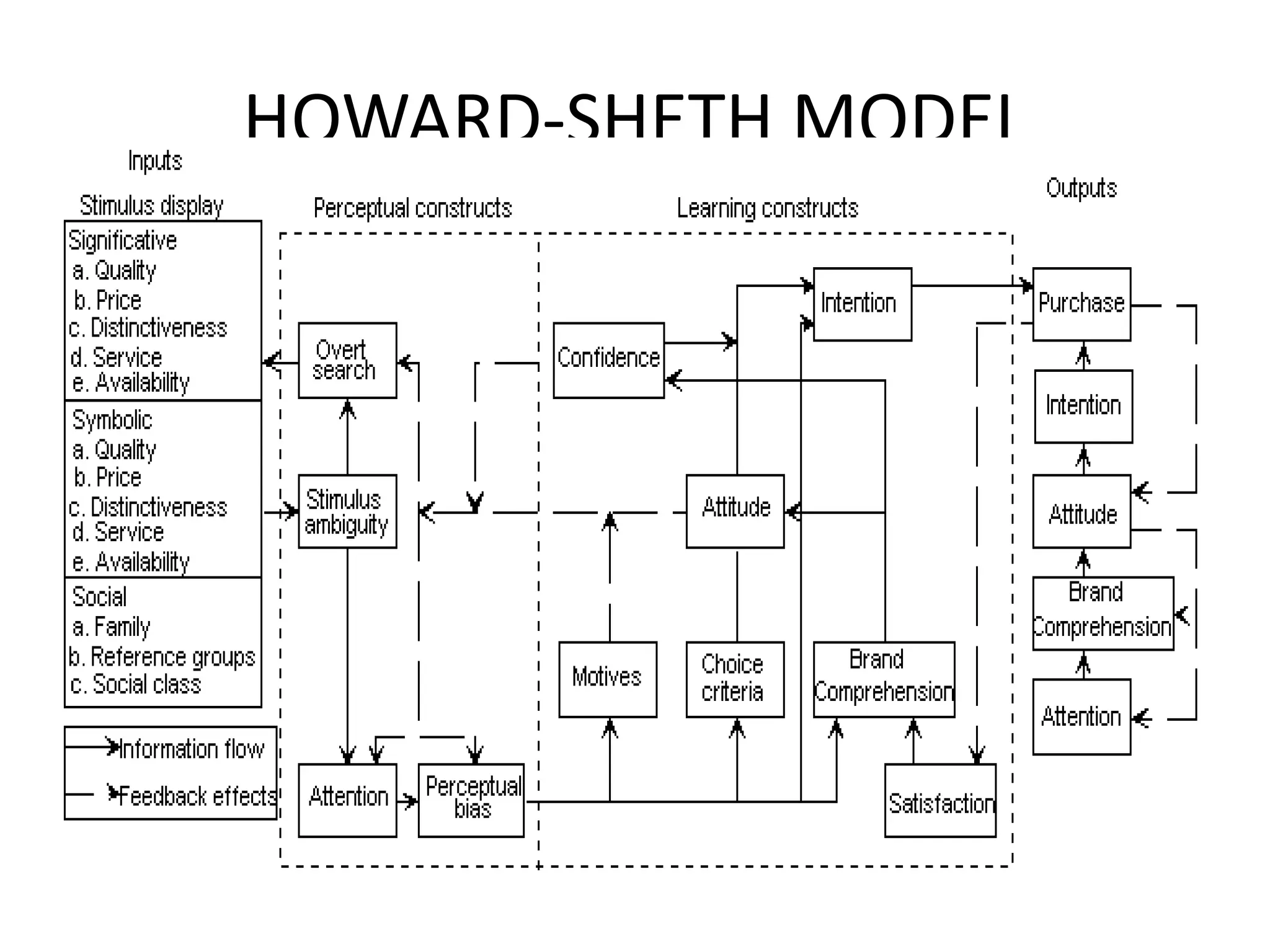
2) The Howard-Sheth Model which views consumer behavior as a rational problem solving process influenced by stimuli and resulting in actions. It identifies inputs, constructs, and outputs in the consumer's decision process.
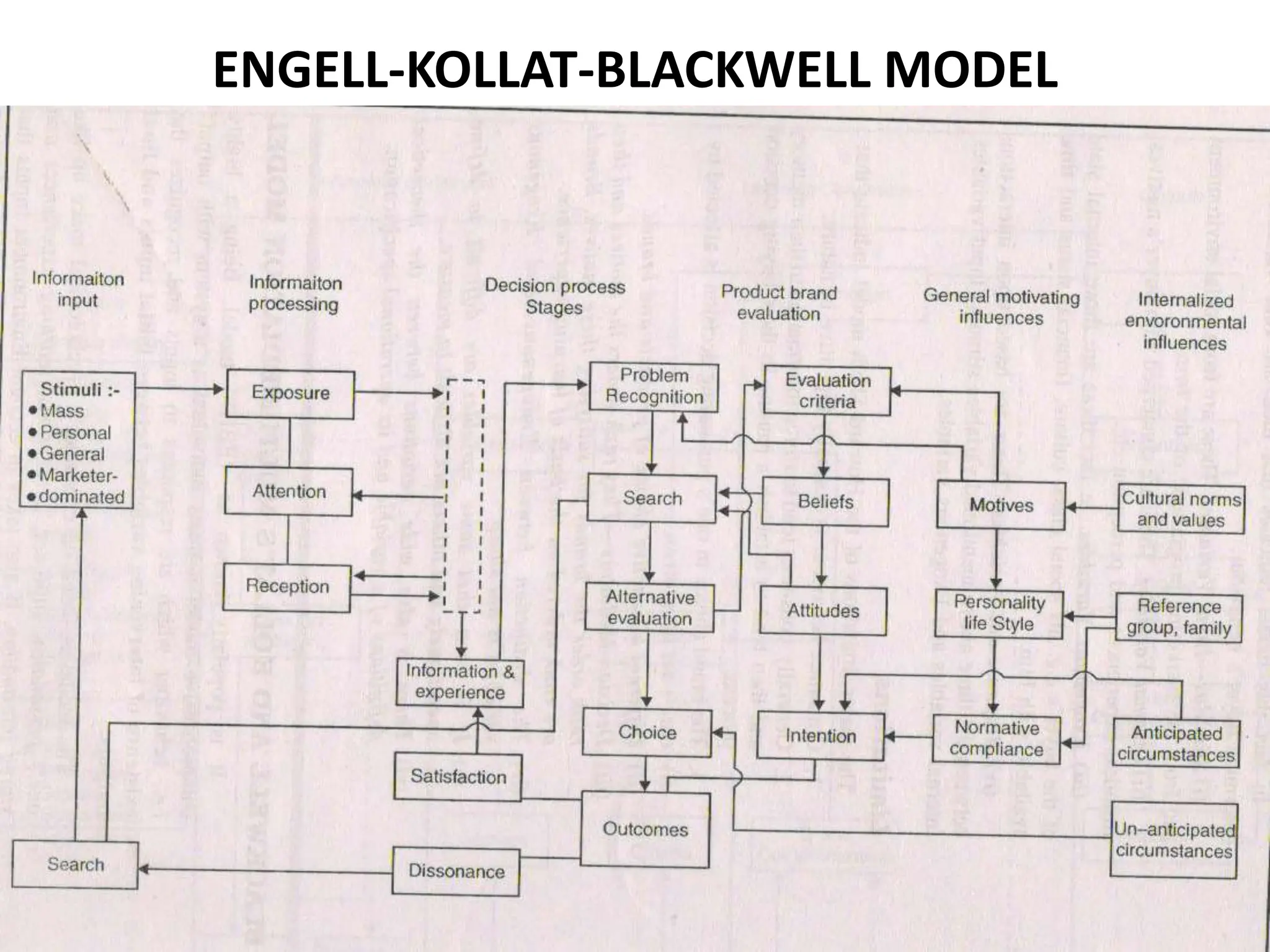
3) The Engel-Kollat-Blackwell Model which is a highly comprehensive, multi-stage model that treats the individual as a system and recognizes intervening variables between initial inputs and final outputs. It takes into account psychological and environmental factors.