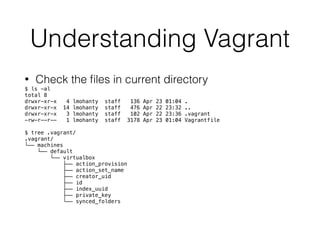
The document discusses the concept of DevOps, emphasizing its role in bridging the gap between development and operations through a culture of rapid and reliable software delivery. It introduces Vagrant as a tool for creating and managing reproducible development environments, alongside its integration with configuration management tools and public cloud services. Additionally, it outlines key commands, setup processes, debugging tips, plugin usage, and future developments related to Vagrant and DevOps practices.