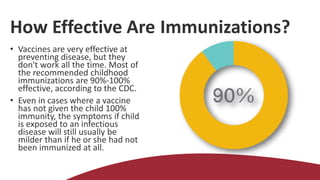
This document discusses immunizations and vaccines. It defines vaccination as providing active acquired immunity against diseases using agents resembling microorganisms that cause disease. Vaccines contain weakened or killed forms of viruses or bacteria. The word "vaccine" comes from cowpox virus, which was used in the first demonstration that one virus could protect against a related one. Vaccines contain small amounts of viruses or bacteria to produce immunity. While rare, serious adverse reactions or death from vaccines can occur. Vaccine types include live-attenuated, inactivated, toxoid, subunit, polysaccharide, and conjugate vaccines. Vaccination provides both individual and community benefits by preventing disease spread and protecting those who cannot receive vaccines.