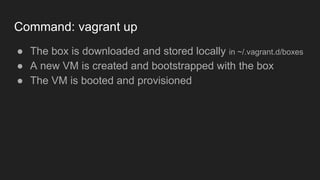
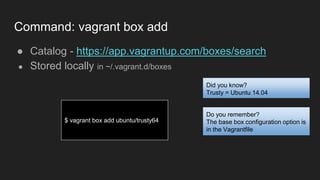
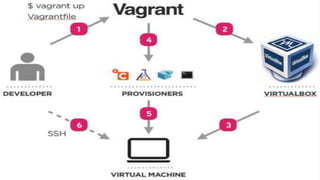
This document outlines an agenda for a Vagrant 101 workshop. The workshop will teach participants about environments and Infrastructure as Code using Vagrant. It will cover setting up a Vagrant environment with VirtualBox, basic Vagrant commands like init, up, ssh, destroy and box add. The agenda includes introducing environments, Vagrant, VirtualBox, commands, and workflow. Requirements are basic Linux knowledge and the latest versions of Vagrant and VirtualBox installed.