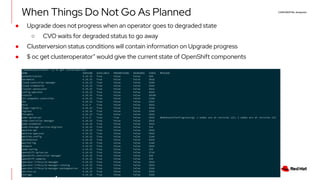
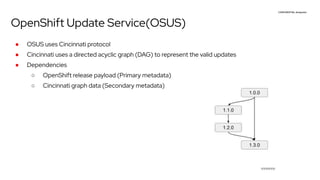
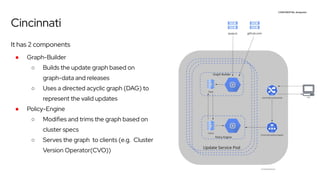
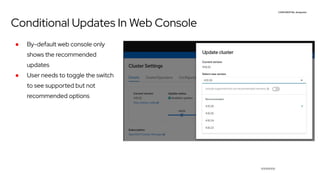
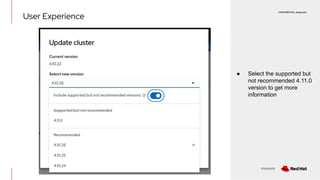
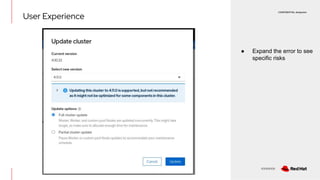
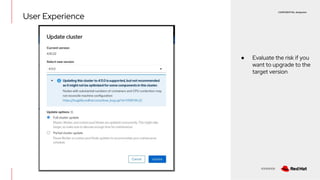
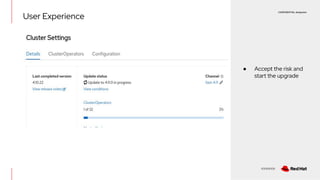
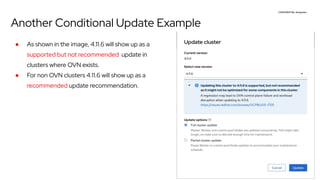
The document discusses OpenShift upgrades and how they are automated and handled to avoid disruption. It describes how all OpenShift components are Kubernetes operators and how the cluster-version-operator initiates upgrades. It details the upgrade graph and how the OpenShift update service uses Cincinnati to represent valid upgrades as a directed acyclic graph. Conditional edges allow showing upgrades as supported but not recommended based on cluster risks.