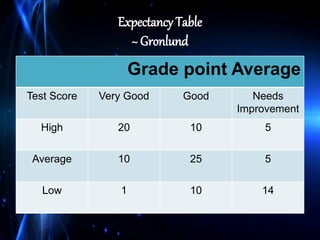
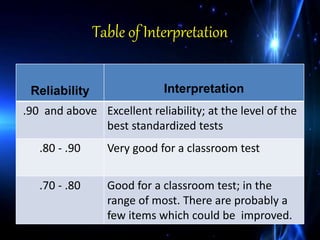
Validation and reliability are important concepts for determining the quality of a test. There are three main types of validation evidence: content-related, criterion-related, and construct-related evidence. Content-related evidence examines how well the test covers the intended content area. Criterion-related evidence looks at how scores on the test correlate with other measures. Construct-related evidence determines how well the test measures the intended psychological construct. Reliability refers to the consistency of scores and is measured using reliability coefficients, with coefficients above 0.8 indicating good reliability for classroom tests.