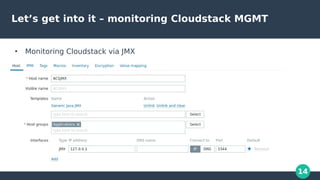
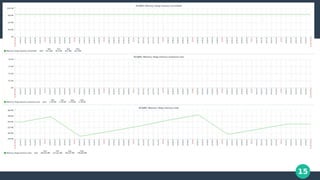
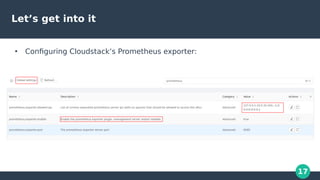
The document discusses monitoring in CloudStack, highlighting the use of Zabbix and Prometheus as popular monitoring solutions. It elaborates on the features, installation, and configuration of both tools for effective monitoring of CloudStack management and virtual machines. The document also emphasizes the benefits of combining Zabbix and Prometheus for a comprehensive monitoring setup, along with practical demonstrations of their implementation.