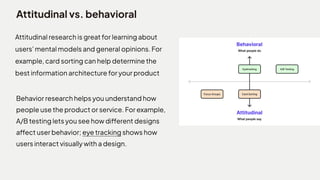
The document discusses various research methodologies in UX research, emphasizing the importance of choosing the correct methods to understand user behaviors, needs, and motivations. It contrasts qualitative and quantitative research, detailing the benefits and drawbacks of different techniques such as interviews, surveys, and usability testing. The document also underlines the significance of establishing clear research goals and objectives to inform product design based on user-centered insights.